Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Is Matter Around Us Pure
3: Atoms and Molecules
4: Structure of the Atom
![Lakhmir Singh solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 9 chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings Lakhmir Singh solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 9 chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-class-9_6:8c392a83d00d42db9c0dc4493c97af82.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 1: Matter in Our Surroundings
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 1 of CBSE Lakhmir Singh for Chemistry [English] Class 9.
Lakhmir Singh solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 9 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Very Short Answers [Pages 17 - 22]
What are the conditions for 'something' to be called 'matter'?
Name two processes which provide the best evidence for the motion of particles in matter.
Which single term is used to describe the mixing of copper sulphate and water kept in a beaker, on its own?
When sugar is dissolved in water, there is no increase in the volume. Which characteristic of matter is illustrated by this observation?
Even two or three crystals of potassium permanganate can impart colour to a very large volume of water. Which characteristic of particles of matter is illustrated by this observation?
When an incense stick (agarbatti) is lighted in one corner of a room, its fragrance spreads in the whole room quickly. Which characteristic of the particles of matter is illustrated by this observation?
A piece of chalk can be broken into small particles by hammering but a piece of iron cannot be taken into small particles by hammering. Which characteristic of the particles of matter is illustrated by these observations?
What is the scientific name of particles which make up mater?
Name the process by which a drop of ink spreads in a beaker of water.

What is the general name of :
- rigid form of matter ?
- fluid forms of matter ?
Out of solids, liquids and gases, which one has :
- maximum movement of particles ?
- maximum interparticle attractions ?
- minimum spaces between particles ?
'A substance has definite volume but no definite shape'. State whether this substance is a solid, a liquid or a gas.
Name the physical state of matter which can be easily compressed.
"A substance has a definite shape as well as a definite volume." Which physical state is represented by this statement?
A substance has neither a fixed shape nor a fixed volume. State whether it is a solid, a liquid or a gas.
Name two gases which are supplied in compressed form in homes and hospitals.
Write the full forms of the following
- LPG
- CNG
Which of the two diffuses faster : a liquid or a gas?
Which of the two diffuses slower : bromine vapour into air or copper sulphate into water ?
State whether the following statement is true or false :
Red-brown bromine vapour diffuse into air in a gas jar but the colourless air molecules do not diffuse into bromine vapour.
A bottle of perfume was opened in a room. The smell of its vapours spread in the entire room. Name the property of gases which is responsible for this behaviour of perfume vapours.
If the fish is being fried in a neighbouring home, we can smell it sitting in our own home. Name the process which brings this smell to us.
Name one property of liquids and gases which tells us that their molecules are moving constantly.
Fill in the following blank with suitable words :
The best evidence that the particles of matter are constantly moving comes from the studies of ................. and ...................
Fill in the following blank with suitable words :
The smell of perfume gradually spreads across a room due to .....................
Fill in the following blank with suitable words :
Solid, liquid and gas are the three ........................ of matter.
Fill in the following blank with suitable words :
At room temperature, the forces of attraction between the particles of solid substances are ....................... then those which exist in the gaseous state.
Fill in the following blank with suitable words :
The arrangement of particles is less ordered in the ______ state. However, there is no order in the ______ state.
State two characteristics of matter demonstrated by diffusion.
State two characteristics of matter demonstrated by Brownian motion.
Name the scientist who studied the movement of pollen grains suspended in water through a microscope. What is this phenomenon known as?
When a crystal of potassium permanganate is placed in a beaker, its purple colour spreads throughout the water. What does this observation tell us about the nature of potassium permanganate and water?
When a gas jar containing air is inverted over a gas jar containing bromine vapour, the red-brown bromine vapour diffuse into air. Explain how bromine vapour diffuse into air.
Describe in your own words, what happens to the particles when salt dissolves in water.
Explain why, we can easily move our hand in air but to do the same through a plank of wood, we need a karate expert.
Give one example of the diffusion of a solid in another solid.
Explain why, the diffusion of a solid in another solid is a very slow process.
Which of the following diffuses fastest and which the slowest?
