Topics
Physical Quantities and Measurement
- Measurements
- Physical Quantities
- Volume and It’s Unit
- Measurement of Volume
- Area and It’s Unit
- Measurement of Area
- Density and It’s Unit
- Measurement of Density
- Determination of Density of a Regular Solid
- Determination of Density of an Irregular Solid
- Determination of Density of a Liquid
- Speed
Force and Pressure: Motion
Energy
- Energy
- Forms of Energy
- Mechanical Energy
- Potential Energy (U)
- Kinetic Energy (K)
- Types of Kinetic Energy
- Conversion of Potential Energy into Kinetic Energy
- Transformation of Energy
- Conservation of Energy
- Electricity Generation using Hydroelectric Energy
Light Energy
- Light
- Reflection of Light
- Plane Mirror
- Terms Used in Reflection of Light
- Law of Reflection of Light
- Verification of the Law of Reflection of Light
- Reflection of a Ray of Light Normally Incident on a Plane Mirror
- Images Formed by a Plane Mirrors
- Formation of Image by Reflection: Real and Virtual Image
- Lateral Inversion
- Types of Reflection
- Speed of Light
- Colour
Heat
- Heat and Its Unit
- Heat Exchange
- The Temperature and a Thermometer
- Measuring Temperature
- Scales of Thermometers
- Effects of Heat
- Expansion of Substances (Thermal Expansion)
- Expansion of Solids
- Expansion of Liquids
- Expansion of Gases
- Transfer of Heat
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
- Conductors and Insulators
- Thermos Flask (Dewar Flask)
Sound
Electricity and Magnetism
- Magnet
- Discovery of Magnets
- Classification of Magnets
- Magnetic Properties
- Laws of Magnetism
- Magnetic Field
- Electromagnet
- Making of an Electromagnet
- Applications of Electromagnets
- Electric Bell
- Earth’s Magnetic Declination
- Electricity
- Sources of Electricity
- Electric Circuit
- Conductors and Insulators
- Analogy of Electric Current with Water Flow
- Flow of Charges (Electrons) Between Conductor
- Symbols and Functions of Various Components of an Electric Circuits
- Types of Circuits: Series Circuit
- Types of Circuits: Parallel Circuit
- Electric cell
- Battery
- Introduction
- Experiment
Introduction:
Magnetism is a force that pulls or pushes objects made of certain metals like iron, nickel, and cobalt. A magnet has two ends called poles-North and South. Opposite poles attract each other, and like poles repel (push away) each other.
- The force created by a magnet is called magnetic force. This force can act from a distance without touching the object.
- Magnetic force can move or lift objects, showing that it is a type of energy.
- In factories, ports, or garbage depots, cranes with powerful magnets are used to lift and move heavy metal objects like cars or metal scraps.
Experiment
1. Aim: To magnetise a steel bar using the single-touch and double-touch methods and compare the magnetism produced by both methods.
2. Requirements: steel bar, bar magnet(s), iron filings, and thread.
3. Procedure
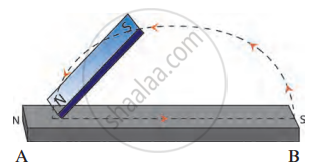
I. Single-Touch Method
- Place the steel bar AB on a table.
- Take a bar magnet and place its N pole on the A end of the steel bar.
- Drag the magnet towards the B end and then lift it.
- Repeat the process 15-20 times.
- Now bring the steel bar near iron filings and observe.
- Hang the bar freely on a thread and observe its behaviour.
Observation: The steel bar shows weak magnetism for a short period.
II. Double-Touch Method
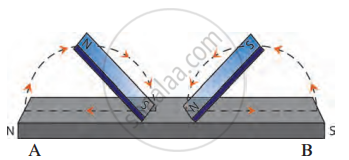
- Place the steel bar on a table.
- Take two bar magnets. Place opposite poles (e.g., N of one magnet, S of the other) at the centre of the steel bar.
- Drag one magnet to the A end and the other to the B end of the bar.
- Repeat the process 15-20 times.
- Now bring the steel bar near iron filings and observe.
Observation: The steel bar shows stronger magnetism that lasts longer than the single-touch method.
4. Conclusion
- Single-Touch Method: produces weak and short-lasting magnetism.
- Double-Touch Method: produces stronger and longer-lasting magnetism.
This experiment shows that different methods of magnetisation affect the strength and duration of the magnetic properties.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
