English Medium
Academic Year: 2023-2024
Date & Time: 2nd March 2024, 10:30 am
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them:
- This question paper comprises 39 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper is divided into five sections - A, B, C, D and E.
- Section A - Questions No. 1 to 20 are Multiple Choice Questions. Each question carries 1 mark.
- Section B - Questions No. 21 to 26 are Very Short Answer type questions. Each question carries 2 marks. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C - Questions No. 27 to 33 are Short Answer type questions. Each question carries 3 marks. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- Section D - Questions No. 34 to 36 are Long Answer type questions. Each question carries 5 marks. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E - Questions No. 37 to 39 are of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment carrying 4 marks each with sub-parts.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in some sections. Only one of the alternatives has to be attempted in such questions.
A chemical reaction in which exchange of ions occurs between the reactants is known as ______.
Endothermic reaction
Exothermic reaction
Double displacement reaction
Displacement reaction
Chapter: [0.01] Chemical Reactions and Equations
A zygote is formed by the fusion of a male gamete and a female gamete. The number of chromosomes in the zygote of a human is ______.
23
44
46
92
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
The part of a seed which is a source of food during germination of seed is ______.
Cotyledon
Radicle
Plumule
Embryo
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
The plants that can be raised by the method of vegetative propagation are ______.
sugarcane, roses, grapes
sugarcane, mustard, potato
banana, orange, mustard
papaya, mustard, potato
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
A plant growth inhibitor hormone which causes wilting of leaves is ______.
Auxin
Cytokinin
Abscisic acid
Gibberellin
Chapter: [0.06] Control and Co-ordination
An aqueous solution of a salt turns blue litmus to red. The salt could be the one obtained by the reaction of ______.
HNO3 and NaOH
H2SO4 and KOH
CH3COOH and NaOH
HCl and NH4OH
Chapter: [0.02] Acids, Bases and Salts
Four solutions, namely glucose, alcohol, hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid filled in four separate beakers are connected one by one in an electric circuit with a bulb. The solutions in which the bulb will glow when current is passed are ______.
Glucose and alcohol
Alcohol and hydrochloric acid
Glucose and sulphuric acid
Hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid
Chapter: [0.02] Acids, Bases and Salts
The metals which are found in both free state as well as combined state are ______.
Gold and platinum
Platinum and silver
Copper and silver
Gold and silver
Chapter: [0.03] Metals and Non Metals
The number of single and double bonds present in a molecule of benzene (C6H6) respectively, are ______.
6 and 6
9 and 3
3 and 9
3 and 3
Chapter: [0.03] Metals and Non Metals [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
In human beings, when the process of digestion is completed, the (i) proteins, (ii) carbohydrates and (iii) fats are respectively finally converted into ______.
(i) amino acids, (ii) glucose, (iii) fatty acids
(i) amino acids, (ii) glucose, (iii) fatty acids and glycerol
(i) glucose, (ii) fatty acids and glycerol, (iii) amino acids
(i) sugars, (ii) amino acids, (iii) fatty acids and glycerol
Chapter: [0.05] Life Processes
Some wastes are given below:
- Garden waste
- Ball point pen refills
- Empty medicine bottles made of glass
- Peels of fruits and vegetables
- Old cotton shirt
The non-biodegradable wastes among these are ______.
(i) and (ii)
(ii) and (iii)
(i), (iv) and (v)
(i), (iii) and (iv)
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
A rectangular loop ABCD carrying a current I is situated near a straight conductor XY, such that the conductor is parallel to the side AB of the loop and is in the plane of the loop. If a steady current I is established in the conductor as shown, the conductor XY will ______.

remain stationary
move towards the side AB of the loop
move away from the side AB
rotate about its axis
Chapter: [0.12] Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Absolute refractive indices of glass and water are `3/2 and 4/3` respectively. If the speed of light in glass is 2 × 108 m/s, the speed of light in water is ______.
`9/4xx10^8` m/s
`5/2xx10^8` m/s
`7/3xx10^8` m/s
`16/9xx10^8` m/s
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
When a beam of white light passes through a region having very fine dust particles, the colour of light mainly scattered in that region is ______.
Red
Orange
Blue
Yellow
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Consider the following combinations of resistors:
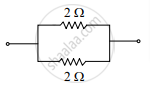



The combinations having equivalent resistance 1 Q is/are ______.
I and IV
Only IV
I and II
I, II and III
Chapter: [0.11] Electricity
An electric iron of resistance 20 Ω draws a current of 5 A. The heat developed in the iron in 30 seconds is ______.
15000 J
6000 J
1500 J
3000 J
Chapter: [0.11] Electricity
Assertion (A): Oxygen is essential for all aerobic forms of life.
