English Medium
Academic Year: 2024-2025
Date & Time: 20th February 2025, 10:30 am
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them:
- This question paper comprises 39 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper is divided into five sections - A, B, C, D and E.
- Section A - Questions No. 1 to 20 are Multiple Choice Questions. Each question carries 1 mark.
- Section B - Questions No. 21 to 26 are Very Short Answer type questions. Each question carries 2 marks. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C - Questions No. 27 to 33 are Short Answer type questions. Each question carries 3 marks. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- Section D - Questions No. 34 to 36 are Long Answer type questions. Each question carries 5 marks. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E - Questions No. 37 to 39 are of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment carrying 4 marks each with sub-parts.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in some sections. Only one of the alternatives has to be attempted in such questions.
The metals obtained from their molten chlorides by the process of electrolytic reduction are ______.
Gold and silver
Calcium and magnesium
Aluminium and silver
Sodium and iron
Chapter:
The formation of magnesium oxide is correctly shown in option:
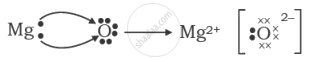


Chapter:
Reaction between two elements A and B, forms a compound C. A loses electrons and B gains electrons. Which one of the following properties will not be shown by compound C?
It has high melting point.
It is highly soluble in water.
It has weak electrostatic forces of attraction between its oppositely charged ions.
It conducts electricity in its molten state or aqueous solution.
Chapter:
Consider the following reactions:
- Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide.
- Magnesium oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
- Carbon dioxide reacts with sodium hydroxide.
It is found that in each case:
Salt and water is formed.
Neutral salts are formed.
Hydrogen gas is formed.
Acidic salts are formed.
Chapter:
Tooth enamel is made up of calcium hydroxyapatite (a crystalline form of calcium phosphate). This chemical starts corroding in the mouth when the pH is ______.
7
5
10
14
Chapter:
The products formed when Aluminium and Magnesium are burnt in the presence of air respectively are ______.
Al3O4 and MgO2
Al2O3 and MgO
Al3O4 and MgO
Al2O3 and MgO2
Chapter:
Electrolysis of water is a decomposition reaction. The mass ratio (MH : MO) of hydrogen and oxygen gases liberated at the electrodes during electrolysis of water is ______.
8 : 1
2 : 1
1 : 2
1 : 8
Chapter:
The breakdown of glucose has taken the following pathway:
\[\ce{Glucose ->[(a)] Pyruvate + Energy ->[(b)] Lactic acid + Energy}\]
The sites ‘a’ and ‘b’ respectively are:
Mitochondria and Oxygen deficient muscle cells
Cytoplasm and Oxygen rich muscle cells
Cytoplasm and Yeast cells
Cytoplasm and Oxygen deficient muscle cells
Chapter:
If pea plants with round and green seeds (RRyy) are crossed with pea plants having wrinkled and yellow seeds (rrYY), the seeds developed by the plants of F1 generation will be ______.
50% round and yellow
75% wrinkled and green
100% round and yellow
75% wrinkled and yellow
Chapter:
The correct/true statement(s) for a bisexual flower is/are:
- They possess both stamen and pistil.
- They possess either stamen or pistil.
- They exhibit either self-pollination or cross-pollination.
- They cannot produce fruits on their own.
(i) only
(iv) only
(i) and (iii)
(i) and (iv)
Chapter:
The plant hormone whose concentration stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light is ______.
Cytokinins
Gibberellins
Adrenaline
Auxins
Chapter:
Secretion of less saliva in mouth will effect the conversion of ______.
proteins into amino acids
fats into fatty acids and glycerol
starch into simple sugars
sugars into alcohol
Chapter:
The percentage of solar energy which is not converted into food energy by the leaves of green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem is about ______.
1%
10%
90%
99%
Chapter:
Which of the following groups do not constitute a food chain?
- Wolf, rabbit, grass, lion
- Plankton, man, grasshopper fish
- Hawk, grass, snake, grasshopper, frog
- Grass, snake, wolf, tiger
(i) and (iv)
(i) and (iii)
(ii) and (iii)
(ii) and (iv)
Chapter:
The phenomenon responsible for making the smoke particles visible when a beam of sunlight enters a smoke filled room through a narrow hole is ______.
scattering of light
dispersion of light
reflection of light
internal reflection of light
Chapter:
Mirror ‘X’ is used to concentrate sunlight in solar furnace and Mirror ‘Y’ is fitted on the side of the vehicle to see the traffic behind the driver. Which of the following statements are true for the two mirrors?
- The image formed by mirror ‘X’ is real, diminished and at its focus.
