Topics
Diversity in the Living World
The Living World
- What is ‘Living’?
- Diversity in the Living World
- Diversity in the Living World
- Taxonomic Hierarchy of Living Organisms: Unit of Classification
- Taxonomical Aids
Structural Organisation in Plants and Animals
Biological Classification
- History of Classification
- Five Kingdom Classification
- Kingdom Monera
- Bacteria
- Classification of Bacteria
- Structure of Bacteria
- Division of Kingdom Monera
- Examples of Kingdom Monera
- Kingdom Protista
- Protozoa
- Kingdom Protista
- Kingdom Fungi
- Fungi
- Structure of Fungi
- Life Processes in Fungi: Nutrition
- Reproduction in Fungi
- Division of Kingdom Fungi
- Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Life Cycle Patterns in Plants
- Kingdom Animalia
- Viruses
- Structure and Function of Viruses
- Viroids
- Prions
- Lichens
Plant Kingdom
Cell: Structure and Function
Plant Physiology
Animal Kingdom
- Kingdom Animalia
- Classification of Kingdom Animalia
- Invertebrata and Vertebrata
- Non Chordates (Invertebrata)
- Class: Cyclostomata
- Class: Chondrichthyes
- Class: Osteichthyes
- Class: Amphibia
- Class: Reptilia
- Class: Aves
- Class: Mammalia
Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Plant Morphology
- Root System
- Shoot System
- The Leaf
- Shoot System
- The Inflorescence
- The Flower
- Parts of Flower
- The Fruit
- The Seed
- Structure of a Dicotyledonous Seed
- Structure of Monocotyledonous Seed
- Semi-technical Description of a Typical Flowering Plant
- Description of Some Important Families
Human Physiology
Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy and Functions of Different Parts of Flowering Plants
- Tissues - “The Teams of Workers”
- Plant and Animals Tissue
- Meristems or Meristematic Tissues
- Permanent Tissue
- Simple Permanent Tissues (Supporting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissues
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Xylem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Phloem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Epidermal Tissue System
- Ground Tissue System
- Vascular Tissue System
- Dicotyledonous Root
- Monocotyledonous Root
- Dicotyledonous Stem
- Monocotyledonous Stem
- Isobilateral (Monocotyledonous) Leaf
- Dorsiventral (Dicotyledonous) Leaf
- Vascular Cambium
- Cork Cambium
- Secondary Growth in Roots
Structural Organisation in Animals
- Introduction of Structural Organisation in Animals
- Epithelial Tissue
- Connective Tissue
- Muscular Tissue
- Neural Tissues
- Earthworm - Lampito Mauritii
- Morphology of Earthworm
- Anatomy of Earthworm
- Morphology of Cockroach
- Anatomy of Cockroach
- Morphology of Frog
- Anatomy of Frog
- Organ and Organ System
Cell : the Unit of Life
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- The Invention of the Microscope and the Discovery of Cell
- Cell Theory
- Overview of Cell
- Organisms Show Variety in Cell Number, Shape and Size
- Prokaryotic Cells
- Cell Envelope and Its Modifications
- Ribosomes and Inclusion Bodies
- Structure of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- Cell Membrane
- Cell Wall
- Endomembrane System
- Mitochondria
- Plastids
- Ribosomes
- Cilia and Flagella
- Centrosome and Centrioles
- Cytoskeleton
- Nucleus
- Microbodies
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
- Structure and Functions of Cell Envelope, Cell Membrane, Cell Wall, Cell Organelles
Biomolecules
- How to Analyse Chemical Composition?
