Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a circle of any radius. Show one diameter, one radius and one chord on that circle.
उत्तर
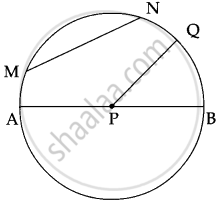
In a circle, P is the centre.
AB is a diameter.
PQ is a radius
MN is a chord
संबंधित प्रश्न
From a point T outside a circle of centre O, tangents TP and TQ are drawn to the circle. Prove that OT is the right bisector of line segment PQ.
Points A(–1, y) and B(5, 7) lie on a circle with centre O(2, –3y). Find the values of y. Hence find the radius of the circle.
In fig. a circle touches all the four sides of quadrilateral ABCD with AB = 6cm, BC = 7cm, CD = 4cm. Find AD.
If the area of a circle is equal to sum of the areas of two circles of diameters 10 cm and 24 cm, then the diameter of the larger circle (in cm) is:
On a semi-circle with AB as diameter, a point C is taken, so that m (∠CAB) = 30°. Find m(∠ACB) and m (∠ABC).
Use the figure given below to fill in the blank:
If PQ is 8 cm long, the length of RS = ________
Given: A circle inscribed in a right angled ΔABC. If ∠ACB = 90° and the radius of the circle is r.
To prove: 2r = a + b – c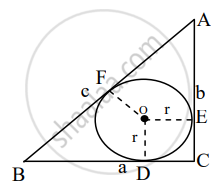
A circle of radius 3 cm can be drawn through two points A, B such that AB = 6 cm.
If A, B, C and D are four points such that ∠BAC = 45° and ∠BDC = 45°, then A, B, C, D are concyclic.
AB and AC are two equal chords of a circle. Prove that the bisector of the angle BAC passes through the centre of the circle.