Solid, Liquid, Gas Give reasons for your answer.
Explain the following :
When an incense stick is lighted in the corner of a room, its fragrance spreads quickly in the entire room.
Name the three states of matter. Give one example of each.
State two characteristic properties of a solid.
State two characteristic properties of a liquid.
State two characteristic properties of a gas.
Why do gases have neither a fixed shape nor a fixed volume?
How do solids, liquids and gases differ in shape and volume?
Arrange the following substances in increasing order of force of attraction between their particles (keeping the substance having the minimum force of attraction first) : Water, Sugar, Oxygen
Give two reasons to justify that Water is a liquid at room temperature.
Give two reasons to justify that An iron almirah is a solid.
When an incense stick (agarbatti) is lighted in one corner of a room, its fragrance quickly spreads in the entire room. Name the process involved in this.
A girl is cooking some food in the kitchen. The smell of food being cooked soon reaches her brother's room. Explain how the smell could have reached her brother's room.
What does the diffusion of gases tell us about their particles?
Give one example of diffusion of gases in a liquid.
Define the following terms Condensation
Give reason for the following observation :
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches us even from a considerable distance but to get the smell from cold food, we have to go close to it.
Explain how, the smell of food being cooked in the kitchen reaches us even from a considerable distance.
Explain why, when a bottle of perfume is opened in a room, we can smell it even from a considerable distance.
When a crystal of copper sulphate is placed at the bottom of a beaker containing water, the water slowly turns blue. Why?
Honey is more viscous than water. Can you suggest why?
Explain why air is used to inflate tyres.
Explain why steel is used to make railway lines.
Explain why, diffusion occurs more quickly in a gas than in a liquid.
What is meant by 'diffusion'? Give one example of diffusion in gases.
Why do gases diffuse very fast?
Name two gases of air which dissolve in water by diffusion. What is the importance of this process in nature?
Compare the properties of solids, liquids and gases in tabular form.
Give two reasons for saying that wood is a solid.
Why does a gas exert pressure?
Why are gases so easily compressible whereas it is almost impossible to compress a solid or a liquid?
Why does a gas fill a vessel completely?
Define matter. Give four examples of matter.
What are the characteristics of matter?
What is Brownian motion? Draw a diagram to show the movement of a particle (like a pollen grain during Brownian motion.
In a beam of sunlight entering a room, we can sometimes see dust particles moving in a haphazard way in the air. Why do these dust particles move?
When a crystal of potassium permanganate is placed at the bottom of water in a beaker, the water in the whole beaker turns purple on its own, even without stirring. This is an example of :
distribution
intrusion
diffusion
effusion
Which one of the following statement is correct in respect of fluids?
only gases behave as fluids
gases and solids behave as fluids
gases and liquids behave as fluids
only liquids are fluids
A few substances are arranged in the increasing order of 'forces of attraction' between their particles. Which one of the following represents the correct arrangement?
water, air, wind
air, sugar, oil
oxygen, water, sugar
salt, juice, air
In which of the following conditions, the distance between the molecules of hydrogen gas would increase?
- increasing pressure on hydrogen contained in a closed container
- some hydrogen gas leaking out of the container
- increasing the volume of the container of hydrogen gas
- adding more hydrogen gas to the container without increasing the volume of the container
(i) and (iii)
(i) and (iv)
(ii) and (iii)
(ii) and (iv)
Out of the following, an example of matter which can be termed as fluid is :
carbon
sulphur
oxygen
phosphorus
The best evidence for the existence and movement of particles in liquids was provided by :
John Dalton
Ernest Rutherford
J.J. Thomson
Robert Brown
A form of matter has no fixed shape but it has a fixed volume. An example of this form of matter is :
krypton
kerosene
carbon steel
carbon dioxide
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
the particles of matter are very, very small
the particles of matter attract one another
the particles of some of the matter are moving constantly
the particles of all the matter have spaces between them
When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red-brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. In this experiment :
air is heavier than bromine
both air and bromine have the same density
bromine is heavier than air
bromine cannot be heavier than air because it is going upwards against gravity
When a gas jar containing colourless air is kept upside down over a gas jar full of brown-coloured bromine vapour, then after some time, the brown colour of bromine vapour spreads into the upper gas jar making both the gas jars appear brown in colour. Which of the following conclusion obtained from these observations is incorrect?
bromine vapour is made of tiny particles which are moving
air is made up of tiny particles which are moving
the particles of bromine are moving but those of air are not moving
even though bromine vapour is heavier that air, it can move up against gravity
Which one of the following statements is not true?