Reason (R): Free oxygen atoms combine with molecular oxygen to form ozone.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.05] Life Processes
Assertion (A): Most of the plants close their stomata at night.
Reason (R): Closing of stomata helps to conserve water as large amount of water evaporates from the leaves.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Assertion (A): The extraction of metals from their sulphide ores cannot take place without roasting the ore.
Reason (R): Roasting converts sulphide ores directly into metals.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.03] Metals and Non Metals
Assertion (A): Magnetic field lines never intersect each other.
Reason (R): If they intersect, then at the point of intersection, the compass needle would point towards two directions, which is not possible.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.12] Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
We need to water the soil in plants on a regular basis but it ultimately reaches the leaves of the plant. Explain how this takes place.
Chapter: [0.05] Life Processes
Advertisements
Name the type of nutrition exhibited by Amoeba. Explain how food is taken in and digested by this organism.
Chapter: [0.05] Life Processes
A spatula full of sodium carbonate is taken in a test tube and 2 mL of dilute ethanoic acid is added to it.
Write a chemical equation for the reaction.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A spatula full of sodium carbonate is taken in a test tube and 2 mL of dilute ethanoic acid is added to it.
Suggest a method of testing the gas liberated in the reaction.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
1 gram of solid sodium chloride was taken in a clean and dry test tube and concentrated sulphuric acid was added to it.
- Name the gas evolved in the reaction.
- What will be observed when this gas is tested with (1) dry and (II) wet blue litmus paper?
Write your conclusion about the nature (acidic/basic) of this gas.
Chapter: [0.05] Life Processes
Some metals react with acids to produce salt and hydrogen gas. Illustrate it with an example. How will you test the presence of this gas?
Chapter: [0.02] Acids, Bases and Salts
Mendel crossed pea plants with two pairs of contrasting characters.
| RRYY | × |
rryy |
| Round, Yellow | Wrinkled, Green |
He observed 4 types of combinations in F2 generation. Which of the combinations were new? Write the conclusion drawn by this experiment.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Name the phenomenon of light responsible for Tyndall effect. Write an event where this phenomenon can be observed.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Write Joule's law of heating.
Chapter: [0.11] Electricity
How is Joule's law effect useful in electric circuits where fuse is used as a safety device?
Chapter: [0.11] Electricity
A small amount of copper oxide was taken in a beaker and dilute hydrochloric acid was added with continuous stirring of the solution. Name the compound formed and state the colour of its solution. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction that occurs. Based on the reaction, state the nature (acidic/basic) of copper oxide.
Chapter: [0.02] Acids, Bases and Salts
Define the term "power of accommodation" of human eye.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye?
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Name the muscles of the eye responsible for the power of accommodation.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Explain the role of the part of human eye responsible for power of accommodation of human eye.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Study the picture given below showing three food chains (a), (b) and (c) and answer the following questions:

- Name the type of ecosystems that exist in food chains (b) and (c).
- The first trophic level in all food chains is producers. Why? What percentage of solar energy do these producers capture for their use?
- Why are the arrows shown in the diagram in one direction only and not vice versa? Justify.
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
How is the sex of a newborn individual determined in different species of animals? Give three examples to support your answer.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Why is the conversion of ethanol into ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction?
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Name the oxidising agent used in the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Write the chemical equation for the ethanol to ethanoic acid of an oxidation reaction.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
How is ethanol to ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction different from the reaction in which ethanol burns in the presence of oxygen?
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
How is a solenoid prepared?
Chapter: [0.12] Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Differentiate between a circular coil and a solenoid.
Chapter: [0.12] Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Draw the pattern of magnetic field lines of a solenoid through which a steady current flows. What does the pattern of field lines inside the solenoid indicate?
Chapter: [0.12] Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Explain with the help of a labelled diagram, the process of reproduction in Hydra by budding. Name the cells used for reproduction in this process.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
List two roles of Seminal vesicles and prostate gland in the human reproductive system.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Advertisements
List two roles of the Oviduct in the human reproductive system.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
List two roles of the Testis in the human reproductive system.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
When lead nitrate is heated strongly in a boiling tube, two gases are liberated and a solid residue is left behind in the test tube.
- Name the type of chemical reaction and define it.
- Write the name and formula of the coloured gas liberated.
- Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
- Name the residue left in the test tube and state the method of testing its nature (acidic/basic).
Chapter: [0.01] Chemical Reactions and Equations
Write balanced chemical equation for the following word equation.
Lead nitrate + Potassium iodide → Lead iodide + Potassium nitrate
Is this a double displacement reaction? Justify your answer. Name the compound precipitated and write the ions present in it.
