Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2021-2022
Date & Time: 7th May 2022, 10:30 am
Duration: 2h
Advertisements
General Instructions :
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them:
- This question paper contains 12 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper comprises of three sections - Sections A, B, and C.
- Section A - Q. No. 1 to 3 are very short-answer type questions carrying 2 marks each.
- Section B - Q. No. 4 to 11 are short-answer type questions carrying 3 marks each.
- Section C - Q. No 12 is a case-based question carrying 5 marks.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed.
Predict the reagent for carrying out the following transformations:
Benzoyl chloride to Benzaldehyde
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Predict the reagent for carrying out the following transformations:
Ethanal to 3-hydroxy butanal
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Predict the reagent for carrying out the following transformations:
Ethanoic acid to 2-chloroethanoic acid
Chapter:
Why on dilution the m Λm of \[\ce{CH3COOH}\] increases very fast, while that of \[\ce{CH3COONa}\] increases gradually?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
What happens if external potential applied becomes greater than E°cell of electrochemical cell?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
An organic compound (A) with molecular formula C3H7NO on heating with Br2 and KOH forms a compound (B). Compound (B) on heating with CHCl3 and alcoholic KOH produces a foul-smelling compound (C) and on reacting with C6H5SO2Cl forms a compound (D) which is soluble in alkali. Write the structure of (A), (B), (C) and (D).
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Account for the following:
Cu+2 salts are coloured, while Zn2+ salts are white.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Account for the following:
E° value for the Mn3+/Mn2+ couple is much more positive than that for Cr3+/Cr2+.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Account for the following:
Transition metals form alloys.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Calculate ΔrG0 and log Kc for the following cell:
\[\ce{Ni(s) + 2Ag^+(aq) -> Ni^{2+}(aq) + 2Ag(s)}\]
Given that \[\ce{E^0_{cell}}\] = 1.05 V, 1F = 96,500 C mol–1.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Calculate the e.m.f. of the following cell at 298 K:
Fe(s) | Fe2+ (0.001 M) | | H+ (0.01 M) | H2(g) (1 bar) | Pt(s)
Given that \[\ce{E^0_{cell}}\] = 0.44 V
[log 2 = 0.3010, log 3 = 0.4771, log 10 = 1]
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Using valence bond theory, predict the hybridization and magnetic character of the following:
[CoF6]3– [Atomic number of Co = 27]
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Advertisements
Write the IUPAC name of the following complex:
[CoBr2(en)2]+
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
How many ions are produced from the complex Co(NH3)6]Cl2 in solution?
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Differentiate between the following:
Adsorption and Absorption
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Differentiate between the following:
Lyophobic Sol and Lyophilic Sol
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Differentiate between the following:
Multimolecular Colloid and Macromolecular colloid
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Define the following term:
Zeta potential
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Define the following term:
Coagulation
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Why a negatively charged sol is obtained when AgNO3 solution is added to KI solution?
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Define transition metals.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Why Zn, Cd and Hg are not called transition metals?
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
How is the variability in oxidation states of transition metals different from that of p-block elements?
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
What happens when propanone is treated with CH3MgBr and then hydrolysed?
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
What happens when ethanal is treated with excess ethanol and acid?
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Advertisements
What happens when methanal undergoes cannizzaro reaction?
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Write the main product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{2CH3COCl + (CH3)2Cd ->}\]
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Write the main product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2CHO ->[Zn(Hg)/Conc. HCl]}\]
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Write the main product in the following reaction:
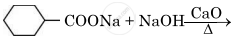
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Give reasons for the following:
Ammonolysis of alkyl halides is not a good method to prepare pure primary amines.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give reasons for the following:
Aniline does not undergo Friedel- Crafts reaction.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Account for the following:
Although the amino group is o, p-directing in aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions, aniline on nitration gives a substantial amount of m-nitroaniline.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Which acid of the following pair would you expect to be stronger?
F−CH2−COOH or CH3−COOH
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points:
CH3CH2OH, CH3−CHO, CH3−COOH
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Which will undergo faster nucleophilic addition reaction?
Acetaldehyde or Propanone
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
What is the composition of Fehling's reagent?
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Draw the structure of the semicarbazone of ethanal.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow:
|
The rate of reaction is concerned with decrease in the concentration of reactants or increase in the concentration of products per unit of time. It can be expressed as instantaneous rate at a particular instant of time and average rate over a large interval of time. A number of factors such as temperature, concentration of reactants, catalyst affect the rate of reaction. Mathematical representation of rate of a reaction is given by rate law: Rate = k[A]x [B]y x and y indicate how sensitive the rate is to change in concentration of A and B. Sum of x + y gives the overall order of a reaction. |
- What is the effect of temperature on the rate constant of a reason? [1]
- For a reaction \[\ce{A + B → Product}\], the rate law is given by, Rate = k[A]2 [B]1/2. What is the order of the reaction? [1]
- How order and molecularity are different for complex reactions? [1]
- A first-order reaction has a rate constant 2 × 10–3 s–1. How long will 6 g of this reactant take to reduce to 2 g? [2]
OR
The half-life for radioactive decay of 14C is 6930 years. An archaeological artifact containing wood had only 75% of the 14C found in a living tree. Find the age of the sample.
[log 4 = 0.6021, log 3 = 0.4771, log 2 = 0.3010, log 10 = 1] [2]
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Chemistry with solutions 2021 - 2022
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 -2022 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Chemistry, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Chemistry will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