- the molecules in a solid vibrate about a fixed position
- the molecules in a liquid are arranged in a regular pattern
- the molecules in a gas exert negligibly small forces on each other, except during collisions
- the molecules of a gas occupy all the space available
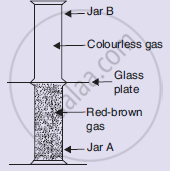
Look at the diagram on the right side. Jar A contains a red-brown gas whereas jar B contains a colourless gas. The two gas jars are separated by a galas plate placed between them
- What will happen when the glass plate between the two jars is pulled away?
- What name is given to the phenomenon which takes place?
- Name the brown gas which could be in jar A.
- Which is the colourless gas most likely to be present in jar B?
- Name one coloured solid and one colourless liquid which can show the same phenomenon.
Bromine and air take about 15 minutes to diffuse completely but bromine diffuses into a vacuum very rapidly. Why is this so?
Bromine particles are almost twice as heavy as chlorine particles. Which gas will diffuse faster; bromine (vapour) or chlorine? Explain your answer.
Why is liquid (the hydraulic fluid) used to operate the brakes in a car?
Explain why, a small volume of water in a kettle can fill a kitchen with steam.
Explain why, osmosis can be considered to be a special kind of diffusion. Classify the following into
(i) osmosis, and (ii) diffusion :
- swelling up of a raisin on keeping in water
- spreading of virus on sneezing
- earthworm dying on coming in contact with common salt
- shrinking of grapes kept in thick sugar syrup
- preserving of pickles in salt
- spreading of smell of cake being baked in the kitchen
- aquatic animals using oxygen dissolved in water during respiration
A student placed a gas jar containing air in the upside down position over a gas jar full of red-brown bromine vapours. He observed that the red-brown colour spread upwards into the jar containing air. Based on this observation, the student concluded that it is only the bromine vapour which moves up and diffuses into air in the upper jar, the air from the upper jar does not move down by diffusion into the lower jar containing bromine vapours. Do you agree with this conclusion of the student? Give reason for your answer.
An inflated balloon full of air goes down slowly (becomes smaller and smaller slowly) even though the knot at the mouth of the balloon is airtight. And after a week all the air has escaped from the balloon. Explain how the air particles got out of the balloon.
When extremely small particles X derived from the anther of a flower were suspended in a liquid Y and observed through a microscope, it was found that the particles X were moving throughout the liquid Y in a very zig-zag way. It was also observed that warmer the liquid Y, faster the particles X moved on its surface.
- What could particles X be ?
- What do you think liquid Y is ?
- What is the zig-zag movement of X known as ?
- What is causing the zig-zag movement of particles X ?
- Name the scientist who discovered this phenomenon.
- What does this experiment tell us about the nature of liquid Y?
When a beam of sunlight enters a room through a window, we can see tiny particles X suspended in a gas (or rather a mixture of gases) Y which are moving rapidly in a very haphazard manner.
- What could particles X be ?
- Name the gas (or mixture of gases) Y.
- What is the phenomenon exhibited by particles X known as ?
- What is causing the movement of particles X ?
- What conclusion does the existence of this phenomenon give us about the nature of matter ?
Lakhmir Singh solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 9 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Very Short Answers [Pages 36 - 40]
The boiling point of water is 100° C. Express this in SI units (Kelvin scale).
The Kelvin temperature is 270 K. What is the corresponding Celsius scale temperature ?
Convert the temperature of 573 K to the Celsius scale.
Convert the temperature of 373° C to the Kelvin scale.
The boiling point of alcohol is 78° C. What is this temperature on Kelvin scale ?
