Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Derive an expression for the work done during an isothermal process.
उत्तर
Consider the isothermal expansion of an ideal gas. Let its initial volume be Vi and the final volumes be Vf. The work done in an infinitesimally small isothermal expansion is given by
dW = pdV
The total work done in bringing out the expansion from the initial volume Vi to the final volume Vf is given by,
W = `int_{V_i}^{V_f} pdV`
∴ W = `int_{V_i}^{V_f} (nRT)/V`dV .............`("for an ideal gas", p = "nRT"/V)`
∴ W = `nRTint_{V_i}^{V_f}(dV)/V`
∴ W = nRT(In Vf - In Vi)
∴ W = nRT In `V_f/V_i`

This is the required expression for the work done during an isothermal process.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A thermally insulated, closed copper vessel contains water at 15°C. When the vessel is shaken vigorously for 15 minutes, the temperature rises to 17°C. The mass of the vessel is 100 g and that of the water is 200 g. The specific heat capacities of copper and water are 420 J kg−1 K−1 and 4200 J kg−1 K−1 respectively. Neglect any thermal expansion. (a) How much heat is transferred to the liquid-vessel system? (b) How much work has been done on this system? (c) How much is the increase in internal energy of the system?
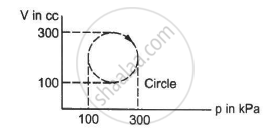
Calculate the heat absorbed by a system in going through the cyclic process shown in figure.
The internal energy of a gas is given by U = 1.5 pV. It expands from 100 cm3 to 200 cm3against a constant pressure of 1.0 × 105 Pa. Calculate the heat absorbed by the gas in the process.
A gas is enclosed in a cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston. The gas is slowly heated for some time. During the process, 10 J of heat is supplied and the piston is found to move out 10 cm. Find the increase in the internal energy of the gas. The area of cross section of the cylinder = 4 cm2 and the atmospheric pressure = 100 kPa.
For an Isothermal process
The compressibility of water is 5 × 10-10 m2/N. Pressure of 15 × 106 Pa is applied on 100 ml volume of water. The change in the volume of water is ______.
"The mass and energy both are conserved in an isolated system", is the statement of ______.
For a particular reaction, the system absorbs 8 kJ of heat and does 2.5 kJ of work on its surrounding. What will be the change in internal energy of the system?
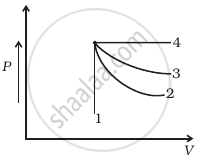
An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (figure). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of 1, 2, 3 and 4 which one is adiabatic.
An ideal gas undergoes isothermal process from some initial state i to final state f. Choose the correct alternatives.
- dU = 0
- dQ= 0
- dQ = dU
- dQ = dW
Consider a cycle followed by an engine (Figure)
1 to 2 is isothermal
2 to 3 is adiabatic
3 to 1 is adiabatic
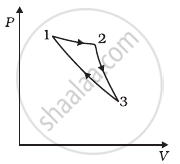
Such a process does not exist because ______.
- heat is completely converted to mechanical energy in such a process, which is not possible.
- mechanical energy is completely converted to heat in this process, which is not possible.
- curves representing two adiabatic processes don’t intersect.
- curves representing an adiabatic process and an isothermal process don’t intersect.
Can a system be heated and its temperature remains constant?
Consider a cycle tyre being filled with air by a pump. Let V be the volume of the tyre (fixed) and at each stroke of the pump ∆V(V) of air is transferred to the tube adiabatically. What is the work done when the pressure in the tube is increased from P1 to P2?
Consider a P-V diagram in which the path followed by one mole of perfect gas in a cylindrical container is shown in figure.
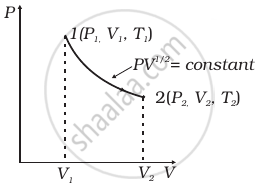
- Find the work done when the gas is taken from state 1 to state 2.
- What is the ratio of temperature T1/T2, if V2 = 2V1?
- Given the internal energy for one mole of gas at temperature T is (3/2) RT, find the heat supplied to the gas when it is taken from state 1 to 2, with V2 = 2V1.
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure. Find heat exchanged by the engine, with the surroundings for each section of the cycle. (Cv = (3/2)R)
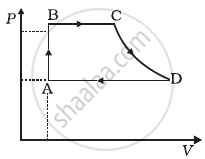
- AB : constant volume
- BC : constant pressure
- CD : adiabatic
- DA : constant pressure
Consider that an ideal gas (n moles) is expanding in a process given by P = f(V), which passes through a point (V0, P0). Show that the gas is absorbing heat at (P0, V0) if the slope of the curve P = f(V) is larger than the slope of the adiabat passing through (P0, V0).
Write the mathematical equation for the first law of thermodynamics for:
Isothermal process
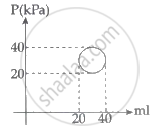
In the reported figure, heat energy absorbed by a system in going through a cyclic process is ______ πJ.
An electric appliance supplies 6000 J/min heat to the system. If the system delivers a power of 90 W. How long it would take to increase the internal energy by 2.5 × 103 J?
Which among the following equations represents the first law of thermodynamics under isobaric conditions?
An ideal gas (γ = 1.5) is expanded adiabatically. How many times has the gas had to be expanded to reduce the root mean square velocity of molecules two times?
A given system undergoes a change in which the work done by the system equals the decrease in its internal energy. The system must have undergone an ______.
104 J of work is done on a certain volume of a gas. If the gas releases 125 kJ of heat, calculate the change in internal energy of the gas.
In an adiabatic process, W = ______.
For an isothermal and reversible expansion of 0.5 mol of an ideal gas Wmax is - 3.918 kJ. The value of ΔU is ______.
What is Isobaric process?
Choose the correct relation with reason.
Define the isothermal process.
