Topics
Matter in Our Surroundings
- Matter (Substance)
- Characteristics of Particles (Molecules) of Matter
- The Solid State
- The Liquid State
- The Gaseous State
- Plasma
- Bose-einstein Condensate
- Heat and change of physical state
- Concept of Evaporation
- Concept of Melting (Fusion)
- Concept of Boiling (Vaporization)
- Concept of Sublimation
- Concept of Freezing (Solidification)
- Concept of Condensation (Liquefaction)
- Concept of Desublimation (Deposition)
Is Matter Around Us Pure
- Matter (Substance)
- Natural substances
- Mixture
- Types of Mixtures
- Solution
- Concentration of a Solution
- Suspension Solution
- Colloidal Solution
- Evaporation Method
- Solvent Extraction (Using a Separating Funnel Method)
- Sublimation Method
- Chromatography Method
- Simple Distillation Method
- Fractional Distillation Method
- Crystallisation Method
- Classification of Change: Physical Changes
- Chemical Reaction
- Pure Substances
- Compound
- Elements
Atoms and Molecules
- History of Atom
- Laws of Chemical Combination
- Law of Conservation of Mass
- Law of Constant Proportions (Law of Definite Proportions)
- Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter
- Symbols Used to Represent Atoms of Different Elements
- Atomic Mass
- Relative Atomic Mass (RAM)
- Molecules
- Classification of Molecules
- Difference Between Atoms and Molecules
- Ions (Radicals) and Its Types
- Chemical Formula or Molecular Formula
- Molecular Mass
- Formula Unit Mass
- Mole Concept
- Atoms and Molecules Numericals
Structure of the Atom
- Existence of Charged Particles in Matter
- Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter
- Discovery of Charged Particles in Matter
- Protons (p)
- Electrons (e)
- Neutrons (n)
- J. J. Thomson’s Atomic Model
- Advantage and Limitations of Thomson’s Atomic Model
- Lord Rutherford’s Atomic model
- Limitations of Rutherford’s Atomic Model
- Neils Bohr’s Model of an Atom
- Electronic Configuration of Atom
- Valency
- Different Ways to Determine Valency
- Atomic Number (Z), Mass Number (A), and Number of Neutrons (n)
- Atomic Mass
- Isotopes
- Uses of Radioactive Isotopes
- Isobars
- Atoms and Molecules Numericals
The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- The Invention of the Microscope and the Discovery of Cell
- Cell Theory
- Organisms Show Variety in Cell Number, Shape and Size
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell
- Simple Diffusion
- Concept of Osmosis
- Osmotic Pressure
- Structure of the Cell
- Plasma Membrane
- Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane)
- Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”
- Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell
- Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Golgi Apparatus - "The delivery system of the cell"
- Lysosome - “Suicidal Bag”
- Mitochondria - “Power House of the Cell”
- Plastids
- Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
- Cell Division: an Essential Life Process
Tissues
- Tissues - “The Teams of Workers”
- Plant and Animals Tissue
- Plant Tissues
- Meristems or Meristematic Tissues
- Permanent Tissue
- Simple Permanent Tissues (Supporting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissues
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Xylem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Phloem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Animal Tissues
- Epithelial Tissue
- Connective Tissue
- Muscular Tissue
- Nervous Tissue
Motion
- Motion and Rest
- Describing Motion
- Motion Along a Straight Line
- Types of Motion
- Measuring the Rate of Motion - Speed with Direction
- Rate of Change of Velocity
- Distance and Displacement
- Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph
- Velocity - Time Graphs
- Equations of Motion by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Velocity - Time Relation by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Displacement - Time Relation by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Displacement - Velocity Relation by Graphical Method
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
- Motion (Numerical)
Diversity in Living Organisms
- Biodiversity
- Biological Classification
- Classification of Living Organisms
- Taxonomic Hierarchy of Living Organisms: Unit of Classification
- Five Kingdom Classification
- Kingdom Monera
- Kingdom Protista
- Kingdom Fungi
- Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Kingdom Animalia
- Differences Between Plantae (Plants) and Animalia (Animals)
- Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Kingdom Plantae: Thallophyta (Algae)
- Kingdom Plantae: Thallophyta (Fungi)
- Division II- Bryophytes
- Division III- Pteridophytes
- Division I-Gymnosperms
- Division II- Angiosperms
- Kingdom Animalia
- Phylum: Porifera
- Phylum: Cnidaria/Coelenterata
- Phylum: Platyhelminthes
- Invertebrate: Phylum Nematoda
- Phylum: Annelida
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Phylum: Mollusca
- Phylum: Echinodermata
- Subphylum: Prochordata
- Chordata: Vertebrata
