Topics
Nutrition in Plants
Nutrition in Animals
- Different Ways of Taking Food
- Human Digestive System
- The Mouth and Buccal Cavity
- The Teeth and Its Structure
- The Salivary Glands
- The Food Pipe/Oesophagus
- The Stomach
- The Small Intestine
- Pancreas
- Absorption of Food
- The Large Intestine
- Assimilation of Food
- Liver
- Digestion in Grass-eating Animal
- Feeding and Digestion in Amoeba
Fibre to Fabric
- Fibre
- Fabrics
- Animal Fibres: Wool
- Animal Fibre: Silk
- Fibre to Yarn to Fabric
Heat
- Heat and Its Unit
- Heat Exchange
- The Temperature and a Thermometer
- Thermometer and Its Types
- Measuring Temperature
- Transfer of Heat
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
- Kinds of Clothes Wear in Summer and Winter
Acids, Bases and Salts
- Acids
- Bases (Alkalis)
- Indicators
- Types of Double Displacement: Neutralization Reaction
- Neutralization Reactions in Our Daily Life
- Similarities and Differences Between Acids and Bases
Physical and Chemical Changes
- Classification of Change: Physical Changes
- Chemical Reaction
- Experiment of Chemical Change
- Corrosion of Metals
- Crystallisation Method
Respiration in Organisms
- Respiration
- Respiration
- Types of Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
- Mechanism of respiration-Breathing
- Human Respiratory System
- Breathing in Other Animals
- Breathing Under Water
- Respiration in Plant
Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Blood
- Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Blood Vessels
- Heart Beat - Heart Sounds "LUBB" and "DUP"
- Blood Circulatory System in Human
- Human Heart
- Circulation of Blood in the Heart (Functioning of Heart)
- Excretion
- Human Excretory System
- Transport System in Plants
- Water absorbing organ
- Complex Permanent Tissues
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Phloem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Xylem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Transpiration
Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Weather and Climate
- Climate
- Climate and Adaptation
- Adaptations and Its Types
- Adaptation in Animals
- Adaptation in animals of snowy regions
- Adaptations in Tropical Rainforests
Reproduction in Plants
Wind Storms and Cyclones
- Wind: The Movement of Air
- Atmospheric Pressure
- High Speed Winds Are Accompanied by Reduced Air Pressure
- Air Expands on Heating
- Wind Currents Are Generated Due to Uneven Heating on the Earth
- Thunderstorms
- Cyclones
- Thunderstorm and Cyclone: Destruction Causes, Safety Measures and Role of Advanced Technology
Soil
- Properties of Soil
- Soil Profile
- Types of Soil
- Moisture in Soil
- Water Retention in Soil
- Soil and Crops
Motion and Time
- Motion and Rest
- Speed
- Types of Speed
- Types of Motion
- Measurement of Time
- Devices for Measuring Time
- Simple Pendulum for Time
- A Time Period of Oscillation and Frequency
- Measuring Speed
- Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph
Electric Current and Its Effects
Light
- Light
- The propagation of light
- Reflection of Light
- Mirrors
- Plane Mirror
- Lateral Inversion
- Divergence and Convergence of Light
- Spherical Mirrors
- Formation of Image by Reflection: Real and Virtual Image
- Concave Mirror
- Convex Mirror
- Concept of Lenses
- Images Formed by Sperical Lenses
- Colour
- Prism
- Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum
Forests: Our Lifeline
- Forests: Our Lifeline
- Forest Biome
- Habitat
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
- Classification of Plants
- Biogeochemical Cycle
- The Oxygen Cycle
- The Carbon Cycle
- Water Cycle
- Importance of Forest
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Consequences of Deforestation
Wastewater Story
- Water: Our Lifeline
- Sewage and Its Management
- Purification of Water
- Wastewater Treatment Plant (WWTP)
- Better Housekeeping Practices
- Controlling the Wastage of Water
- Sanitation and Disease
Water: A Precious Resource
- Water: Our Lifeline
- Availability of Water
- Water Cycle
- Sources of Water
- Scarcity of Water
- Distribution of Water in India
- Water Management (Conservation of Water)
- Fresh Water Management
- Controlling the Wastage of Water
- Scarcity of Water
Connecting cells:
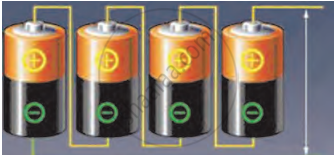
In many devices, like transistor radios, you may see multiple electric cells connected together in a series circuit, as shown in Fig. a. Connecting cells in this way helps to increase the total potential difference (voltage), which allows the circuit to produce a stronger current.
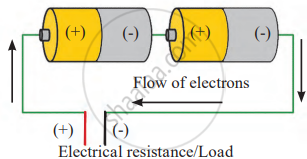
Series Connection:
In a series setup, the positive terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the next cell, as shown in Fig (b). This arrangement creates a continuous path for electric current, combining the voltage of each cell. By connecting cells in series, the total voltage increases, allowing devices to operate with more power. When multiple cells are connected in this way, they are called a battery of cells.
For example, if each cell provides 1V, connecting three cells in series results in a total potential difference of 3V (1V + 1V + 1V).
(a)
(b)
Connecting Cells
