Topics
Gravitation
- Concept of Gravitation
- Force
- Motion and Rest
- Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force
- Kepler’s Laws
- Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
- Earth’s Gravitational force
- Acceleration Due to Gravity (Earth’s Gravitational Acceleration)
- Concept of Mass and Weight
- Gravitational Waves
- Free Fall
- Gravitational Potential Energy
- Weightlessness in Space
Periodic Classification of Elements
- History of Periodic Table: Early Attempts at the Classification of Elements
- Dobereiner’s Triads
- Newland's Law of Octaves
- Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Merits and Demerits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Modern Periodic Law
- The Modern Periodic Table
- Structure of the Modern Periodic Table
- Modern Periodic Table and Electronic Configuration of Elements
- Groups and Electronic Configuration
- Periods and Electronic Configuration
- Periodic Properties
- Valency
- Atomic Radius Or Atomic Size
- Metallic and Non-metallic Characters
- Group VIIA Or Group 17 (The Halogens)
Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chemical Reaction
- Chemical Equation
- Balancing Chemical Equation
- Types of Chemical Change or Chemical Reaction
- Direct Combination (or Synthesis) Reaction
- Decomposition Reactions
- Single Displacement Reactions
- Double Displacement Reaction
- Energy Change in Chemical Reactions
- Rate of Chemical Reaction
- Factors Affecting the Rate of a Chemical Reaction
- Oxidation, Reduction and Redox Reactions
- Corrosion of Metals
- Rancidity of Food and Its Prevention
Effects of Electric Current
- Electric Circuit
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Heating Effect of Electric Current
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
- Electric Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Galvanometer
- Fleming’s Right Hand Rule
- Types of Current
- Electric Generator
Heat
Refraction of Light
Lenses
- Concept of Lenses
- Spherical Lens
- Convex Lens
- Images Formed by Convex Lenses
- Concave Lens
- Images Formed by Concave Lenses
- Sign Convention
- Lens Formula
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
- Combination of Lenses
- Human Eye
- Working of the Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia
- Persistence of Vision
Metallurgy
- Types of Element: Metals
- Physical Properties of Metals
- Chemical Properties of Metal
- Reactions of Metal
- Reactivity Series of Metals
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Physical Properties of Non-metal
- Chemical Properties of Non-metal
- Ionic Compounds
- Metallurgy
- Basic Principles of Metallurgy
- Extraction of Reactive Metals
- Extraction of Aluminium
- Extraction of Moderately Reactive Metals
- Extraction of Less Reactive Metals
- Refining of Metals
- Corrosion of Metals
- Prevention of Corrosion
Carbon Compounds
- Carbon Compounds in Everyday Life
- Bonds in Carbon Compounds
- Carbon: a Versatile Element
- Properties of Carbon
- Hydrocarbons
- Structural Variations of Carbon Chains in Hydrocarbons
- Functional Groups in Carbon Compounds
- Homologous Series of Carbon Compound
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
- The IUPAC System of Nomenclature
- Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
- Ethanol
- Ethanoic Acid
- Macromolecules and Polymers
Space Missions
- Concept of Space Missions
- Artificial Satellites
- Types of Satellite
- Orbits of Artificial Satellites
- Space launch technology
- Space Missions Away from Earth
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 1
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 2
- India’s Space Programmes: Chandrayaan – 3
- India’s Space Programmes: Mangalyaan (Mars vehicle)
- India’s Space Programmes: Missions to Other Planets
- India and Space Technology
- Space Debris and Its Management
School of Elements
The Magic of Chemical Reactions
The Acid Base Chemistry
- Properties of Acids
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Acids, Bases and Their Reactivity
- Acid or a Base in a Water Solution
- Preparation and Uses of Baking Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Bleaching Powder
