Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
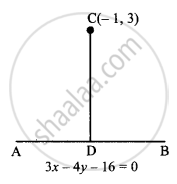
Find the coordinates of the foot of perpendicular from the point (–1, 3) to the line 3x – 4y – 16 = 0.
उत्तर
Let the equation of line AB be, 3x – 4y – 16 = 0 ....…(i)
or y = `3/4"x" - 4`
Slope of line AB = `3/4`
The perpendicular drawn from point C(−1, 3) to AB is CD.
∴ AB ⊥ CD
∴ Slope of CD = `(-1)/(("Slope of line AB")"`
= `(-1)/(3/4)`
= `(-4)/3`
Hence, the equation of line CD,
y – y1 = m(x – x1)
y – 3 = `(-4)/3 ("x" + 1)`
or 3y – 9 = –4x – 4
or 4x + 3y – 5 = 0 ....…(ii)
Multiplying equation (i) by 3 and equation (ii) by 4,
9x – 12y = 48
16x + 12y = 20
on adding these
25x = 68 or x = `68/25`
Putting the value of x in (i),
`3 xx 68/25 - 4"y" = 16`
∴ `4"y" = 204/25 - 16`
= `(204 - 400)/25`
∴ y = `-196/25 xx 1/4 = -49/25`
Hence, the coordinates of perpendicular foot D are `(68/25, -49/25)`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Reduce the following equation into intercept form and find their intercepts on the axes.
3y + 2 = 0
Find equation of the line parallel to the line 3x – 4y + 2 = 0 and passing through the point (–2, 3).
Prove that the line through the point (x1, y1) and parallel to the line Ax + By + C = 0 is A (x –x1) + B (y – y1) = 0.
If p and q are the lengths of perpendiculars from the origin to the lines x cos θ – y sin θ = k cos 2θ and xsec θ+ y cosec θ = k, respectively, prove that p2 + 4q2 = k2.
If p is the length of perpendicular from the origin to the line whose intercepts on the axes are a and b, then show that `1/p^2 = 1/a^2 + 1/b^2`.
Find the equation of a line that has y-intercept −4 and is parallel to the line joining (2, −5) and (1, 2).
Find the equation of the right bisector of the line segment joining the points (3, 4) and (−1, 2).
For what values of a and b the intercepts cut off on the coordinate axes by the line ax + by + 8 = 0 are equal in length but opposite in signs to those cut off by the line 2x − 3y + 6 = 0 on the axes.
Find the equation of the straight line on which the length of the perpendicular from the origin is 2 and the perpendicular makes an angle α with x-axis such that sin α = \[\frac{1}{3}\].
Find the value of θ and p, if the equation x cos θ + y sin θ = p is the normal form of the line \[\sqrt{3}x + y + 2 = 0\].
Find the equation of a straight line on which the perpendicular from the origin makes an angle of 30° with x-axis and which forms a triangle of area \[50/\sqrt{3}\] with the axes.
Reduce the equation\[\sqrt{3}\] x + y + 2 = 0 to intercept form and find intercept on the axes.
Reduce the following equation to the normal form and find p and α in \[x + \sqrt{3}y - 4 = 0\] .
Reduce the following equation to the normal form and find p and α in \[x + y + \sqrt{2} = 0\].
Reduce the following equation to the normal form and find p and α in \[x - y + 2\sqrt{2} = 0\].
Put the equation \[\frac{x}{a} + \frac{y}{b} = 1\] to the slope intercept form and find its slope and y-intercept.
Show that the origin is equidistant from the lines 4x + 3y + 10 = 0; 5x − 12y + 26 = 0 and 7x + 24y = 50.
Reduce the equation 3x − 2y + 6 = 0 to the intercept form and find the x and y intercepts.
Find the point of intersection of the following pairs of lines:
2x − y + 3 = 0 and x + y − 5 = 0
Find the area of the triangle formed by the line x + y − 6 = 0, x − 3y − 2 = 0 and 5x − 3y + 2 = 0.
Prove that the lines \[y = \sqrt{3}x + 1, y = 4 \text { and } y = - \sqrt{3}x + 2\] form an equilateral triangle.
Find the equation of the line joining the point (3, 5) to the point of intersection of the lines 4x + y − 1 = 0 and 7x − 3y − 35 = 0.
Find the orthocentre of the triangle the equations of whose sides are x + y = 1, 2x + 3y = 6 and 4x − y + 4 = 0.
Prove that the following sets of three lines are concurrent:
3x − 5y − 11 = 0, 5x + 3y − 7 = 0 and x + 2y = 0
For what value of λ are the three lines 2x − 5y + 3 = 0, 5x − 9y + λ = 0 and x − 2y + 1 = 0 concurrent?
Show that the straight lines L1 = (b + c) x + ay + 1 = 0, L2 = (c + a) x + by + 1 = 0 and L3 = (a + b) x + cy + 1 = 0 are concurrent.
If the three lines ax + a2y + 1 = 0, bx + b2y + 1 = 0 and cx + c2y + 1 = 0 are concurrent, show that at least two of three constants a, b, c are equal.
Find the equation of a line which is perpendicular to the line \[\sqrt{3}x - y + 5 = 0\] and which cuts off an intercept of 4 units with the negative direction of y-axis.
Find the projection of the point (1, 0) on the line joining the points (−1, 2) and (5, 4).
Write the coordinates of the orthocentre of the triangle formed by the lines xy = 0 and x + y = 1.
The inclination of the line x – y + 3 = 0 with the positive direction of x-axis is ______.
For what values of a and b the intercepts cut off on the coordinate axes by the line ax + by + 8 = 0 are equal in length but opposite in signs to those cut off by the line 2x – 3y + 6 = 0 on the axes.
If the intercept of a line between the coordinate axes is divided by the point (–5, 4) in the ratio 1 : 2, then find the equation of the line.
A line cutting off intercept – 3 from the y-axis and the tangent at angle to the x-axis is `3/5`, its equation is ______.
If the coordinates of the middle point of the portion of a line intercepted between the coordinate axes is (3, 2), then the equation of the line will be ______.
The line which cuts off equal intercept from the axes and pass through the point (1, –2) is ______.
Reduce the following equation into slope-intercept form and find their slopes and the y-intercepts.
x + 7y = 0
Reduce the following equation into normal form. Find their perpendicular distances from the origin and angle between perpendicular and the positive x-axis.
x − y = 4
