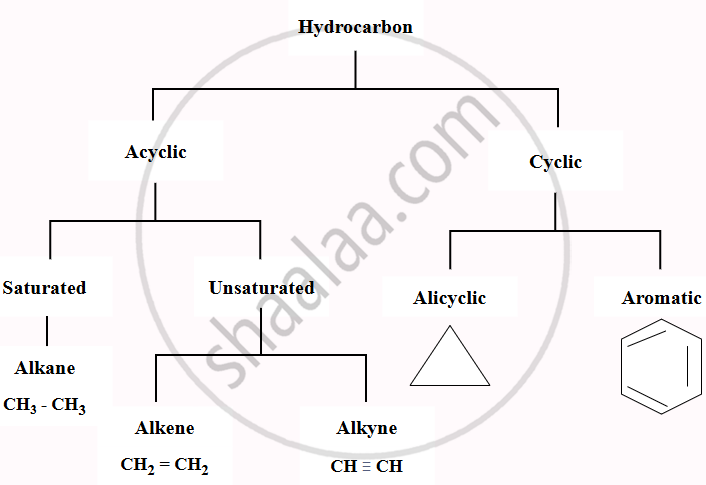
A hydrocarbon is a type of organic chemical compound made up only of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms. The carbon atoms form the structure of the compound, while hydrogen atoms are attached to them in various arrangements.
- Hydrocarbons are the main components of petroleum and natural gas. Carbon, with an electronic configuration of 2,4, requires four additional electrons to complete its octet and become stable like the inert gas neon (2,8).
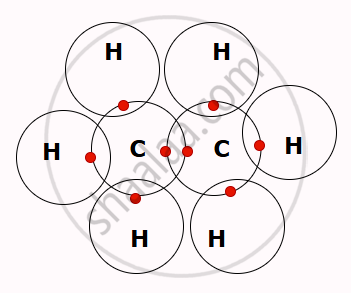
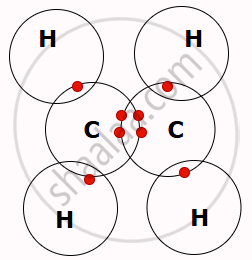
- Instead of gaining or losing electrons, carbon shares its electrons through covalent bonding. This allows a carbon atom to form four covalent bonds, either with other carbon atoms or with atoms of other elements.
- For example, when a carbon atom bonds with four hydrogen atoms by sharing electrons, it forms a methane molecule (CH₄), which is the simplest hydrocarbon.
- They are widely used as fuels and lubricants and serve as raw materials for producing plastics, fibres, rubbers, solvents, explosives, and many industrial chemicals.