- The image formed by mirror ‘Y’ is virtual, diminished and erect.
- The image formed by mirror ‘X’ is virtual, diminished and erect.
- The image formed by mirror ‘Y’ is real. diminished and at its focus.
(i) and (ii)
(ii) and (iii)
(iii) and (v)
(i) and (iv)
Chapter:
Assertion (A): The amount of ozone in the atmosphere began to drop sharply in the 1980s.
Reason (R): The oxygen atoms combine with molecular oxygen to form ozone.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): No two magnetic field lines are found to cross each other.
Reason (R): The compass needle cannot point towards two directions at the point of intersection of two magnetic field lines.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): A human child bears all the basic features of human beings.
Reason (R): It looks exactly like its parents, showing very little variations.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): Decomposition reactions are generally endothermic reactions.
Reason (R): Decomposition of organic matter into compost is an exothermic process.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter:
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. Use mirror formula to determine the position of the image formed by this mirror.
Chapter:
Consider two lamps A and B of rating 50 W; 220 V and 25 W; 220 V respectively. Find the ratio of the resistances of the two lamps (i.e., RA : RB).
Chapter:
Heat produced per second due to a current in a resistor of 4 Ω is 400 joules. Calculate the potential difference across the resistor.
Chapter:
Draw a labelled diagram in proper sequence to show budding in hydra.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Besides minimising the loss of blood, why is it essential to plug any leak in a blood vessel? Name the component of blood which helps in this process and state how this component performs this function.
Chapter:
Advertisements
The transport system in plants is relatively slower than in animals. Give reasons.
Chapter:
State the role of phloem in the transport of materials in plants.
Chapter:
A student performs the following experiment in his school laboratory.
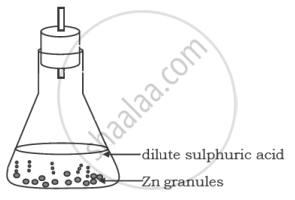
List two observations to justify that in this experiment a chemical change has taken place.
Chapter:
Translate the following statement into a chemical equation and then balance it:
Nitric acid reacts with calcium hydroxide to form calcium nitrate and water.
Chapter:
Translate the following statement into a chemical equation and then balance it:
Sodium chloride reacts with silver nitrate to form silver chloride and sodium nitrate.
Chapter:
Draw a schematic diagram of an electric circuit of a cell of 1.5 V, 5 Ω and 10 Ω resistor and a plug key, all connected in series. Calculate the current drawn from the cell when the key is closed.
Chapter:
Consider the following electric circuit:
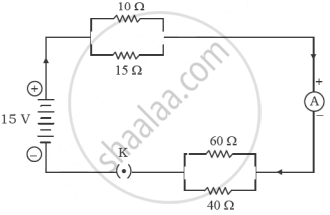
Calculate the values of the following:
- The total resistance of the circuit.
- The total current drawn from the source.
- Potential difference across the parallel combination of 10 Ω and 15 Ω resistors.
Chapter:
Draw ray diagram to show the nature, position, and relative size of the image formed by a convex mirror when the object is placed at infinity.
Chapter:
Draw ray diagram to show the nature, position, and relative size of the image formed by a convex mirror when the object is placed at the infinity pole P of the mirror.
Chapter:
How many pairs of chromosomes are present in human beings? Out of these how many are sex chromosomes?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Explain how, in sexually reproducing organisms, the number of chromosomes in the progeny is maintained.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
A hormone ‘X’ is secreted in blood when a person is under scary situation.
- Identify the hormone ‘X’ and the gland that secretes it.
- Explain its role in dealing with scary or emergency situations.
Chapter:
With the help of an activity, explain the conditions under which iron articles get rusted.
Chapter:
Name two metals which react violently with cold water. Write any three observations you would make when such a metal is dropped into water.
Chapter: [0.03] Metals and Non Metals
“Displacement reactions also play a key role in extracting metals in the middle of the reactivity series.” Justify this statement with two examples.
Chapter:
Why can metals high up in the reactivity series not be obtained by reduction of their oxides by carbon?
Chapter:
The power of a lens ‘X’ is −2.5 D. Name the lens and determine its focal length in cm. For which eye defect of vision will an optician prescribe this type of lens as a corrective lens?
Chapter:
“The value of magnification ‘m’ for a lens is −2.” Using the new Cartesian Sign Convention and considering that an object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from the optical centre of this lens, state:
- the nature of the image formed;
- size of the image compared to the size of the object;
- position of the image, and
- sign of the height of the image.
Chapter:
The numerical values of the focal lengths of two lenses A and B are 10 cm and 20 cm respectively. Which one of the two will show higher degree of convergence/divergence? Give reason to justify your answer.
