Topics
Matter in Our Surroundings
- Matter (Substance)
- Characteristics of Particles (Molecules) of Matter
- The Solid State
- The Liquid State
- The Gaseous State
- Plasma
- Bose-einstein Condensate
- Heat and change of physical state
- Concept of Evaporation
- Concept of Melting (Fusion)
- Concept of Boiling (Vaporization)
- Concept of Sublimation
- Concept of Freezing (Solidification)
- Concept of Condensation (Liquefaction)
- Concept of Desublimation (Deposition)
Is Matter Around Us Pure
- Matter (Substance)
- Natural substances
- Mixture
- Types of Mixtures
- Solution
- Concentration of a Solution
- Suspension Solution
- Colloidal Solution
- Evaporation Method
- Solvent Extraction (Using a Separating Funnel Method)
- Sublimation Method
- Chromatography Method
- Simple Distillation Method
- Fractional Distillation Method
- Crystallisation Method
- Classification of Change: Physical Changes
- Chemical Reaction
- Pure Substances
- Compound
- Elements
Atoms and Molecules
- History of Atom
- Laws of Chemical Combination
- Law of Conservation of Mass
- Law of Constant Proportions (Law of Definite Proportions)
- Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter
- Symbols Used to Represent Atoms of Different Elements
- Atomic Mass
- Relative Atomic Mass (RAM)
- Molecules
- Classification of Molecules
- Difference Between Atoms and Molecules
- Ions (Radicals) and Its Types
- Chemical Formula or Molecular Formula
- Molecular Mass
- Formula Unit Mass
- Mole Concept
- Atoms and Molecules Numericals
Structure of the Atom
- Existence of Charged Particles in Matter
- Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter
- Discovery of Charged Particles in Matter
- Protons (p)
- Electrons (e)
- Neutrons (n)
- J. J. Thomson’s Atomic Model
- Advantage and Limitations of Thomson’s Atomic Model
- Lord Rutherford’s Atomic model
- Limitations of Rutherford’s Atomic Model
- Neils Bohr’s Model of an Atom
- Electronic Configuration of Atom
- Valency
- Different Ways to Determine Valency
- Atomic Number (Z), Mass Number (A), and Number of Neutrons (n)
- Atomic Mass
- Isotopes
- Uses of Radioactive Isotopes
- Isobars
- Atoms and Molecules Numericals
The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- The Invention of the Microscope and the Discovery of Cell
- Cell Theory
- Organisms Show Variety in Cell Number, Shape and Size
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell
- Simple Diffusion
- Concept of Osmosis
- Osmotic Pressure
- Structure of the Cell
- Plasma Membrane
- Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane)
- Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”
- Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell
- Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Golgi Apparatus - "The delivery system of the cell"
- Lysosome - “Suicidal Bag”
- Mitochondria - “Power House of the Cell”
- Plastids
- Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
- Cell Division: an Essential Life Process
Tissues
- Tissues - “The Teams of Workers”
- Plant and Animals Tissue
- Plant Tissues
- Meristems or Meristematic Tissues
- Permanent Tissue
- Simple Permanent Tissues (Supporting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissues
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Xylem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Phloem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Animal Tissues
- Epithelial Tissue
- Connective Tissue
- Muscular Tissue
- Nervous Tissue
Motion
- Motion and Rest
- Describing Motion
- Motion Along a Straight Line
- Types of Motion
- Measuring the Rate of Motion - Speed with Direction
- Rate of Change of Velocity
- Distance and Displacement
- Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph
- Velocity - Time Graphs
- Equations of Motion by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Velocity - Time Relation by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Displacement - Time Relation by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Displacement - Velocity Relation by Graphical Method
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
- Motion (Numerical)
Diversity in Living Organisms
- Biodiversity
- Biological Classification
- Classification of Living Organisms
- Taxonomic Hierarchy of Living Organisms: Unit of Classification
- Five Kingdom Classification
- Kingdom Monera
- Kingdom Protista
- Kingdom Fungi
- Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Kingdom Animalia
- Differences Between Plantae (Plants) and Animalia (Animals)
- Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Kingdom Plantae: Thallophyta (Algae)
- Kingdom Plantae: Thallophyta (Fungi)
- Division II- Bryophytes
- Division III- Pteridophytes
- Division I-Gymnosperms
- Division II- Angiosperms
- Kingdom Animalia
- Phylum: Porifera
- Phylum: Cnidaria/Coelenterata
- Phylum: Platyhelminthes
- Invertebrate: Phylum Nematoda
- Phylum: Annelida
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Phylum: Mollusca
- Phylum: Echinodermata
- Subphylum: Prochordata
- Chordata: Vertebrata
- Invertebrata and Vertebrata
- Taxonomy and Systematics
- Nomenclature
Force and Laws of Motion
Gravitation
Work and Energy
Sound
- Sound
- Production of Sound
- Propagation of Sound
- Sound Need a Medium to Travel
- Sound Waves Are Longitudinal Waves
- Characteristics of a Sound Wave
- Speed of Sound (Velocity of Sound)
- Reflection of Sound
- Echoes
- Reverberation
- Uses of Multiple Reflection of Sound
- Range of Hearing in Humans
- Ultrasonic Sound Or Ultrasound
- SONAR
- Human Ear
- Sound (Numerical)
Improvement in Food Resources
- Improvements in Food Resources
- Improvement in Crop Yields
- Crop Variety Improvement
- Crop Production Improvement
- Crop Protection Management
- Methods to Replenish Nutrients in Your Soil
- Manuring (Biomanuring)
- Fertilizers
- Improved methods of agriculture
- Agricultural Assistance Programme
- Animal Husbandry (Livestock)
- Dairy Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Pisciculture (Fish Farming)
- Apiculture (Bee Farming)
Why Do We Fall ill
- Health
- Disease
- Categories of Disease
- Acute and Chronic Diseases
- Causes of Disease
- Communicable Or Infectious Diseases
- Infectious Agents
- Manifestation of Diseases
- Modes of Transmission of Diseases
- Organ-specific and Tissue-specific Manifestations
- Principles of Prevention of Diseases
- Principles of Treatment of Diseases
Natural Resources
- Natural Resources
- Biosphere: The Domain of Life
- Air is a Mixture
- Atmosphere and Its Layers
- Wind: The Movement of Air
- Rain
- Water: Our Lifeline
- Where Do We Get Water From?
- Availability of Water
- Importance of Water
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Mineral Riches in the Soil
- Biogeochemical Cycle
- Water Cycle
- Nitrogen Cycle
- The Carbon Cycle
- The Oxygen Cycle
- Ozone
- Ozone Layer Depletion
- Introduction
- Types of Complex Permanent Tissues
Introduction:
Complex permanent tissue is a type of plant tissue made up of different kinds of cells that work together as a team to perform various functions. Unlike simple permanent tissues, which consist of only one type of cell, complex tissues are composed of multiple cell types. These tissues are essential for the transportation of water, minerals, and food throughout the plant, playing a crucial role in the plant's survival and growth. They are also known as vascular tissues because they form the plant's transport system.
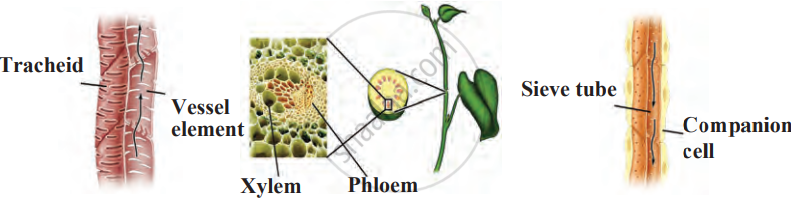
The two main types of complex permanent tissues are: Xylem and Phloem
Types of Complex Permanent Tissues:
| Name of Tissue |
Xylem | Phloem |
| Characteristics | Consists of thick-walled dead cells | Consists of cytoplasm containing living cells |
| Cell Wall Material | Lignin (rigid) | Cellulose |
| Permeability | Impermeable | Permeable |
| Types of Cells | Tracheids, vessels and xylem fibre-dead cells Xylem parenchyma-living cells |
Sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma-living cells Phloem fibres—dead cells |
| Transports | Water and minerals | Food |
| Function | Structures like interconnected tubes conduct water and minerals only in an upward direction. | Tubes joined to each other conduct sugar and amino acids from leaves to various parts in upward and downward direction |
Example
What are the constituents of phloem?
Phloem is a living tissue in vascular plants which conducts the soluble organic compounds synthesized during photosynthesis downward from the leaves.
Listed below are the constituents of phloem:
- Companion cells: It appear to check the activity of the adjacent sieve element and participates in loading and unloading of the sugar into the sieve element.
- Sieve tubes: These elongated living cells, conveys carbohydrates, chiefly sucrose, from leaves to roots and fruits.
- Phloem fibres: They are commercially useful as they possess great pliability and tensile strength.
- Phloem parenchyma: Also known as transfer cells, they are found near the finest branches, ends of sieve tubes in leaf veinlets, functional here in conveying food.