Name a non-metal which is a good conductor of electricity.
The Kelvin scale temperature is 0 K. What is the corresponding Celsius scale temperature ?
Give the usual name for the following :
Heat required to change the state of a substance without changing the temperature.
What is the (a) common unit of temperature, and (b) SI unit of temperature ?
Write the relation between Kelvin scale and Celsius scale of temperature.
What should be added to a Celsius scale reading so as to obtain the corresponding Kelvin scale reading ?
What is meant by saying that the latent heat of fusion of ice is 3.34 × 105 J/kg ?
What is meant by saying that the latent heat of vaporisation of water is 22.5 × 105 J/kg ?
Name the temperature at which :
- a liquid changes into a gas.
- a solid changes into a liquid.
Name one common substance which can be easily changed from one state to another by heating or cooling.
What is the name of the process in which a solid turns directly into a gas ?
What is the name of the process in which a gas turns directly into a solid ?
Name one property which is shown by ammonium chloride but not by sodium chloride.
What is the name of the process due to which dry ice changes into carbon dioxide gas ?
What is the common name of solid carbon dioxide ?
Why is solid carbon dioxide known as dry ice ?
State one condition necessary to liquefy gases (other than applying high pressure).
State whether the following statement is true or false :
Solid carbon dioxide is stored under low pressure.
What is the chemical name of dry ice ?
Fill in the following blank with suitable words :
Gases can be liquefied by applying ....................... and lowering .....................
Fill in the following blank with suitable words :
When steam condenses to form water, heat is .......................
Fill in the following blank with suitable words :
Temp on Kelvin scale = Temp on Celsius scale + ........................
Fill in the following blank with suitable words :
Scientists say that there are actually five states of matter : solid, liquid, gas, .................... and ...................
Fill in the following blank with suitable words :
The state of matter called ........................ makes a fluorescent tube (or neon sign bulb) to glow.
What do you understand by the term 'latent heat' ? What are the two types of latent heat ?
Why is heat energy needed to melt a solid ? What is this heat energy called ?
Under what conditions heat can be given to a substance without raising its temperature ?
Why does the temperature remain constant during the melting of ice even though heat is supplied continuously ?
Why does the temperature remain constant during the boiling of water even though heat is supplied continuously ?
Explain why, ice at 0° C is more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature.
Would you cool a bucket of water more quickly by placing it on ice or by placing ice in it ? Give reasons for your answer.
Why does steam cause more severe burns than boiling water ?
Which contains more heat, 1 kg of ice of 0° C or 1 kg of water at 0° C ? Give reason for your answer.
Which contains more heat, 1 kg of water at 100° C or 1 kg of steam at 100° C ? Give reason for your answer.
Explain why, steam at 100° C is better for heating purposes than boiling water at 100° C.
Which produces more severe burns : boiling water or steam ? Why ?
Why does the temperature of a substance remain constant during the change of state ?
What is the physical state of water at 0°C.
What is the physical state of water at 25°C.
What is the physical state of water at 100°C.
What is the physical state of water at 250°C.
Explain why, there is no rise in temperature of a substance when it undergoes a change of state though heat is supplied continuously.
Define 'melting point' of a substance ? What is the melting point of ice
Define 'boiling point' of a substance ? What is the boiling point of water ?
Define the following term Melting.
Define the following term Boiling.
Define the following term Freezing.
Explain why, naphthalene balls kept in stored clothes in our homes disappear over a period of time.
Explain briefly, how gases can be liquefied.
How is ammonia gas liquefied ?
How does applying pressure (or compression) help in the liquefaction of a gas ?
How does perspiration or sweating help keep our body cool on a hot day ?
Why does all the water of the earth not get evaporated during hot summer days ?
If the back of your hand is moistened with alcohol, you will find that it rapidly becomes dry. Why is it that while it is drying, your hand feels cool ?
Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot, dry day ?
How does the water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cold during summer ?
What type of clothes should we wear in summer ? Why ?
Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer rather than from a cup ?
Why does our palm feel cold when we put some acetone (or perfume) on it ?
