|
Feature |
Concave Mirror |
Convex Mirror |
|---|---|---|
|
Type of Reflection |
Converges light rays |
Diverges light rays |
|
Image Nature (Close) |
Virtual, erect, and magnified |
Always virtual, erect, and smaller |
|
Image Nature (Far) |
Real, inverted, and size vary based on object distance |
Always smaller, virtual, and erect |
|
Field of View |
Limited, focused view |
Wide field of view |
|
Common Use |
Shaving mirrors, makeup mirrors |
Rear-view mirrors in vehicles |
Topics
Nutrition in Plants
Nutrition in Animals
- Different Ways of Taking Food
- Human Digestive System
- The Mouth and Buccal Cavity
- The Teeth and Its Structure
- The Salivary Glands
- The Food Pipe/Oesophagus
- The Stomach
- The Small Intestine
- Pancreas
- Absorption of Food
- The Large Intestine
- Assimilation of Food
- Liver
- Digestion in Grass-eating Animal
- Feeding and Digestion in Amoeba
Fibre to Fabric
- Fibre
- Fabrics
- Animal Fibres: Wool
- Animal Fibre: Silk
- Fibre to Yarn to Fabric
Heat
- Heat and Its Unit
- Heat Exchange
- The Temperature and a Thermometer
- Thermometer and Its Types
- Measuring Temperature
- Transfer of Heat
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
- Kinds of Clothes Wear in Summer and Winter
Acids, Bases and Salts
- Acids
- Bases (Alkalis)
- Indicators
- Types of Double Displacement: Neutralization Reaction
- Neutralization Reactions in Our Daily Life
- Similarities and Differences Between Acids and Bases
Physical and Chemical Changes
- Classification of Change: Physical Changes
- Chemical Reaction
- Experiment of Chemical Change
- Corrosion of Metals
- Crystallisation Method
Respiration in Organisms
- Respiration
- Respiration
- Types of Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
- Mechanism of respiration-Breathing
- Human Respiratory System
- Breathing in Other Animals
- Breathing Under Water
- Respiration in Plant
Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Blood
- Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Blood Vessels
- Heart Beat - Heart Sounds "LUBB" and "DUP"
- Blood Circulatory System in Human
- Human Heart
- Circulation of Blood in the Heart (Functioning of Heart)
- Excretion
- Human Excretory System
- Transport System in Plants
- Water absorbing organ
- Complex Permanent Tissues
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Phloem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Xylem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Transpiration
Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Weather and Climate
- Climate
- Climate and Adaptation
- Adaptations and Its Types
- Adaptation in Animals
- Adaptation in animals of snowy regions
- Adaptations in Tropical Rainforests
Reproduction in Plants
Wind Storms and Cyclones
- Wind: The Movement of Air
- Atmospheric Pressure
- High Speed Winds Are Accompanied by Reduced Air Pressure
- Air Expands on Heating
- Wind Currents Are Generated Due to Uneven Heating on the Earth
- Thunderstorms
- Cyclones
- Thunderstorm and Cyclone: Destruction Causes, Safety Measures and Role of Advanced Technology
Soil
- Properties of Soil
- Soil Profile
- Types of Soil
- Moisture in Soil
- Water Retention in Soil
- Soil and Crops
Motion and Time
- Motion and Rest
- Speed
- Types of Speed
- Types of Motion
- Measurement of Time
- Devices for Measuring Time
- Simple Pendulum for Time
- A Time Period of Oscillation and Frequency
- Measuring Speed
- Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph
Electric Current and Its Effects
Light
- Light
- The propagation of light
- Reflection of Light
- Mirrors
- Plane Mirror
- Lateral Inversion
- Divergence and Convergence of Light
- Spherical Mirrors
- Formation of Image by Reflection: Real and Virtual Image
- Concave Mirror
- Convex Mirror
- Concept of Lenses
- Images Formed by Sperical Lenses
- Colour
- Prism
- Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum
Forests: Our Lifeline
- Forests: Our Lifeline
- Forest Biome
- Habitat
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
- Classification of Plants
- Biogeochemical Cycle
- The Oxygen Cycle
- The Carbon Cycle
- Water Cycle
- Importance of Forest
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Consequences of Deforestation
Wastewater Story
- Water: Our Lifeline
- Sewage and Its Management
- Purification of Water
- Wastewater Treatment Plant (WWTP)
- Better Housekeeping Practices
- Controlling the Wastage of Water
- Sanitation and Disease
Water: A Precious Resource
- Water: Our Lifeline
- Availability of Water
- Water Cycle
- Sources of Water
- Scarcity of Water
- Distribution of Water in India
- Water Management (Conservation of Water)
- Fresh Water Management
- Controlling the Wastage of Water
- Scarcity of Water
- Introduction
- Experiment
- Distinguishing Concave and Convex Mirrors
Introduction:
Light exhibits two important behaviours: convergence and divergence, which describe how light rays come together or spread apart after reflection or refraction. Convergence occurs when light rays are focused at a single point, while divergence happens when light rays spread out from a source. Mirrors, particularly concave and convex mirrors, play a significant role in demonstrating these phenomena. A concave mirror, also known as a focusing mirror, converges parallel rays to a single focal point and forms images that vary in size and orientation based on the object's distance. Conversely, a convex mirror, known as a dispersing mirror, causes parallel rays to diverge and always forms smaller, virtual, and erect images. These principles are widely applied in real-life scenarios, such as in shaving mirrors (concave) for magnified views or vehicle rear-view mirrors (convex) to provide a broader field of vision.
Experiment
1. Aim: To demonstrate the concepts of convergence and divergence using matchsticks and to study the behaviour of concave and convex mirrors with light.
2. Requirements: 5 matchsticks, a concave mirror, a convex mirror, and a light source.
3. Procedure
- Arrange 5 matchsticks so that their heads come together at a single point. This shows the convergence of the matchstick heads.
- Rearrange the matchsticks so that their uncoated ends are together and the heads are spread out. This shows the divergence of the matchstick heads.
- Direct parallel rays of light onto a concave mirror. Observe that the rays converge to a single focus point after reflection.
- Direct parallel rays of light onto a convex mirror. Observe that the rays diverge after reflection, spreading outward.
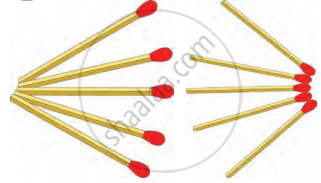
Divergence and convergence
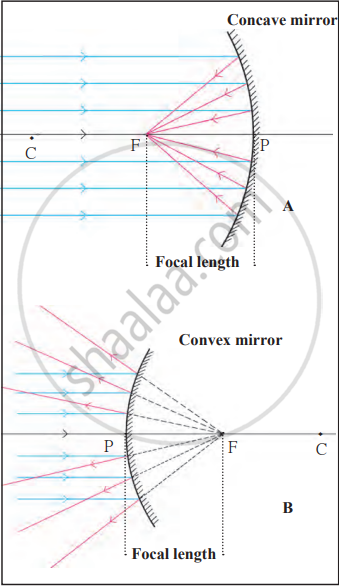
Concave and convex mirror
4. Conclusion
- A concave mirror focuses parallel rays on a single point, demonstrating convergence.
- A convex mirror disperses parallel rays, demonstrating divergence.
The size of the image in a concave mirror depends on the object’s distance, whereas a convex mirror always forms a smaller, virtual, and erect image.
Distinguishing Concave and Convex Mirrors
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