Chapter:
Advertisements
Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab when it falls obliquely from air into glass.
Chapter:
How will you differentiate between a convex and a concave lens by looking at
- a distant object,
- a printed page?
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
List two functions ovary of human female reproductive system.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Write the function of the following part in a human female reproductive system:
Fallopian tube
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Write the function of the following part in a human female reproductive system:
Uterus
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
State briefly two contraceptive methods used by human males.
Chapter:
Explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Chapter:
Identify A, B and C in the diagram given below and write one function of each.
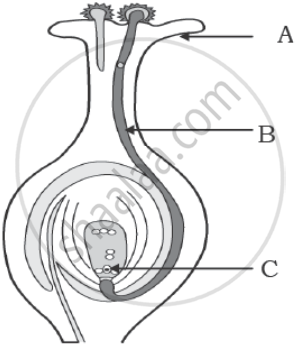
Chapter:
In electron dot structure, the valence shell electrons are represented by crosses or dots.
- The atomic number of chlorine is 17. Write its electronic configuration
- Draw the electron dot structure of chlorine molecule.
Chapter:
What happens when methane reacts with chlorine? Give equation of the reaction which takes place.
Chapter:
Name the two oxidising agents used for the conversion of alcohols to acids.
Chapter:
Compare the properties of ionic compounds and covalent compounds.
Chapter: [0.03] Metals and Non Metals [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Give reason why carbon forms compounds mainly by covalent bonding.
Chapter:
Why do covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points?
Chapter:
State the reason to explain why covalent compounds "are bad conductors of electricity".
Chapter: [0.03] Metals and Non Metals [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Give reason for the following:
Carbon shows catenation.
Chapter:
The following question is a source-based/case-based question that follows. Read the case carefully and answer the questions that follow.
| In our homes, we receive the supply of electric power through a main supply also called mains, either supported through overhead electric poles or by underground cables. In our country the potential difference between the two wires (live wire and neutral wire) of this supply is 220 V. |
- Write the colours of the insulation covers of the line wires through which supply comes to our homes. (1)
- What should be the current rating of the electric circuit (220 V) so that an electric iron of 1 kW power rating can be operated? (1)
-
- What is the function of the earth wire? State the advantage of the earth wire in domestic electric appliances such as electric iron. (2)
OR - List two precautions to be taken to avoid electrical accidents. State how these precautions prevent possible damage to the circuit/appliance. (2)
- What is the function of the earth wire? State the advantage of the earth wire in domestic electric appliances such as electric iron. (2)
Chapter:
The following question is a source-based/case-based question that follows. Read the case carefully and answer the questions that follow.
| Seawater contains many salts dissolved in it. Common salt is separated from these salts. Deposits of solid salt are also found in several parts of the world. These large crystals are often brown due to impurities. This is called rock salt and is mined like coal. The common salt is an important raw material for chemicals of daily use. |
- Write balanced chemical equations to show the products formed during the electrolysis of brine. (1)
- List two uses of any one product obtained during the electrolysis of brine. (1)
-
- A mild, non-corrosive basic salt ‘A’, used for faster cooking, is strongly heated to produce a compound ‘B’, that is used for removing the permanent hardness of water. Identify A and B and also write the equation for the reaction that occurs when A is heated. (2)
OR - Define water of crystallisation. Give two examples of salts that have water of crystallisation. (2)
- A mild, non-corrosive basic salt ‘A’, used for faster cooking, is strongly heated to produce a compound ‘B’, that is used for removing the permanent hardness of water. Identify A and B and also write the equation for the reaction that occurs when A is heated. (2)
Chapter:
The following question is a source-based/case-based question that follows. Read the case carefully and answer the questions that follow.
| The maintenance functions of all living organisms must go on even when they are not doing anything particular. Even when we are just sitting in a class or even asleep, this maintenance job has to go on. These maintenance processes require energy to prevent damage and break-down of cells and tissues, which is obtained by the individual organism from the food prepared by the autotrophs, called producers. |
- Name and define the process by which green plants prepare food. (1)
- Write chemical equation involved in the above process. (1)
-
- State in proper sequence the events that occur in synthesis of food by desert plants. (2)
OR - Explain giving reasons what happens to the rate at which the green plants will prepare food: (2)
- during cloudy weather, and
- when stomata get blocked due to dust.
- State in proper sequence the events that occur in synthesis of food by desert plants. (2)
Chapter:
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 10 Science with solutions 2024 - 2025
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 10 Science-2025 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Science, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 10.
How CBSE Class 10 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Science will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