How will you demonstrate that water vapour is present in air ?
Define the term 'latent heat of fusion' of a solid. How much is the latent heat of fusion of ice ?
Draw a labelled diagram of the experimental set-up to study the latent heat of fusion of ice.
Define the term 'latent heat of vaporisation' of a liquid. What is the value of the latent heat of vaporisation of water ?
Draw a labelled diagram of the experimental set-up to study the latent heat of vaporisation of water.
What is sublimation ? Name two substances (other than ammonium chloride) which undergo sublimation.
Draw a labelled diagram of the experimental set-up to demonstrate the sublimation of ammonium chloride.
What are the two ways in which the physical states of matter can be changed ?
Draw the 'states of matter triangle' to show the interconversion of states of matter.
How can the evaporation of a liquid be made faster ?
What is evaporation ? State the various factors which affect evaporation.
Why does evaporation cool a liquid ?
Which of the following are also considered to be the states of matter ?
- Plasma
- Platelets
- BEC
- BHC
(i) and (ii)
(ii) and (iii)
(ii) and (iii)
(ii) and (iv)
One of the following does not undergo sublimation. This one is :
iodine
sodium chloride
ammonium chloride
camphor
Which of the following process/processes release heat ?
- condensation
- vaporisation
- freezing
- melting
only (i)
only (iv)
(i) and (iii)
(ii) and (iv)
If the temperature of an object is 268 K, it will be equivalent to :
– 5°C
+ 5°C
368°C
– 25°C
The boiling point of ethane is – 88°C. This temperature will be equivalent to :
285 K
288 K
185 K
361 K
When heat is constantly supplied by a gas burner with small flame to melt ice, then the temperature of ice during melting :
increases very slowly
does not increase at all
first remains constant and then increases
increases to form liquid water
When water at 0°C freezes to form ice at the same temperature of 0°C, then it :
absorbs some heat
releases some heat
neither absorbs nor releases heat
absorbs exactly 3.34 × 105 J/kg of heat
When heat is constantly supplied by a burner to boiling water, then the temperature of water during vaporisation :
rises very slowly
rises rapidly until steam is produced
first rises and then becomes constant
does not rise at all
The latent heat of fusion of ice is :
33.4 × 105 J/kg
22.5 × 105 J/kg
33.4 × 104 J/kg
22.5 × 104 J/kg
The latent heat of vaporisation of water is :
2.25 × 106 J/kg
3.34 × 106 J/kg
22.5 × 104 J/kg
33.4 × 105 J/kg
Which one of the following set of phenomena would increase on raising the temperature ?
diffusion, evaporation, compression of gases
evaporation, compression of gases, solubility
evaporation, diffusion, expansion of gases
evaporation, solubility, diffusion, compression of gases
Which of the following represent the suitable conditions for the liquefaction of gases ?
low temperature, low pressure
high temperature, low pressure
low temperature, high pressure
high temperature, high pressure
During summer days, water kept in an earthen pot (pitcher) becomes cool because of the phenomenon of :
diffusion
transpiration
osmosis
evaporation
On converting 25°C, 38°C and 66°C to Kelvin scale, the correct sequence of temperatures will be :
298 K, 311 K and 339 K
298 K, 300 K and 338 K
273 K, 278 K and 543 K
298 K, 310 K and 338 K
The conversion of a solid into vapours without passing through the liquid state is called :
vaporisation
fusion
sublimation
freezing
The evaporation of water increases under the following conditions :
increase in temperature, decrease in surface area
increase in surface area, decrease in temperature
increase in surface area, rise in temperature
increase in temperature, increase in surface area, addition of common salt
On converting 308 K, 329 K and 391 K to Celsius scale, the correct sequence of temperatures will be :
33°C, 56°C and 118°C
35°C, 56°C and 119°C
35°C, 56°C and 118°C
56°, 119°C and 35° C
Which of the following energy is absorbed during the change of state of a substance ?
specific heat
latent heat
heat capacity
heat of solution
Which of the following factors are responsible for the change in state of solid carbon dioxide when kept exposed to air ?
