Topics
Diversity in the Living World
The Living World
- What is ‘Living’?
- Diversity in the Living World
- Diversity in the Living World
- Taxonomic Hierarchy of Living Organisms: Unit of Classification
- Taxonomical Aids
Structural Organisation in Plants and Animals
Biological Classification
- Biological Classification
- History of Classification
- Five Kingdom Classification
- Kingdom Monera
- Bacteria
- Classification of Bacteria
- Structure of Bacteria
- Division of Kingdom Monera
- Examples of Kingdom Monera
- Kingdom Protista
- Protozoa
- Kingdom Protista
- Kingdom Fungi
- Fungi
- Structure of Fungi
- Life Processes in Fungi: Nutrition
- Reproduction in Fungi
- Division of Kingdom Fungi
- Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Life Cycle Patterns in Plants
- Kingdom Animalia
- Viruses
- Structure and Function of Viruses
- Viroids
- Prions
- Lichens
Plant Kingdom
Cell: Structure and Function
Plant Physiology
Animal Kingdom
- Kingdom Animalia
- New Criteria for Basis of Classification
- Classification of Kingdom Animalia
- Invertebrata and Vertebrata
- Non Chordates (Invertebrata)
- Phylum: Porifera
- Phylum: Cnidaria/Coelenterata
- Phylum: Ctenophora
- Phylum: Platyhelminthes
- Phylum: Aschelminthes
- Phylum: Annelida
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Phylum: Mollusca
- Phylum: Echinodermata
- Phylum: Hemichordata
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Cyclostomata
- Class: Chondrichthyes
- Class: Osteichthyes
- Class: Amphibia
- Class: Reptilia
- Class: Aves
- Class: Mammalia
Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Plant Morphology
- Root System
- Shoot System
- The Leaf
- Shoot System
- The Inflorescence
- The Flower
- Parts of Flower
- The Fruit
- The Seed
- Structure of a Dicotyledonous Seed
- Structure of Monocotyledonous Seed
- Semi-technical Description of a Typical Flowering Plant
- Description of Some Important Families
Human Physiology
Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy and Functions of Different Parts of Flowering Plants
- Tissues - “The Teams of Workers”
- Plant and Animals Tissue
- Meristems or Meristematic Tissues
- Permanent Tissue
- Simple Permanent Tissues (Supporting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissues
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Xylem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Phloem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Epidermal Tissue System
- Ground Tissue System
- Vascular Tissue System
- Dicotyledonous Root
- Monocotyledonous Root
- Dicotyledonous Stem
- Monocotyledonous Stem
- Isobilateral (Monocotyledonous) Leaf
- Dorsiventral (Dicotyledonous) Leaf
- Vascular Cambium
- Cork Cambium
- Secondary Growth in Roots
Structural Organisation in Animals
- Introduction of Structural Organisation in Animals
- Epithelial Tissue
- Connective Tissue
- Muscular Tissue
- Neural Tissues
- Earthworm - Lampito Mauritii
- Morphology of Earthworm
- Anatomy of Earthworm
- Morphology of Cockroach
- Anatomy of Cockroach
- Morphology of Frog
- Anatomy of Frog
- Organ and Organ System
Cell : the Unit of Life
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- The Invention of the Microscope and the Discovery of Cell
- Cell Theory
- Overview of Cell
- Organisms Show Variety in Cell Number, Shape and Size
- Prokaryotic Cells
- Cell Envelope and Its Modifications
- Ribosomes and Inclusion Bodies
- Structure of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- Cell Membrane
- Cell Wall
- Endomembrane System
- Mitochondria
- Plastids
- Ribosomes
- Cilia and Flagella
- Centrosome and Centrioles
- Cytoskeleton
- Nucleus
- Microbodies
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
- Structure and Functions of Cell Envelope, Cell Membrane, Cell Wall, Cell Organelles
Biomolecules
- How to Analyse Chemical Composition?
