Topics
Nutrition in Plants
Nutrition in Animals
- Different Ways of Taking Food
- Human Digestive System
- The Mouth and Buccal Cavity
- The Teeth and Its Structure
- The Salivary Glands
- The Food Pipe/Oesophagus
- The Stomach
- The Small Intestine
- Pancreas
- Absorption of Food
- The Large Intestine
- Assimilation of Food
- Liver
- Digestion in Grass-eating Animal
- Feeding and Digestion in Amoeba
Fibre to Fabric
- Fibre
- Fabrics
- Animal Fibres: Wool
- Animal Fibre: Silk
- Fibre to Yarn to Fabric
Heat
- Heat and Its Unit
- Heat Exchange
- The Temperature and a Thermometer
- Thermometer and Its Types
- Measuring Temperature
- Transfer of Heat
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
- Kinds of Clothes Wear in Summer and Winter
Acids, Bases and Salts
- Acids
- Bases (Alkalis)
- Indicators
- Types of Double Displacement: Neutralization Reaction
- Neutralization Reactions in Our Daily Life
- Similarities and Differences Between Acids and Bases
Physical and Chemical Changes
- Classification of Change: Physical Changes
- Chemical Reaction
- Experiment of Chemical Change
- Corrosion of Metals
- Crystallisation Method
Respiration in Organisms
- Respiration
- Respiration
- Types of Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
- Mechanism of respiration-Breathing
- Human Respiratory System
- Breathing in Other Animals
- Breathing Under Water
- Respiration in Plant
Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Blood
- Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Blood Vessels
- Heart Beat - Heart Sounds "LUBB" and "DUP"
- Blood Circulatory System in Human
- Human Heart
- Circulation of Blood in the Heart (Functioning of Heart)
- Excretion
- Human Excretory System
- Transport System in Plants
- Water absorbing organ
- Complex Permanent Tissues
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Phloem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Xylem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Transpiration
Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Weather and Climate
- Climate
- Climate and Adaptation
- Adaptations and Its Types
- Adaptation in Animals
- Adaptation in animals of snowy regions
- Adaptations in Tropical Rainforests
Reproduction in Plants
Wind Storms and Cyclones
- Wind: The Movement of Air
- Atmospheric Pressure
- High Speed Winds Are Accompanied by Reduced Air Pressure
- Air Expands on Heating
- Wind Currents Are Generated Due to Uneven Heating on the Earth
- Thunderstorms
- Cyclones
- Thunderstorm and Cyclone: Destruction Causes, Safety Measures and Role of Advanced Technology
Soil
- Properties of Soil
- Soil Profile
- Types of Soil
- Moisture in Soil
- Water Retention in Soil
- Soil and Crops
Motion and Time
- Motion and Rest
- Speed
- Types of Speed
- Types of Motion
- Measurement of Time
- Devices for Measuring Time
- Simple Pendulum for Time
- A Time Period of Oscillation and Frequency
- Measuring Speed
- Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph
Electric Current and Its Effects
Light
- Light
- The propagation of light
- Reflection of Light
- Mirrors
- Plane Mirror
- Lateral Inversion
- Divergence and Convergence of Light
- Spherical Mirrors
- Formation of Image by Reflection: Real and Virtual Image
- Concave Mirror
- Convex Mirror
- Concept of Lenses
- Images Formed by Sperical Lenses
- Colour
- Prism
- Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum
Forests: Our Lifeline
- Forests: Our Lifeline
- Forest Biome
- Habitat
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
- Classification of Plants
- Biogeochemical Cycle
- The Oxygen Cycle
- The Carbon Cycle
- Water Cycle
- Importance of Forest
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Consequences of Deforestation
Wastewater Story
- Water: Our Lifeline
- Sewage and Its Management
- Purification of Water
- Wastewater Treatment Plant (WWTP)
- Better Housekeeping Practices
- Controlling the Wastage of Water
- Sanitation and Disease
Water: A Precious Resource
- Water: Our Lifeline
- Availability of Water
- Water Cycle
- Sources of Water
- Scarcity of Water
- Distribution of Water in India
- Water Management (Conservation of Water)
- Fresh Water Management
- Controlling the Wastage of Water
- Scarcity of Water
Sources of Water:
Water is essential for all living things, and it comes from various sources on Earth.
- Rivers and streams: Rivers and streams, originating from mountains or hills, are freshwater bodies that are utilised for drinking, farming, and electricity generation by people.
- Lakes and Ponds: Lakes and ponds are non-flowing bodies of water, typically larger and deeper, used for freshwater purposes like fishing, swimming, and providing water to towns and cities.
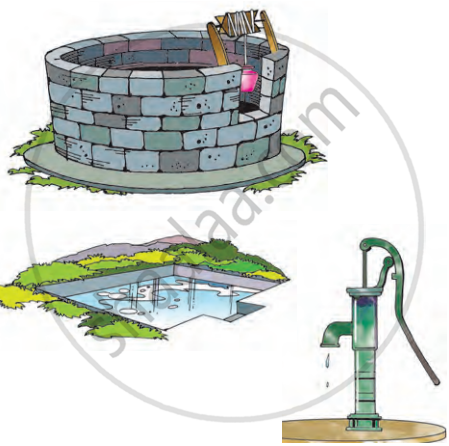
- Groundwater: Groundwater is water that soaks into the soil and is stored underground in spaces between rocks and soil particles. People access groundwater by digging wells and boreholes. It's a crucial source of drinking water, especially in places where rivers and lakes are not available.
- Oceans and Seas: Oceans and seas are large bodies of salty water that cover about 71% of the Earth's surface. Although ocean water is too salty for drinking, it is a source of fish and other sea life. It also plays a big role in regulating the Earth's climate.
- Rainwater: Rain, a natural source of freshwater, falls from clouds when atmospheric vapour cools and condenses. Rainwater helps fill rivers, lakes, and ponds, and it also soaks into the ground to become groundwater. Collecting rainwater is an important way to get water in some areas.
- Glaciers and Icecaps: In cold regions, water is stored as ice in glaciers and icecaps. When the ice melts during warmer seasons, it provides water to rivers and streams. Glaciers are a vital source of freshwater for many people living in mountainous areas.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
