5. Conclusion: The experiments show that chemical changes result in the formation of new substances with distinct properties, whereas physical changes are reversible and do not alter the composition of the substance.
Topics
Gravitation
- Concept of Gravitation
- Force
- Motion and Rest
- Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force
- Kepler’s Laws
- Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
- Earth’s Gravitational force
- Acceleration Due to Gravity (Earth’s Gravitational Acceleration)
- Concept of Mass and Weight
- Gravitational Waves
- Free Fall
- Gravitational Potential Energy
- Weightlessness in Space
Periodic Classification of Elements
- History of Periodic Table: Early Attempts at the Classification of Elements
- Dobereiner’s Triads
- Newland's Law of Octaves
- Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Merits and Demerits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Modern Periodic Law
- The Modern Periodic Table
- Structure of the Modern Periodic Table
- Modern Periodic Table and Electronic Configuration of Elements
- Groups and Electronic Configuration
- Periods and Electronic Configuration
- Periodic Properties
- Valency
- Atomic Radius Or Atomic Size
- Metallic and Non-metallic Characters
- Group VIIA Or Group 17 (The Halogens)
Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chemical Reaction
- Chemical Equation
- Balancing Chemical Equation
- Types of Chemical Change or Chemical Reaction
- Direct Combination (or Synthesis) Reaction
- Decomposition Reactions
- Single Displacement Reactions
- Double Displacement Reaction
- Energy Change in Chemical Reactions
- Rate of Chemical Reaction
- Factors Affecting the Rate of a Chemical Reaction
- Oxidation, Reduction and Redox Reactions
- Corrosion of Metals
- Rancidity of Food and Its Prevention
Effects of Electric Current
- Electric Circuit
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Heating Effect of Electric Current
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
- Electric Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Galvanometer
- Fleming’s Right Hand Rule
- Types of Current
- Electric Generator
Heat
Refraction of Light
Lenses
- Concept of Lenses
- Spherical Lens
- Convex Lens
- Images Formed by Convex Lenses
- Concave Lens
- Images Formed by Concave Lenses
- Sign Convention
- Lens Formula
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
- Combination of Lenses
- Human Eye
- Working of the Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia
- Persistence of Vision
Metallurgy
- Types of Element: Metals
- Physical Properties of Metals
- Chemical Properties of Metal
- Reactions of Metal
- Reactivity Series of Metals
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Physical Properties of Non-metal
- Chemical Properties of Non-metal
- Ionic Compounds
- Metallurgy
- Basic Principles of Metallurgy
- Extraction of Reactive Metals
- Extraction of Aluminium
- Extraction of Moderately Reactive Metals
- Extraction of Less Reactive Metals
- Refining of Metals
- Corrosion of Metals
- Prevention of Corrosion
Carbon Compounds
- Carbon Compounds in Everyday Life
- Bonds in Carbon Compounds
- Carbon: a Versatile Element
- Properties of Carbon
- Hydrocarbons
- Structural Variations of Carbon Chains in Hydrocarbons
- Functional Groups in Carbon Compounds
- Homologous Series of Carbon Compound
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
- The IUPAC System of Nomenclature
- Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
- Ethanol
- Ethanoic Acid
- Macromolecules and Polymers
Space Missions
- Concept of Space Missions
- Artificial Satellites
- Types of Satellite
- Orbits of Artificial Satellites
- Space launch technology
- Space Missions Away from Earth
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 1
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 2
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 3
- India’s Space Programmes: Mangalyaan (Mars vehicle)
- India’s Space Programmes: Missions to Other Planets
- India and Space Technology
- Space Debris and Its Management
School of Elements
The Magic of Chemical Reactions
The Acid Base Chemistry
- Properties of Acids
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Acids, Bases and Their Reactivity
- Acid or a Base in a Water Solution
- Preparation and Uses of Baking Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Bleaching Powder
- Preparation and Uses of Washing Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Plaster of Paris
- Chemicals from Common Salt - Soap as a Salt
The Electric Spark
All about Electromagnetism
- Magnetic Force
- The Bar Magnet
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Electric Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator
- Direct Current Motor
- Household Electrical Circuits
Wonders of Light 1
- Spherical Mirrors
- Concave Mirror
- Concave Mirror
- Sign Convention
- Linear Magnification (M) Due to Spherical Mirrors
- Images Formed by Sperical Lenses
- Convex Lens
- Sign Convention
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
- Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Spherical Mirrors
Wonders of Light 2
Striving for better Environment 1
- Pollution and Its Types
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Air Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Water Pollution
- Soil Pollution and its Causes
- Effects of Soil Pollution
- Noise Pollution
- Radioactive Pollution and Effects
- Abatement of Pollution
- Sustainable Use of Resources
- Introduction
- Types of Chemical Reaction
- Experiment
Introduction:
Scientists in the 18th and 19th centuries conducted fundamental experiments to study chemical reactions. Their findings established that chemical reactions result in a permanent change in the composition of matter, forming new substances. In contrast, physical changes affect only the state of matter, are often reversible, and do not alter its composition.