- Primary and Secondary Metabolites
- Biomacromolecules
- Polysaccharides
- Proteins
- Nucleic Acids
- Structure of Proteins
- Nature of Bond Linking Monomers in a Polymer
- Dynamic State of Body Constituents – Concept of Metabolism
- Metabolic Basis for Living
- The Living State
- Enzymes
- Enzymes - Chemical Reactions
- Enzymes - High Rates of Chemical Conversions
- Nature of Enzyme Action
- Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
- Classification and Nomenclature of Enzymes
- Enzymes - Co-factors
- Biomolecules in Living System
- Chemical Constituents of Living Cells
- Carbohydrates
- Structure and Function of Lipids
Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Introduction of Cell Division
- Phases of Cell Cycle
- Karyokinesis (Nuclear Division)
- Cytokinesis
- Significance of Meiosis
- Meiosis I
- Meiosis II
- Significance of Mitosis
- Cell Cycle
Transport in Plants
- Introduction of Transport in Plants
- Movement of Water, Gases and Nutrients
- Cell to Cell Transport
- Simple Diffusion
- Facilitated Diffusion
- Active Transport
- Comparison of Different Transport Processes
- Concept of Plant-water Relations
- Water Potential (ψ)
- Osmosi
- Turgidity and Flaccidity (Plasmolysis)
- Concept of Imbibition
- Introduction of Long Distance Transport of Water
- Plants Absorb Water
- Water Movement up a Plant
- Transpiration
- Transpiration - Transpiration and Photosynthesis – a Compromise
- Uptake of Mineral Ions
- Transport of Mineral Ions
- Phloem Transport - Flow from Source to Sink
- Phloem Transport - Pressure Flow Or Mass Flow Hypothesis
- Structure of Stomatal Apparatus
- Diffusion of Gases
- Transport in Plants (Numericals)
Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Early Experiments on Photosynthesis
- Where Does Photosynthesis Take Place?
- Pigments Are Involved in Photosynthesis
- Light Dependent Reaction (Hill Reaction \ Light Reaction)
- Electron Transport
- Electron Transport - Photolysis / Splitting of Water
- Electron Transport - Cyclic and Non-cyclic Photo-phosphorylation
- Electron Transport - Chemiosmotic Hypothesis
- Primary Acceptor of CO2
- The Calvin Cycle
- The C4 Pathway
- Photorespiration
- Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis as a Mean of Autotrophic Nutrition
- Chloroplast Structure
- Site of Photosynthesis
- Light-independent Reactions
- Photosynthesis Reaction
- Photochemical and Biosynthetic Phases of Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants (Questions)
Respiration in Plants
- Respiration in Plant
- Plants Breathe
- Phases of Respiration: Glycolysis
- Phases of Respiration: Fermentation
- Oxidation of Pyruvate
- Types of Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
- Phases of Respiration: Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle Or Kreb’s Cycle)
- Phases of Respiration: Electron Transport System (Ets) and Oxidative Phosphorylation
- Respiratory Balance Sheet
- Amphibolic Pathways
- Respiratory Quotient (R.Q.)
