Topics
Matter in Our Surroundings
- Matter (Substance)
- Characteristics of Particles (Molecules) of Matter
- The Solid State
- The Liquid State
- The Gaseous State
- Plasma
- Bose-einstein Condensate
- Heat and change of physical state
- Concept of Evaporation
- Concept of Melting (Fusion)
- Concept of Boiling (Vaporization)
- Concept of Sublimation
- Concept of Freezing (Solidification)
- Concept of Condensation (Liquefaction)
- Concept of Desublimation (Deposition)
Is Matter Around Us Pure
- Matter (Substance)
- Natural substances
- Mixture
- Types of Mixtures
- Solution
- Concentration of a Solution
- Suspension Solution
- Colloidal Solution
- Evaporation Method
- Solvent Extraction (Using a Separating Funnel Method)
- Sublimation Method
- Chromatography Method
- Simple Distillation Method
- Fractional Distillation Method
- Crystallisation Method
- Classification of Change: Physical Changes
- Chemical Reaction
- Pure Substances
- Compound
- Elements
Atoms and Molecules
- History of Atom
- Laws of Chemical Combination
- Law of Conservation of Mass
- Law of Constant Proportions (Law of Definite Proportions)
- Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter
- Symbols Used to Represent Atoms of Different Elements
- Atomic Mass
- Relative Atomic Mass (RAM)
- Molecules
- Classification of Molecules
- Difference Between Atoms and Molecules
- Ions (Radicals) and Its Types
- Chemical Formula or Molecular Formula
- Molecular Mass
- Formula Unit Mass
- Mole Concept
- Atoms and Molecules Numericals
Structure of the Atom
- Existence of Charged Particles in Matter
- Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter
- Discovery of Charged Particles in Matter
- Protons (p)
- Electrons (e)
- Neutrons (n)
- J. J. Thomson’s Atomic Model
- Advantage and Limitations of Thomson’s Atomic Model
- Lord Rutherford’s Atomic model
- Limitations of Rutherford’s Atomic Model
- Neils Bohr’s Model of an Atom
- Electronic Configuration of Atom
- Valency
- Different Ways to Determine Valency
- Atomic Number (Z), Mass Number (A), and Number of Neutrons (n)
- Atomic Mass
- Isotopes
- Uses of Radioactive Isotopes
- Isobars
- Atoms and Molecules Numericals
The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- The Invention of the Microscope and the Discovery of Cell
- Cell Theory
- Organisms Show Variety in Cell Number, Shape and Size
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell
- Simple Diffusion
- Concept of Osmosis
- Osmotic Pressure
- Structure of the Cell
- Plasma Membrane
- Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane)
- Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”
- Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell
- Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Golgi Apparatus - "The delivery system of the cell"
- Lysosome - “Suicidal Bag”
- Mitochondria - “Power House of the Cell”
- Plastids
- Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
- Cell Division: an Essential Life Process
Tissues
- Tissues - “The Teams of Workers”
- Plant and Animals Tissue
- Plant Tissues
- Meristems or Meristematic Tissues
- Permanent Tissue
- Simple Permanent Tissues (Supporting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissues
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Xylem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Phloem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Animal Tissues
- Epithelial Tissue
- Connective Tissue
- Muscular Tissue
- Nervous Tissue
Motion
- Motion and Rest
- Describing Motion
- Motion Along a Straight Line
- Types of Motion
- Measuring the Rate of Motion - Speed with Direction
- Rate of Change of Velocity
- Distance and Displacement
- Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph
- Velocity - Time Graphs
- Equations of Motion by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Velocity - Time Relation by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Displacement - Time Relation by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Displacement - Velocity Relation by Graphical Method
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
- Motion (Numerical)
