Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A narrow pencil of parallel light is incident normally on a solid transparent sphere of radius r. What should be the refractive index is the pencil is to be focussed (a) at the surface of the sphere, (b) at the centre of the sphere.
उत्तर
Given,
The radius of the transparent sphere = r
Refraction at convex surface.
As per the question,
u = −∞, μ1 = 1, μ2 = ?
(a) When image is to be focused on the surface,
Image distance (v) = 2r, Radius of curvature (R) = r
We know that,
\[\frac{\mu_2}{v} - \frac{\mu_1}{u} = \frac{\mu_2 - \mu_1}{R}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{\mu_2}{2r} - \left( \frac{1}{- \infty} \right) = \frac{\mu_2 - 1}{r}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{\mu_2}{2r} = \frac{\mu_2 - 1}{r}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \mu_2 = 2 \mu_2 - 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow \mu_2 = 2\]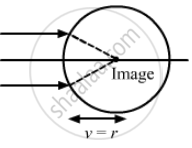
(b) When the image is to be focused at the centre,
Image distance (v) = r, Radius of curvature (R) = r
\[\frac{\mu_2}{v} - \frac{\mu_1}{u} = \frac{\mu_2 - \mu_1}{R}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{\mu_2}{r} - \left( \frac{1}{- \infty} \right) = \frac{\mu_2 - 1}{r}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{\mu_2}{r} = \frac{\mu_2 - 1}{r}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \mu_2 = \mu_2 - 1\]
The above equation is impossible.
Hence, the image cannot be focused at centre.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A small candle, 2.5 cm in size is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image? Describe the nature and size of the image. If the candle is moved closer to the mirror, how would the screen have to be moved?
A 4.5 cm needle is placed 12 cm away from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Give the location of the image and the magnification. Describe what happens as the needle is moved farther from the mirror.
A double convex lens is made of a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. Find the radius of curvature required, if the focal length is 20 cm.
In motor vehicles, a convex mirror is attached near the driver's seat to give him the view of the traffic behind. What is the special function of this convex mirror which a plane mirror can not do?
If an object far away from a convex mirror moves towards the mirror, the image also moves. Does it move faster, slower or at the same speed as compared to the object?
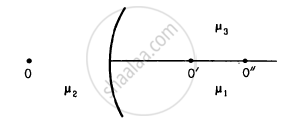
Following figure shows three transparent media of refractive indices \[\mu_1 , \mu_2 \text{ and } \mu_3\]. A point object O is placed in the medium \[\mu_2\]. If the entire medium on the right of the spherical surface has refractive index \[\mu_3\], the image forms at O". In the situation shown,
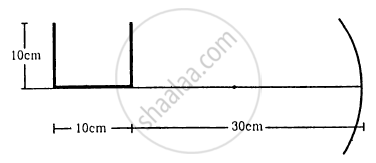
A U-shaped wire is placed before a concave mirror having radius of curvature 20 cm as shown in figure. Find the total length of the image.
A diverging lens of focal length 20 cm and a converging mirror of focal length 10 cm are placed coaxially at a separation of 5 cm. Where should an object be placed so that a real image is formed at the object itself?
How can the spherical aberration produced by a lens be minimized?
Two thin lenses having optical powers of -10D and+ 6D are placed in contact with each other. The focal length of the combination is:
Answer the following question.
Under what conditions is the phenomenon of total internal reflection of light observed? Obtain the relation between the critical angle of incidence and the refractive index of the medium.
Answer the following question.
Three lenses of focal length +10 cm, —10 cm and +30 cm are arranged coaxially as in the figure given below. Find the position of the final image formed by the combination.

According to Cartesian sign convention, all distances are measured from the _______.
Focal length of a mirror is given by ______.
The focal length of a convex lens made of glass of refractive index (1.5) is 20 cm.
What will be its new focal length when placed in a medium of refractive index 1.25?
Is focal length positive or negative? What does it signify?
You are given four sources of light each one providing a light of a single colour – red, blue, green and yellow. Suppose the angle of refraction for a beam of yellow light corresponding to a particular angle of incidence at the interface of two media is 90°. Which of the following statements is correct if the source of yellow light is replaced with that of other lights without changing the angle of incidence?
(i) Consider a thin lens placed between a source (S) and an observer (O) (Figure). Let the thickness of the lens vary as `w(b) = w_0 - b^2/α`, where b is the verticle distance from the pole. `w_0` is a constant. Using Fermat’s principle i.e. the time of transit for a ray between the source and observer is an extremum, find the condition that all paraxial rays starting from the source will converge at a point O on the axis. Find the focal length.
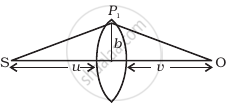
(ii) A gravitational lens may be assumed to have a varying width of the form
`w(b) = k_1ln(k_2/b) b_("min") < b < b_("max")`
= `k_1ln (K_2/b_("min")) b < b_("min")`
Show that an observer will see an image of a point object as a ring about the center of the lens with an angular radius
`β = sqrt((n - 1)k_1 u/v)/(u + v)`
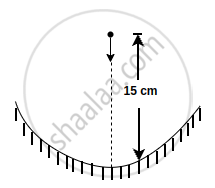
A particle is dropped along the axis from a height 15 cm on a concave mirror of focal length 30 cm as shown in figure. The acceleration due to gravity is 10 m/s2. Find the maximum speed of image in m/s:
If an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm in front of a concave mirror of a focal length of 20 cm, the image formed will be ______.
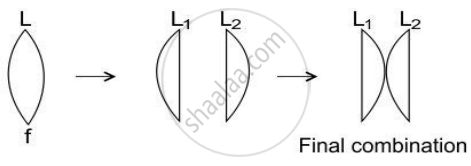
A lens of focal length f is divided into two equal parts and then these parts are put in a combination as shown in the figure below.
- What is the focal length of L1?
- What is the focal length of the final combination?