- Exchange of Gases - in Plants
- Energy Relations - Number of ATP Molecules Generated
- Respiration in Plant
Mineral Nutrition
- Plant Mineral Nutrition
- Methods to Study the Mineral Requirements of Plants
- Elementary Idea of Hydroponics
- Criteria for Essentiality
- Macro and Micro Nutrients and Their Role
- Deficiency Symptoms of Essential Elements
- Toxicity of Micronutrients
- Mechanism of Absorption of Elements
- Translocation of Solutes
- Nitrogen Metabolism
- Soil as Reservoir of Essential Elements
- Nitrogen Cycle
- Biological Nitrogen Fixation
- Nitrogen to Ammonia Conversion and Nitrogenase
- Mineral Nutrition (Questions)
Plant Growth and Development
- Introduction of Plant Growth and Development
- Plant Growth Generally is Indeterminate
- Phases of Plant Growth
- Plant Growth Rate
- Conditions Necessary for Plant Growth
- Differentiation, Dedifferentiation and Redifferentiation
- Concept of Development
- Characteristics of Growth Regulators
- Discovery of Plant Growth Regulators
- Physiological Effects of Plant Growth Regulators
- Photoperiodism
- Vernalisation
- Coordination in Plant: Tropism in Plants
- Formation of Seed and Fruit
- Formation of Seed and Fruit
- Plant Growth and Development (Questions)
Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Introduction of Breating and Exchange of Gases
- Respiratory Organs
- Human Respiratory System
- Respiratory Volumes and Capacities
- Exchange of Gases
- Transport of Gases - Transport of Oxygen
- Transport of Gases - Transport of Carbon Dioxide
- Regulation of Breathing / Respiration
- Disorders of Respiratory System
- Breating and Exchange of Gases (Questions)
- Mechanism of Breathing
Body Fluids and Circulation
- Introduction of Body Fluids and Circulation
- Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood)
- Blood Transfusion and Blood Groups (ABO and Rh system)
- Function of Platelets - Clotting of Blood (Coagulation)
- Lymph and Lymphatic System
- Human Circulatory System
- Cardiac Cycle
- Electrocardiograph (ECG)
- Types of Closed Circulation
- Regulation of Cardiac Activity
- Disorders of Circulatory System
- Cardiac Output
- Compatibility of Antigen
- Body Fluids and Circulation (Questions)
Excretory Products and Their Elimination
- Human Excretory System
- Function of the Kidney - “Production of Urine”
- Function of the Tubules
- Mechanism of Concentration of the Filtrate
- Regulation of Kidney Function
- Micturition
- Accessory Excretory Organs
- Common Disorders of the Urinary System
- Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism
- Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism
- Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism
- Osmoregulation
- Dialysis and Artificial Kidney
- Introduction of Excretory Products and Their Elimination
Digestion and Absorption
- Introduction of Digestion and Absorption
- Alimentary Canal
- Digestive Glands
- Digestion of Food
- Absorption of Digested Products
- Nutritional and Digestive Tract Disorders
- Role of Digestive Enzymes and Gastrointestinal Hormones
- Peristalsis, Digestion, Absorption and Assimilation of Proteins, Carbohydrates and Fats
- Digestion and Absorption Questions
- Calorific Values of Proteins
- Calorific Values of Carbohydrates
- Calorific Values of Fats
- Egestion of Food
Locomotion and Movement
- Introduction of Locomotion and Movement
- Types of Movement
- Muscles
- Structure of Contractile Proteins
- Mechanism of Muscle Contraction
- Skeletal System
- Joints and Its Classification
- Disorders of Muscular and Skeletal System
- Locomotion and Movement (Questions)
Neural Control and Coordination
Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Introduction of Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Human Endocrine System
- The Hypothalamus
- Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Gland
- The Pineal Gland
- Thyroid Gland
- Parathyroid Gland
- Thymus Gland
- Adrenal Gland (Suprarenal Gland)
- Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
- Testis
- Ovary
- Hormones of Heart, Kidney and Gastrointestinal Tract
- Mechanism of Hormone Action
- Role of Hormones as Messengers and Regulators
- Hypo and Hyperactivity and Related Disorders
- Chemical Coordination and Integration (Questions)
Viruses:
The sizes of viruses are very small, about 10 nanometres to 100 nanometres, which is 10 to 100 times smaller than bacteria. They can only be seen with an electron microscope.
- Viruses are considered to be "on the edge of living and nonliving" because they do not show signs of life until they enter a host cell.
- They exist as independent particles and are made up of a long molecule of DNA or RNA. Surrounded by a protective protein coat.
- Viruses can only reproduce inside living plant or animal cells. They use the host cell’s machinery to create many copies of themselves.
- Once they have multiplied, they destroy the host cell and are released to infect more cells. Viruses cause a variety of diseases in plants and animals.
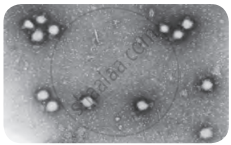
Tomato Wilt Virus
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
