Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A sonometer wire of length l vibrates in fundamental mode when excited by a tuning fork of frequency 416. Hz. If the length is doubled keeping other things same, the string will ______.
विकल्प
vibrate with a frequency of 416 Hz
vibrate with a frequency of 208 Hz
vibrate with a frequency of 832 Hz
stop vibrating.
उत्तर
vibrate with a frequency of 208 Hz
According to the relation of the fundamental frequency of a string
\[\nu = \frac{1}{2l}\sqrt{\frac{F}{\mu}}\]
where
l is the length of the string
F is the tension
μ is the linear mass density
We know that ν1 = 416 Hz, l1 = l and l2 = 2l.
\[v_1 \propto \frac{1}{l_1}\]
\[ v_1 l_1 = v_2 l_2 \]
\[\left( 416 \right)l = v_2 \left( 2l \right)\]
\[ v_2 = 208 Hz\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A bat emits an ultrasonic sound of frequency 1000 kHz in the air. If the sound meets a water surface, what is the wavelength of the transmitted sound? The speed of sound in air is 340 m s–1 and in water 1486 m s–1.
A wire stretched between two rigid supports vibrates in its fundamental mode with a frequency of 45 Hz. The mass of the wire is 3.5 × 10–2 kg and its linear mass density is 4.0 × 10–2 kg m–1. What is (a) the speed of a transverse wave on the string, and (b) the tension in the string?
A SONAR system fixed in a submarine operates at a frequency 40.0 kHz. An enemy submarine moves towards the SONAR with a speed of 360 km h–1. What is the frequency of sound reflected by the submarine? Take the speed of sound in water to be 1450 m s–1.
Earthquakes generate sound waves inside the earth. Unlike a gas, the earth can experience both transverse (S) and longitudinal (P) sound waves. Typically the speed of S wave is about 4.0 km s–1, and that of P wave is 8.0 km s–1. A seismograph records P and S waves from an earthquake. The first P wave arrives 4 min before the first S wave. Assuming the waves travel in straight line, at what distance does the earthquake occur?
A sine wave is travelling in a medium. The minimum distance between the two particles, always having same speed, is
Two strings A and B, made of same material, are stretched by same tension. The radius of string A is double of the radius of B. A transverse wave travels on A with speed `v_A` and on B with speed `v_B`. The ratio `v_A/v_B` is ______.
Velocity of sound in air is 332 m s−1. Its velocity in vacuum will be
Two sine waves travel in the same direction in a medium. The amplitude of each wave is A and the phase difference between the two waves is 120°. The resultant amplitude will be
The equation of a wave travelling on a string stretched along the X-axis is given by
\[y = A e {}^- \left( \frac{x}{a} + \frac{t}{T} \right)^2 .\]
(a) Write the dimensions of A, a and T. (b) Find the wave speed. (c) In which direction is the wave travelling? (d) Where is the maximum of the pulse located at t = T? At t = 2 T?
A sonometer wire supports a 4 kg load and vibrates in fundamental mode with a tuning fork of frequency 416. Hz. The length of the wire between the bridges is now doubled. In order to maintain fundamental mode, the load should be changed to
A travelling wave is produced on a long horizontal string by vibrating an end up and down sinusoidally. The amplitude of vibration is 1⋅0 and the displacement becomes zero 200 times per second. The linear mass density of the string is 0⋅10 kg m−1 and it is kept under a tension of 90 N. (a) Find the speed and the wavelength of the wave. (b) Assume that the wave moves in the positive x-direction and at t = 0, the end x = 0 is at its positive extreme position. Write the wave equation. (c) Find the velocity and acceleration of the particle at x = 50 cm at time t = 10 ms.
Two long strings A and B, each having linear mass density
\[1 \cdot 2 \times {10}^{- 2} kg m^{- 1}\] , are stretched by different tensions 4⋅8 N and 7⋅5 N respectively and are kept parallel to each other with their left ends at x = 0. Wave pulses are produced on the strings at the left ends at t = 0 on string A and at t = 20 ms on string B. When and where will the pulse on B overtake that on A?
Two waves, travelling in the same direction through the same region, have equal frequencies, wavelengths and amplitudes. If the amplitude of each wave is 4 mm and the phase difference between the waves is 90°, what is the resultant amplitude?
A wire of length 2⋅00 m is stretched to a tension of 160 N. If the fundamental frequency of vibration is 100 Hz, find its linear mass density.
The equation for the vibration of a string, fixed at both ends vibrating in its third harmonic, is given by
\[y = \left( 0 \cdot 4 cm \right) \sin\left[ \left( 0 \cdot 314 {cm}^{- 1} \right) x \right] \cos \left[ \left( 600\pi s^{- 1} \right) t \right]\]
(a) What is the frequency of vibration? (b) What are the positions of the nodes? (c) What is the length of the string? (d) What is the wavelength and the speed of two travelling waves that can interfere to give this vibration?
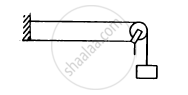
Following figure shows a string stretched by a block going over a pulley. The string vibrates in its tenth harmonic in unison with a particular tuning for. When a beaker containing water is brought under the block so that the block is completely dipped into the beaker, the string vibrates in its eleventh harmonic. Find the density of the material of the block.
What is the interference of sound waves?
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement of an elastic wave.
- y = 5 cos (4x) sin (20t)
- y = 4 sin (5x – t/2) + 3 cos (5x – t/2)
- y = 10 cos [(252 – 250) πt] cos [(252 + 250)πt]
- y = 100 cos (100πt + 0.5x)
State which of these represent
- a travelling wave along –x direction
- a stationary wave
- beats
- a travelling wave along +x direction.
Given reasons for your answers.
The displacement y of a particle in a medium can be expressed as, y = `10^-6sin(100t + 20x + pi/4)` m where t is in second and x in meter. The speed of the wave is ______.
