Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 3) (x^2 - 9)/(x^2(x^2 - 6x + 9))`
उत्तर
`lim_(x -> 3) (x^2 - 9)/(x^2(x^2 - 6x + 9)) = lim_(x -> 3) ((x + 3)(x - 3))/(x^2(x - 3)2`
= `lim_(x -> 3) (x +3)/(x^2(x - 3))`
To find he left limit
Put x = 3 – h
Where h > 0
When x → 3
We have h → 0
`lim_(x -> 3^-) (x^2 - 9)/(x^2(x^2 - 6x + 9)) = lim_("h" -> 0) (3 - "h" + 3)/((3 - "h")^2 (3 - "h" - 3))`
= `lim_("h" -> 0) (6 - "h")/(-"h"(3- "h")^2`
= `- lim_("h" -> 0) (6 - "h")/("h"(3 - "h")^2`
= `- (6 - 0)/(0(3 - 0)^2`
= `- 6/0`
`lim_(x -> 3^-) (x^2 - 9)/(x^2(x^2 - 6x + 9)) = - oo`
To find he right limit
Put x = 3 + h
Where h > 0
When x → 3
We have h → 0
`lim_(x -> 3^+) (x^2 - 9)/(x^2(x^2 - 6x + 9)) = lim_("h" -> 0) (3 + "h" + 3)/((3 + "h")^2 (3 + "h" - 3))`
= `lim_("h" -> 0) (6 + "h")/("h"(3 + "h")^2`
= `lim_("h" -> 0) (6 + "h")/("h"(3 + "h")^2`
= `(6 + 0)/(0(3 + 0)^2`
= `6/0`
`lim_(x -> 3^+) (x^2 - 9)/(x^2(x^2 - 6x + 9)) = oo`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Evaluate the following limit:
`lim_(y -> -3) [(y^5 + 243)/(y^3 + 27)]`
Evaluate the following limit:
`lim_(z -> -5)[((1/z + 1/5))/(z + 5)]`
Evaluate the following limit:
`lim_(x -> 2)[(x^(-3) - 2^(-3))/(x - 2)]`
Evaluate the following limit :
`lim_(x -> 7)[((root(3)(x) - root(3)(7))(root(3)(x) + root(3)(7)))/(x - 7)]`
Evaluate the following limit :
`lim_(x -> 1) [(x + x^3 + x^5 + ... + x^(2"n" - 1) - "n")/(x - 1)]`
Evaluate the following :
`lim_(x -> 0)[x/(|x| + x^2)]`
In problems 1 – 6, using the table estimate the value of the limit
`lim_(x -> 0) (sqrt(x + 3) - sqrt(3))/x`
| x | – 0.1 | – 0.01 | – 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.1 |
| f(x) | 0.2911 | 0.2891 | 0.2886 | 0.2886 | 0.2885 | 0.28631 |
In exercise problems 7 – 15, use the graph to find the limits (if it exists). If the limit does not exist, explain why?
`lim_(x -> 3) (4 - x)`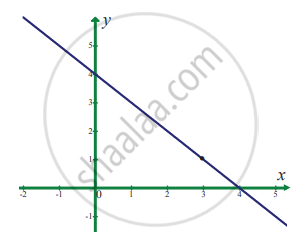
Sketch the graph of f, then identify the values of x0 for which `lim_(x -> x_0)` f(x) exists.
f(x) = `{{:(x^2",", x ≤ 2),(8 - 2x",", 2 < x < 4),(4",", x ≥ 4):}`
Sketch the graph of a function f that satisfies the given value:
f(– 2) = 0
f(2) = 0
`lim_(x -> 2) f(x)` = 0
`lim_(x -> 2) f(x)` does not exist.
If f(2) = 4, can you conclude anything about the limit of f(x) as x approaches 2?
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 2) (1/x - 1/2)/(x - 2)`
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 0) (sqrt(x^2 + 1) - 1)/(sqrt(x^2 + 16) - 4)`
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> oo)(1 + 1/x)^(7x)`
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 0)(1 + x)^(1/(3x))`
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 0) (sqrt(x^2 + "a"^2) - "a")/(sqrt(x^2 + "b"^2) - "b")`
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 0) (2 "arc"sinx)/(3x)`
Choose the correct alternative:
`lim_(x - pi/2) (2x - pi)/cos x`
Choose the correct alternative:
`lim_(alpha - pi/4) (sin alpha - cos alpha)/(alpha - pi/4)` is
Choose the correct alternative:
`lim_(x -> 0) ("e"^tanx - "e"^x)/(tan x - x)` =