- Primary and Secondary Metabolites
- Biomacromolecules
- Polysaccharides
- Proteins
- Nucleic Acids
- Structure of Proteins
- Nature of Bond Linking Monomers in a Polymer
- Dynamic State of Body Constituents – Concept of Metabolism
- Metabolic Basis for Living
- The Living State
- Enzymes
- Enzymes - Chemical Reactions
- Enzymes - High Rates of Chemical Conversions
- Nature of Enzyme Action
- Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
- Classification and Nomenclature of Enzymes
- Enzymes - Co-factors
- Biomolecules in Living System
- Chemical Constituents of Living Cells
- Carbohydrates
- Structure and Function of Lipids
Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Phases of Cell Cycle
- Karyokinesis (Nuclear Division)
- Cytokinesis
- Cell Cycle
Transport in Plants
- Introduction of Transport in Plants
- Movement of Water, Gases and Nutrients
- Cell to Cell Transport
- Simple Diffusion
- Facilitated Diffusion
- Active Transport
- Comparison of Different Transport Processes
- Concept of Plant-water Relations
- Water Potential (ψ)
- Osmosi
- Turgidity and Flaccidity (Plasmolysis)
- Concept of Imbibition
- Introduction of Long Distance Transport of Water
- Plants Absorb Water
- Water Movement up a Plant
- Transpiration
- Transpiration - Transpiration and Photosynthesis – a Compromise
- Uptake of Mineral Ions
- Transport of Mineral Ions
- Phloem Transport - Flow from Source to Sink
- Phloem Transport - Pressure Flow Or Mass Flow Hypothesis
- Structure of Stomatal Apparatus
- Diffusion of Gases
- Transport in Plants (Numericals)
Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Early Experiments on Photosynthesis
- Where Does Photosynthesis Take Place?
- Pigments Are Involved in Photosynthesis
- Light Dependent Reaction (Hill Reaction \ Light Reaction)
- Electron Transport
- Electron Transport - Photolysis / Splitting of Water
- Electron Transport - Cyclic and Non-cyclic Photo-phosphorylation
- Electron Transport - Chemiosmotic Hypothesis
- Primary Acceptor of CO2
- The Calvin Cycle
- The C4 Pathway
- Photorespiration
- Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis as a Mean of Autotrophic Nutrition
- Chloroplast Structure
- Site of Photosynthesis
- Light-independent Reactions
- Photosynthesis Reaction
- Photochemical and Biosynthetic Phases of Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants (Questions)
Respiration in Plants
- Respiration in Plant
- Plants Breathe
- Phases of Respiration: Glycolysis
- Phases of Respiration: Fermentation
- Oxidation of Pyruvate
- Phases of Respiration: Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle Or Kreb’s Cycle)
- Phases of Respiration: Electron Transport System (Ets) and Oxidative Phosphorylation
- Respiratory Balance Sheet
- Amphibolic Pathways
- Respiratory Quotient (R.Q.)
- Exchange of Gases - in Plants
- Energy Relations - Number of ATP Molecules Generated
- Respiration in Plant
Mineral Nutrition
- Plant Mineral Nutrition
- Methods to Study the Mineral Requirements of Plants
- Elementary Idea of Hydroponics
- Criteria for Essentiality
- Macro and Micro Nutrients and Their Role
- Deficiency Symptoms of Essential Elements
- Toxicity of Micronutrients
- Mechanism of Absorption of Elements
- Translocation of Solutes
- Nitrogen Metabolism
- Soil as Reservoir of Essential Elements
- Nitrogen Cycle
- Biological Nitrogen Fixation
- Nitrogen to Ammonia Conversion and Nitrogenase
- Mineral Nutrition (Questions)
Plant Growth and Development
- Introduction of Plant Growth and Development
- Plant Growth Generally is Indeterminate
- Phases of Plant Growth
- Plant Growth Rate
- Conditions Necessary for Plant Growth
- Differentiation, Dedifferentiation and Redifferentiation
- Concept of Development
- Characteristics of Growth Regulators
- Discovery of Plant Growth Regulators
- Physiological Effects of Plant Growth Regulators
- Photoperiodism
- Vernalisation
- Coordination in Plant: Tropism in Plants
- Formation of Seed and Fruit
- Formation of Seed and Fruit
- Plant Growth and Development (Questions)
Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Introduction of Breating and Exchange of Gases
- Respiratory Organs
- Human Respiratory System
- Respiratory Volumes and Capacities
- Exchange of Gases
- Transport of Gases - Transport of Oxygen
- Transport of Gases - Transport of Carbon Dioxide
- Regulation of Breathing / Respiration
- Disorders of Respiratory System
