Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define coefficient of restitution.
उत्तर
For two colliding bodies, the negative of the ratio of the relative velocity of separation to the relative velocity of approach is called the coefficient of restitution.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State if the following statement is true or false. Give a reason for your answer.
In an elastic collision of two bodies, the momentum and energy of each body is conserved.
State if the following statement is true or false. Give a reason for your answer.
Total energy of a system is always conserved, no matter what internal and external forces on the body are present.
Answer carefully, with reason:
In an elastic collision of two billiard balls, is the total kinetic energy conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e. when they are in contact)?
Answer carefully, with reason:
Is the total linear momentum conserved during the short time of an elastic collision of two balls?
Answer carefully, with reason:
In an inelastic collision of two billiard balls, is the total kinetic energy conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e., when they are in contact)?
The bob A of a pendulum released from 30° to the vertical hits another bob B of the same mass at rest on a table, as shown in the figure. How high does the bob A rise after the collision? Neglect the size of the bobs and assume the collision to be elastic.

Consider the decay of a free neutron at rest : n → p + e–
Show that the two-body decay of this type must necessarily give an electron of fixed energy and, therefore, cannot account for the observed continuous energy distribution in the β-decay of a neutron or a nucleus

Explain the characteristics of elastic and inelastic collision.
Define the following:
Coefficient of restitution
Arrive at an expression for elastic collision in one dimension and discuss various cases.
Two different unknown masses A and B collide. A is initially at rest when B has a speed v. After collision B has a speed v/2 and moves at right angles to its original direction of motion. Find the direction in which A moves after the collision.
In Rutherford experiment, for head-on collision of a-particles with a gold nucleus, the impact parameter is ______.
A ball of mass 0.1 kg makes an elastic head-on collision with a ball of unknown mass, initially at rest. If the 0 .1 kg ball rebounds at one-third of its original speed, the mass of the other ball is ______.
A mass M moving with velocity 'v' along x-axis collides and sticks to another mass 2M which is moving along Y-axis with velocity 3v. After collision, the velocity of the combination is ______.
A bullet fired from gun with a velocity 30 m/s at an angle of 60° with horizontal direction. At the highest point of its path, the bullet explodes into two parts with masses in the ratio 1:3. The lighter mass comes to rest immediately. Then the speed of the heavier mass is
During inelastic collision between two bodies, which of the following quantities always remain conserved?
Two blocks M1 and M2 having equal mass are free to move on a horizontal frictionless surface. M2 is attached to a massless spring as shown in figure. Iniially M2 is at rest and M1 is moving toward M2 with speed v and collides head-on with M2.
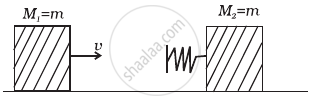
- While spring is fully compressed all the KE of M1 is stored as PE of spring.
- While spring is fully compressed the system momentum is not conserved, though final momentum is equal to initial momentum.
- If spring is massless, the final state of the M1 is state of rest.
- If the surface on which blocks are moving has friction, then collision cannot be elastic.
In an elastic collision of two billiard balls, which of the following quantities remain conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e., when they are in contact).
- Kinetic energy.
- Total linear momentum?
Give reason for your answer in each case.
Consider a one-dimensional motion of a particle with total energy E. There are four regions A, B, C and D in which the relation between potential energy V, kinetic energy (K) and total energy E is as given below:
Region A : V > E
Region B : V < E
Region C : K > E
Region D : V > K
State with reason in each case whether a particle can be found in the given region or not.
A drunkard walking in a narrow lane takes 5 steps forward and 3 steps backward, followed again by 5 steps forward and 3 steps backward, and so on. Each step is 1 m long and required 1 s to cover. How long the drunkard takes to fall in a pit 13 m away from the start?
A ball falls from a height of 1 m on a ground and it loses half its kinetic energy when it hits the ground. What would be the total distance covered by the ball after sufficiently long time?
An insect moves with a constant velocity v from one corner of a room to other corner which is opposite of the first corner along the largest diagonal of room. If the insect can not fly and dimensions of room is a × a × a, then the minimum time in which the insect can move is `"a"/"v"`. times the square root of a number n, then n is equal to ______.
A bag of sand of mass 9.8 kg is suspended by a rope. A bullet of 200 g travelling with speed 10 ms-1 gets embedded in it, then loss of kinetic energy will be ______.
An alpha-particle of mass m suffers 1-dimensional elastic collision with a nucleus at rest of unknown mass. It is scattered directly backwards losing, 64% of its initial kinetic energy. The mass of the nucleus is ______.
A sphere of mass 'm' moving with velocity 'v' collides head-on another sphere of same mass which is at rest. The ratio of final velocity of second sphere to the initial velocity of the first sphere is ______. ( e is coefficient of restitution and collision is inelastic)