Chapter: [0.01] Chemical Reactions and Equations
Write the method of preparation of Ca(OH)2. What happens when CO2 is passed through it? Write balanced chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Chapter: [0.01] Chemical Reactions and Equations
The variation of image distance (v) with object distance (u) for a convex lens is given in the following observation table. Analyse it and answer the questions that follow:
| Sr. No. | Object distance (u) cm | image distance (v) cm |
| 1 | -150 | +30 |
| 2 | -75 | +37.5 |
| 3 | -50 | +50 |
| 4 | -37.5 | +75 |
| 5 | -30 | +150 |
| 6 | -15 | +37.5 |
- Without calculation, find the focal length of the convex lens. Justify your answer.
- Which observation is not correct? Why? Draw ray diagram to find the position of the image formed for this position of the object.
- Find the approximate value of magnification for u = – 30 cm.
Chapter:
Define the term principal axis of a lens.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Draw a ray diagram to show what happens when a ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a concave lens passes through it.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
The focal length of a concave lens is 20 cm. At what distance from the lens should a 5 cm tall object be placed so that its image is formed at a distance of 15 cm from the lens? Also calculate the size of the image formed.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Define the following:
Reflex arc
Chapter: [0.06] Control and Co-ordination
Why have reflex arcs evolved in animals?
Chapter: [0.06] Control and Co-ordination
Trace the sequence of events which occur when you suddenly touch a hot object.
Chapter: [0.06] Control and Co-ordination
Name the part of the nervous system which helps in communication between the central nervous system and other parts of the body.
Chapter:
What are the two components of the central nervous system?
Chapter:
The leaves of the 'chhui-mui' plant begin to fold up and droop in response to a stimulus. Name the stimulus and write the cause for such a rapid movement. Is there any growth involved in the movement?
Chapter: [0.06] Control and Co-ordination
Define geotropism.
Chapter: [0.06] Control and Co-ordination
What is meant by ‘positive geotropism’ and ‘negative geotropism’? Give one example of each type. Draw a labelled diagram to illustrate your answer, indicating the plant part, which shows positive geotropism, and the plant part, which shows negative geotropism.
Chapter: [0.06] Control and Co-ordination
Study the following circuit:
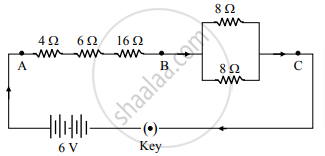
On the basis of this circuit, answer the following questions:
i. Find the value of total resistance between the points A and B.
ii. Find the resistance between the points B and C.
iii. Calculate the current drawn from the battery, when the key is closed
OR
iii. In the above circuit, the 16Ω resistor or the parallel combination of two resistors of 8 Ω, which one of the two will have more potential difference across its two ends? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.11] Electricity
Three metal samples of magnesium, aluminium and iron were taken and rubbed with sandpaper. These samples were then put separately in test tubes containing dilute hydrochloric acid. Thermometers were also suspended in each test tube so that their bulbs dipped in the acid. The rate of formation of bubbles was observed. The above activity was repeated with dilute nitric acid and the observations were recorded.
Answer the following questions:
(i) When the activity was done with dilute hydrochloric acid, then in which one of the test tubes was the rate of formation of bubbles the fastest and the thermometer showed the highest temperature?
(ii) Which metal did not react with dilute hydrochloric acid? Give reason.
(iii) Why is hydrogen gas not evolved when a metal reacts with dilute nitric acid? Name the ultimate products formed in the reaction.
OR
Name the type of reaction on the basis of which the reactivity of metals is decided. You have two metals X and Y. How would you decide which is more reactive than the other?
Chapter: [0.03] Metals and Non Metals
Kidneys are vital organs for survival. Several factors like infections, injury or restricted blood flow to kidneys reduce the activity of kidneys. This leads to the accumulation of poisonous wastes in the body, which can even lead to death. In case of kidney failure, an artificial kidney can be used. An artificial kidney is a device to remove waste products from the blood through dialysis.
i. a. Name the artery that brings oxygenated blood to the kidney.
b. Name the cluster of the thin-walled blood capillaries present in the Bowman's capsule.
ii. In the human excretory system, name the organ which stores urine. Is this organ under hormonal control or nervous control?
iii. List two major steps involved in the formation of urine and state in brief their functions.
OR
iii. In which part of the nephron does selective reabsorption take place? List the factors which the amount of water reabsorbed depends on.
Chapter: [0.05] Life Processes
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 10 Science with solutions 2023 - 2024
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 10 Science-2024 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Science, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 10.
How CBSE Class 10 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Science will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