- Breating and Exchange of Gases (Questions)
- Mechanism of Breathing
Body Fluids and Circulation
- Introduction of Body Fluids and Circulation
- Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood)
- Blood Transfusion and Blood Groups (ABO and Rh system)
- Function of Platelets - Clotting of Blood (Coagulation)
- Lymph and Lymphatic System
- Human Circulatory System
- Cardiac Cycle
- Electrocardiograph (ECG)
- Types of Closed Circulation
- Regulation of Cardiac Activity
- Disorders of Circulatory System
- Cardiac Output
- Compatibility of Antigen
- Body Fluids and Circulation (Questions)
Excretory Products and Their Elimination
- Human Excretory System
- Function of the Kidney - “Production of Urine”
- Function of the Tubules
- Mechanism of Concentration of the Filtrate
- Regulation of Kidney Function
- Micturition
- Accessory Excretory Organs
- Common Disorders of the Urinary System
- Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism
- Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism
- Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism
- Osmoregulation
- Dialysis and Artificial Kidney
- Introduction of Excretory Products and Their Elimination
Digestion and Absorption
- Introduction of Digestion and Absorption
- Alimentary Canal
- Digestive Glands
- Digestion of Food
- Absorption of Digested Products
- Nutritional and Digestive Tract Disorders
- Role of Digestive Enzymes and Gastrointestinal Hormones
- Peristalsis, Digestion, Absorption and Assimilation of Proteins, Carbohydrates and Fats
- Digestion and Absorption Questions
- Calorific Values of Proteins
- Calorific Values of Carbohydrates
- Calorific Values of Fats
- Egestion of Food
Locomotion and Movement
- Introduction of Locomotion and Movement
- Types of Movement
- Muscles
- Structure of Contractile Proteins
- Mechanism of Muscle Contraction
- Skeletal System
- Joints and Its Classification
- Disorders of Muscular and Skeletal System
- Locomotion and Movement (Questions)
Neural Control and Coordination
Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Introduction of Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Human Endocrine System
- The Hypothalamus
- Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Gland
- The Pineal Gland
- Thyroid Gland
- Parathyroid Gland
- Thymus Gland
- Adrenal Gland (Suprarenal Gland)
- Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
- Testis
- Ovary
- Hormones of Heart, Kidney and Gastrointestinal Tract
- Mechanism of Hormone Action
- Role of Hormones as Messengers and Regulators
- Hypo and Hyperactivity and Related Disorders
- Chemical Coordination and Integration (Questions)
Thallophyta:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Habitat | Mostly aquatic, living in both freshwater and saline environments. |
| Structure | Plants lack specific organs like roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. Bodies are soft, simple, and fibre-like. |
| Chlorophyll and Autotrophy | Algae are autotrophic due to the presence of chlorophyll, enabling photosynthesis. They may be unicellular or multicellular, microscopic or large. |
| Examples of Algae |
Freshwater: Spirogyra, Ulothrix. Saline water: Ulva, Sargassum. |
| Fungi in Thallophyta | Includes organisms like yeasts and moulds that lack chlorophyll. Unlike algae, fungi are heterotrophic, obtaining nutrients through decomposition or symbiosis. |
| Diversity | Algae show significant diversity in size, form, and habitat. For example, Spirogyra (filamentous) and Sargassum (large and leafy). |
| Ecological Importance | Algae produce oxygen through photosynthesis, serve as food sources, and provide bioactive compounds. Fungi help in nutrient cycling and decomposition. |
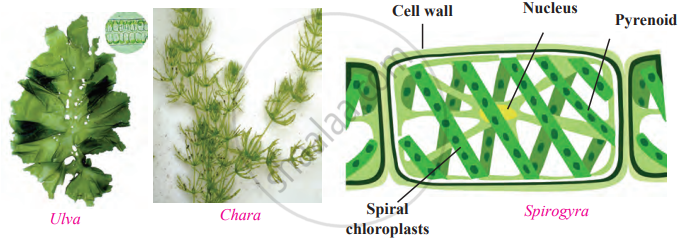
Plants of the Thallophyta division
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
Related QuestionsVIEW ALL [4]
Which of the following is not correctly matched for the organism and its cell wall degrading enzyme?
Match the proper terms from columns A and C with the description in column B.
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ | ‘C’ |
| Thallophyta | Seeds are formed in fruits. | Fern |
| Bryophyta | No natural covering on seeds. | Cycas |
| Pteridophyta | These plants mainly grow in water. | Tamarind |
| Gymnosperms | These plants need water for reproduction. | Moss |
| Angiosperms | Tissues are present for the conduction of water and food | Algae |