Diversity in Living Organisms
- Biodiversity
- Biological Classification
- Classification of Living Organisms
- Taxonomic Hierarchy of Living Organisms: Unit of Classification
- Five Kingdom Classification
- Kingdom Monera
- Kingdom Protista
- Kingdom Fungi
- Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Kingdom Animalia
- Differences Between Plantae (Plants) and Animalia (Animals)
- Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Kingdom Plantae: Thallophyta (Algae)
- Kingdom Plantae: Thallophyta (Fungi)
- Division II- Bryophytes
- Division III- Pteridophytes
- Division I-Gymnosperms
- Division II- Angiosperms
- Kingdom Animalia
- Phylum: Porifera
- Phylum: Cnidaria/Coelenterata
- Phylum: Platyhelminthes
- Invertebrate: Phylum Nematoda
- Phylum: Annelida
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Phylum: Mollusca
- Phylum: Echinodermata
- Subphylum: Prochordata
- Chordata: Vertebrata
- Invertebrata and Vertebrata
- Taxonomy and Systematics
- Nomenclature
Force and Laws of Motion
Gravitation
Work and Energy
Sound
- Sound
- Production of Sound
- Propagation of Sound
- Sound Need a Medium to Travel
- Sound Waves Are Longitudinal Waves
- Characteristics of a Sound Wave
- Speed of Sound (Velocity of Sound)
- Reflection of Sound
- Echoes
- Reverberation
- Uses of Multiple Reflection of Sound
- Range of Hearing in Humans
- Ultrasonic Sound Or Ultrasound
- SONAR
- Human Ear
- Sound (Numerical)
Improvement in Food Resources
- Improvements in Food Resources
- Improvement in Crop Yields
- Crop Variety Improvement
- Crop Production Improvement
- Crop Protection Management
- Methods to Replenish Nutrients in Your Soil
- Manuring (Biomanuring)
- Fertilizers
- Improved methods of agriculture
- Agricultural Assistance Programme
- Animal Husbandry (Livestock)
- Dairy Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Pisciculture (Fish Farming)
- Apiculture (Bee Farming)
Why Do We Fall ill
- Health
- Disease
- Categories of Disease
- Acute and Chronic Diseases
- Causes of Disease
- Communicable Or Infectious Diseases
- Infectious Agents
- Manifestation of Diseases
- Modes of Transmission of Diseases
- Organ-specific and Tissue-specific Manifestations
- Principles of Prevention of Diseases
- Principles of Treatment of Diseases
Natural Resources
- Natural Resources
- Biosphere: The Domain of Life
- Air is a Mixture
- Atmosphere and Its Layers
- Wind: The Movement of Air
- Rain
- Water: Our Lifeline
- Where Do We Get Water From?
- Availability of Water
- Importance of Water
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Mineral Riches in the Soil
- Biogeochemical Cycle
- Water Cycle
- Nitrogen Cycle
- The Carbon Cycle
- The Oxygen Cycle
- Ozone
- Ozone Layer Depletion
- Introduction
- Melting and Freezing Point of Water
- Boiling and Condensation Points
Introduction:
Freezing is when a liquid, like water, turns into a solid, like ice. When you put water in the fridge or on ice, its temperature starts falling, and it becomes cooler. As the water cools down, it reaches a point where it doesn’t get any cooler, but instead, it begins to freeze and turn into ice. This happens at a specific temperature, called the freezing point of water. For pure water, the freezing point is 0°C. At this temperature, water turns into ice.
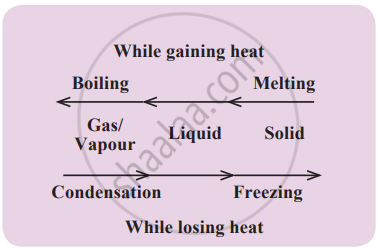
Melting and Freezing Point of Water:
- Each substance also has a specific melting point (the temperature where it melts) and freezing point (the temperature where it freezes), which are the same. For example, water freezes at 0°C and melts at 0°C.
- For example, when ice gets heat, it melts and turns into liquid water at 0°C.
- Temperatures can go below 0°C. For example, the freezer in a fridge has a temperature of around -18°C. At this low temperature, the water stays frozen as ice.
Boiling and Condensation Points:
Every substance has a specific boiling point, which is the temperature at which it changes from liquid to gas. This temperature is the same as its condensation point, where the gas changes back into a liquid. For example, the boiling point of water is 100°C, and the condensation point is also 100°C.