- Invertebrata and Vertebrata
- Taxonomy and Systematics
- Nomenclature
Force and Laws of Motion
Gravitation
Work and Energy
Sound
- Sound
- Production of Sound
- Propagation of Sound
- Sound Need a Medium to Travel
- Sound Waves Are Longitudinal Waves
- Characteristics of a Sound Wave
- Speed of Sound (Velocity of Sound)
- Reflection of Sound
- Echoes
- Reverberation
- Uses of Multiple Reflection of Sound
- Range of Hearing in Humans
- Ultrasonic Sound Or Ultrasound
- SONAR
- Human Ear
- Sound (Numerical)
Improvement in Food Resources
- Improvements in Food Resources
- Improvement in Crop Yields
- Crop Variety Improvement
- Crop Production Improvement
- Crop Protection Management
- Methods to Replenish Nutrients in Your Soil
- Manuring (Biomanuring)
- Fertilizers
- Improved methods of agriculture
- Agricultural Assistance Programme
- Animal Husbandry (Livestock)
- Dairy Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Pisciculture (Fish Farming)
- Apiculture (Bee Farming)
Why Do We Fall ill
- Health
- Disease
- Categories of Disease
- Acute and Chronic Diseases
- Causes of Disease
- Communicable Or Infectious Diseases
- Infectious Agents
- Manifestation of Diseases
- Modes of Transmission of Diseases
- Organ-specific and Tissue-specific Manifestations
- Principles of Prevention of Diseases
- Principles of Treatment of Diseases
Natural Resources
- Natural Resources
- Biosphere: The Domain of Life
- Air is a Mixture
- Atmosphere and Its Layers
- Wind: The Movement of Air
- Rain
- Water: Our Lifeline
- Where Do We Get Water From?
- Availability of Water
- Importance of Water
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Mineral Riches in the Soil
- Biogeochemical Cycle
- Water Cycle
- Nitrogen Cycle
- The Carbon Cycle
- The Oxygen Cycle
- Ozone
- Ozone Layer Depletion
- Introduction of Atom
- Discovery of Charged Particles and the Structure of an Atom
Introduction of Atom:
An atom is the smallest particle of an element. It has two parts: the nucleus and the outer nuclear part. The nucleus of the atom consists of protons and neutrons. Protons are positively charged particles. Neutrons have no charge.
In the outer nuclear part, electrons are present. Electrons are negatively charged particles. The atomic number represents the number of protons in the atom. As an atom is electrically neutral, it may contain as many electrons as it has protons. The total number of protons and electrons present in one atom of an element is known as its mass number.
- Atoms of a given atomic number can have different numbers of neutrons; these are called isotopes.
- The atoms of different elements that have the same mass number but different atomic numbers are called isobars. These have different numbers of protons but equal sums of the number of protons and neutrons.
- The atoms of different elements that have the same number of neutrons but different atomic numbers are called isomers.
Atomic radius is measured in nanometres. It is a typical distance from the centre of the nucleus to the boundary of the surrounding shells of electrons.
- `"1"/(10^9)` m = 1 nm
- 1 m = 109 nm
| Atomic radius (in metres) | Example |
|---|---|
| 10−10 | Hydrogen atom |
| 10−9 | Water molecule |
| 10−8 | Haemoglobin molecule |
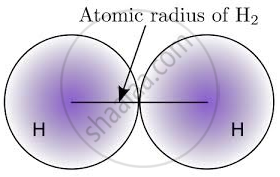
The atomic size depends on the number of electron orbits in the atom. The greater the number of orbits, the larger the size. For example, an atom of K is bigger than an atom of Na. If two atoms have the same outermost orbit, then the atom having the larger number of electrons in the outermost orbit is smaller than the one having fewer electrons in the same outermost orbit. For example, an atom of Mg is smaller than an atom of Na.
Discovery of Charged Particles and the Structure of an Atom:
The discovery of the electron and proton is credited to J.J. Thomson and E. Goldstein, respectively. J.J. Thomson proposed that electrons are embedded in a positive sphere
- Electron was represented as ‘e-‘ and proton as ‘p+’. The mass of a proton is taken as one unit and its charge as plus one, where the mass of an electron was considered to be negligible and its charge minus one
- It seemed that atom consisted of electrons and protons, which balanced their charges mutually
Structure of an Atom:
Dalton’s atomic theory suggested that the atom was indivisible and indestructible. But the discovery of two fundamental particles (electrons and protons) inside the atom led to the failure of this aspect of Dalton’s atomic theory. The arrangement of electrons and protons within an atom became crucial to understand. Many scientists proposed various atomic models to explain this. Thomson proposed the first atom structure model.
Field ion microscope image of iridium atoms (every spot in this image is an atom)
Atoms are very tiny. Modern instruments like the electron microscope, field ion microscope, and scanning tunnelling microscope produce enlarged images of the atom. Examine the image of an atom that a field ion microscope has produced.