- Preparation and Uses of Washing Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Plaster of Paris
- Chemicals from Common Salt - Soap as a Salt
The Electric Spark
All about Electromagnetism
- Magnetic Force
- The Bar Magnet
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Electric Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator
- Direct Current Motor
- Household Electrical Circuits
Wonders of Light 1
- Spherical Mirrors
- Concave Mirror
- Concave Mirror
- Sign Convention
- Linear Magnification (M) Due to Spherical Mirrors
- Images Formed by Sperical Lenses
- Convex Lens
- Sign Convention
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
- Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Spherical Mirrors
Wonders of Light 2
Striving for better Environment 1
- Pollution and Its Types
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Air Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Water Pollution
- Soil Pollution and its Causes
- Effects of Soil Pollution
- Noise Pollution
- Radioactive Pollution and Effects
- Abatement of Pollution
- Sustainable Use of Resources
- Persistence of Vision in Daily Life
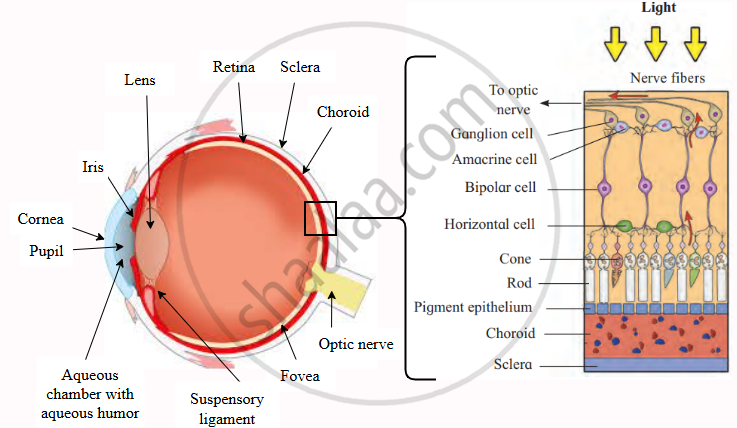
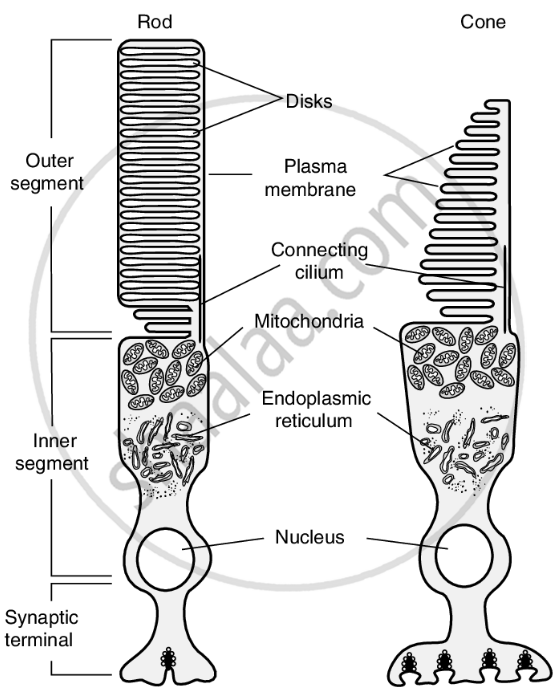
- Role of Rod and Cone Cells in Vision
Persistence of Vision in Daily Life
Persistence of vision is the phenomenon where an image remains on the retina for 1/16th of a second after the object is removed. This occurs because the retina retains the image temporarily before transmitting it to the brain. The brain processes continuous images rapidly, creating the illusion of a smooth, continuous motion.
Examples of Persistence of Vision in Daily Life:
- Movies and Animation: Films and animations run at 24 frames per second (fps) or more. The rapid sequence of images appears as a smooth motion due to persistence of vision.
- Spinning Fan Blades: When a ceiling fan rotates quickly, the blades appear to merge into one blurred disk. This is because each blade's image remains on the retina before the next blade reaches that position.
- Light Trails of Fireworks or Sparklers: When a sparkler or firework moves quickly, it leaves a light trail in the air. This is due to the retina holding onto the previous light image as the spark moves.
- Flipping Book Animations (Flipbooks): A series of slightly different images are drawn on pages. When flipped rapidly, the pictures appear to move, thanks to persistence of vision.
- Digital Screens (TVs and Monitors): Screens refresh at high speeds (e.g., 60 Hz, 120 Hz). Even though pixels are turned off and on, the eye perceives a continuous image.
Role of Rod and Cone Cells in Vision
| Feature | Rod Cells | Cone Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Rod-shaped photoreceptors | Cone-shaped photoreceptors |
| Function | Detect light intensity (brightness/dimness) | Detect colors (Red, Green, Blue) |
| Vision Type | Low-light vision (scotopic vision) | Bright-light vision (photopic vision) |
| Color Vision | No color detection (black & white vision) | Responsible for color vision |
| Location in Retina | Periphery of the retina | Center (fovea) of the retina |
| Number | 120 million (out of 125 million) | 5 million (out of 125 million) |
| Light Sensitivity | Highly sensitive to dim light | Less sensitive to dim light |
| Response Time | Slow response (long integration time) | Fast response (short integration time) |
| Directional Selectivity | No | Yes |
| Amplification | High | Low |
| Convergence in Retinal Pathways | Highly convergent | Less convergent |
| Acuity (Sharpness) | Low (poor detail vision) | High (sharp, detailed vision) |
| Outer Segment Pigment | Rhodopsin (Vitamin A) | Iodopsin (Violet pigment) |
| Wavelength Sensitivity | Peak sensitivity: 480 nm | Sensitive at 420 nm, 534 nm, 563 nm |
| Deficiency Effects | Night blindness (poor night vision) | Color blindness |
| Best Suited For | Dim light and peripheral vision | Detailed and color vision in bright light |
Structure of the Human Eye and Photoreceptor Cells (Rods & Cones)
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.