1. Aim: To observe the water absorption and percolation rates of different types of soil (sand, sandy soil, and clay) and understand how these soil types differ in water-holding capacity.
2. Requirements: Three measuring cylinders, three glass funnels, filter paper, water, fine sand, sandy soil, and clay (soil from an earthen pot).
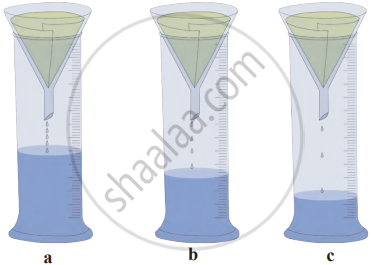
3. Procedure
Fit filter paper cones into the three glass funnels. Fill each funnel with equal quantities of the following materials:
- Funnel A: Fine sand
- Funnel B: Sandy soil
- Funnel C: Clay
Place each funnel on a measuring cylinder. Pour one test tube of water into each funnel. Observe and compare the amount of water that collects in each measuring cylinder.
4. Observation (Based on the Image)
- Funnel A (sand): The most water collects, indicating that sand allows water to pass through quickly.
- Funnel B (sandy soil): A moderate amount of water collects, showing that sandy soil holds some water but still allows percolation.
- Funnel C (clay): The least amount of water collects, as clay retains more water and has low percolation.
5. Conclusion: Different types of soil have different water-holding capacities. Sand allows the most water to pass through, meaning it has the lowest water retention. Clay retains the most water, meaning it has a higher water-holding capacity. This experiment demonstrates that soils differ in their ability to absorb and retain water, which impacts plant growth and water management.