- A chemical reaction involves the breaking and formation of chemical bonds, transforming reactants into new products. A process in which one or more substances, the reactants, are converted to one or more different substances, the products.
- Substances are either chemical elements or compounds. Understanding chemical reactions is essential for studying various natural and industrial processes.
- During a chemical change, the original substance's chemical composition changes, resulting in the formation of new substances with different properties and compositions.
- When the exact changes in chemical composition are known, a chemical equation can be written to represent the reaction. This equation uses the names and chemical formulas of both the original and new substances.
For example,
1. When coal (carbon) burns in the presence of oxygen, it forms carbon dioxide gas. Such reactions are represented using chemical equations, which show the transformation of reactants into products.
C+O₂→CO₂
2. When baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) is added to lemon juice (citric acid), a chemical reaction occurs, producing carbon dioxide gas, sodium citrate, and water. This reaction shows the transformation of reactants (citric acid and sodium bicarbonate) into new products.
Citric acid + Sodium bicarbonate → Carbon dioxide + Sodium citrate + Water
A neutralisation reaction is a specific type of chemical reaction where an acid reacts with an alkali (base), resulting in the formation of a salt, carbon dioxide, and water. The release of carbon dioxide gas can be seen as bubbles forming, and the reaction reduces the sour taste of the acid.

Formation of CO₂ with effervescence
Experiment figure
Types of Chemical Reaction:
| Type of reaction | Definition | Equation |
| Combination | Two or more elements or compounds combine to make a more complex substance. | A + B = AB |
| Decomposition | Compounds break down into simpler substances. | AB = A + B |
| Replacement | Occurs when one element replaces another in a compound | AB + C = AC + B |
| Double replacement | Occurs when different atoms in two different compounds trade places | AB + CD = AC + BD |
Experiment
1. Aim: To observe and differentiate between chemical and physical changes through various experiments.
2. Requirements
- Apparatus: thermometer, evaporating dish, tripod stand, funnel, Bunsen burner.
- Chemicals: limestone powder (CaCO₃), copper sulphate (CuSO₄), zinc dust (Zn), potassium chromate (K₂CrO₄), barium sulphate (BaSO₄), sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃), calcium chloride (CaCl₂), and phthalic anhydride.
3. Procedure
- Heat limestone powder strongly in an evaporating dish over a high blue flame.
- Add zinc dust into the copper sulphate solution and observe any changes.
- Mix potassium chromate solution with barium sulphate solution and note the reaction.
- Add sodium carbonate solution to calcium chloride solution and observe any precipitate formation.
- Heat phthalic anhydride in an evaporating dish with an inverted funnel placed over it and observe changes.
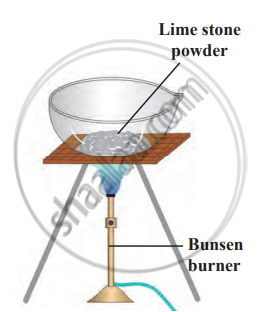
To heat limestone powder
4. Observation
| Activity | Colour Change (if present) | Gas Released (Yes/No) | Temperature Change (if present) | Nature of Change (Chemical/Physical) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No | Yes | Yes | Chemical |
| 2 | Yes | No | Yes | Chemical |
| 3 | Yes | No | Yes | Chemical |
| 4 | Yes | No | Yes | Chemical |
| 5 | No | No | No | Physical |
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
Shaalaa.com | Types of Chemical Reactions
to track your progress