- increase in pressure
- ncrease in temperature
- decrease in pressure
- decrease in temperature
(i) and (ii)
(i) and (iii)
(ii) and (iii)
(ii) and (iv)
During respiration, glucose and oxygen enter our body cells and waste products carbon dioxide and water leave the body cells by the process of :
effusion
osmosis
diffusion
plasmolysis
There are four substances W, X, Y and Z. The substance W is a dark violet solid having diatomic molecules. A solution of W in alcohol is used as a common antiseptic C. The substance X is a white solid which is usually recovered from sea water on a large scale. The substance Y is a white solid which is insoluble in water and used in the form of small balls for the safe storage of woollen clothes. The substance Z is a yet another white solid which is used in making commonly used dry cells.
- Name (i) W (ii) X (iii) Y and (iv) Z.
- Out of W, X, Y and Z, which substance/substances can undergo sublimation ?
- Which substance is organic in nature ?
- What is the name of substance C ?
- Which substance belongs to the halogen family ?
The substance X normally exists in a physical state which can flow easily but does not fill its vessel completely. It also turns anhydrous copper sulphate blue. When substance X is cooled excessively, it changes into a substance Y which has a fixed shape as well as a fixed volume. If, however, the substance X is heated strongly, it changes into a substance Z which has neither a fixed shape nor a fixed volume.
- Name the substances (i) X (ii) Y and (iii) Z.
- What is the process of conversion of X into Y known as ?
- At which temperature X gets converted into Y ?
- What is the process of conversion of X into Z known as ?
- At which temperature X gets converted into Z ?
The scientists now say that there are actually five states of matter A, B, C, D and E. The state A has a fixed volume but no fixed shape. The state B can be compressed very easily by applying pressure and state C has a fixed shape as well as a fixed volume. The state D is a mixture of free electrons and ions whereas state E is named after an Indian scientist and a famous physicist.
- Name the physical states (i) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D, and (v) E
- Name one substance belonging to state C which can directly change into vapours on heating. What is this process known as ?
- Name one substance which normally belongs to state B but whose solid form changes directly into gaseous state.
- Name the most common substance belonging to state A.
- Which state of matter makes the sun and other stars to glow ?
When water is cooled to a temperature x, it gets converted into ice at temperature x by a process called P. And when ice at temperature x is warmed, it gets reconverted into water at the same temperature x in a process called Q.
- What is the value of temperature x in Kelvin ?
- What is the process P known as ?
- What is the name of energy released during process P ?
- What is the process Q known as ?
- What is the name of energy absorbed during process Q ?
When water is heated to a temperature x, it gets converted into steam at temperature x by a process called R. And when steam at temperature x is cooled, it gets reconverted into water at the same temperature x by a process called S.
- How much is the value of x in Kelvin ?
- What is the process R called ?
- What is the name of the energy absorbed during the process R ?
- What is process S known as ?
- What is the name of energy released during the process S known as ?\\
Solutions for 1: Matter in Our Surroundings
![Lakhmir Singh solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 9 chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings Lakhmir Singh solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 9 chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-class-9_6:8c392a83d00d42db9c0dc4493c97af82.jpg)
Lakhmir Singh solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 9 chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 9 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Lakhmir Singh solutions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 9 CBSE 1 (Matter in Our Surroundings) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Lakhmir Singh textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry [English] Class 9 chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings are Heat and change of physical state, Matter (Substance), Characteristics of Particles (Molecules) of Matter, The Solid State, The Liquid State, The Gaseous State, Plasma, Concept of Melting (Fusion), Concept of Boiling (Vaporization), Concept of Evaporation, Bose-einstein Condensate, Concept of Sublimation, Concept of Freezing (Solidification), Concept of Condensation (Liquefaction), Concept of Desublimation (Deposition).
Using Lakhmir Singh Chemistry [English] Class 9 solutions Matter in Our Surroundings exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Lakhmir Singh Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 students prefer Lakhmir Singh Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 1, Matter in Our Surroundings Chemistry [English] Class 9 additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 9 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
