Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the projection of the point (1, 0) on the line joining the points (−1, 2) and (5, 4).
उत्तर
Let A (−1, 2) be the given point whose projection is to be evaluated and C (−1, 2) and D (5, 4) be the other two points.
Also, let M (h, k) be the foot of the perpendicular drawn from A (−1, 2) to the line joining the points C (−1, 2) and D (5, 4).
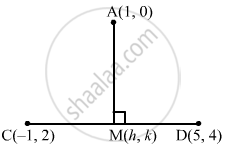
Clearly, the slope of CD and MD are equal.
\[\therefore \frac{4 - k}{5 - h} = \frac{4 - 2}{5 + 1}\]
\[\Rightarrow h - 3k + 7 = 0\] ... (1)
The lines segments AM and CD are perpendicular.
\[\therefore\] \[\frac{k - 0}{h - 1} \times \frac{4 - 2}{5 + 1} = - 1\]
\[\Rightarrow 3h + k - 3 = 0\] ... (2)
Solving (1) and (2) by cross multiplication, we get:
\[\frac{h}{9 - 7} = \frac{k}{21 + 3} = \frac{1}{1 + 9}\]
\[ \Rightarrow h = \frac{1}{5}, k = \frac{12}{5}\]
Hence, the projection of the point (1, 0) on the line joining the points (−1, 2) and (5, 4) is \[\left( \frac{1}{5}, \frac{12}{5} \right)\].
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Reduce the following equation into normal form. Find their perpendicular distances from the origin and angle between perpendicular and the positive x-axis.
`x – sqrt3y + 8 = 0`
Find angles between the lines `sqrt3x + y = 1 and x + sqrt3y = 1`.
Find the equation of the right bisector of the line segment joining the points (3, 4) and (–1, 2).
If p and q are the lengths of perpendiculars from the origin to the lines x cos θ – y sin θ = k cos 2θ and xsec θ+ y cosec θ = k, respectively, prove that p2 + 4q2 = k2.
In the triangle ABC with vertices A (2, 3), B (4, –1) and C (1, 2), find the equation and length of altitude from the vertex A.
If three lines whose equations are y = m1x + c1, y = m2x + c2 and y = m3x + c3 are concurrent, then show that m1(c2 – c3) + m2 (c3 – c1) + m3 (c1 – c2) = 0.
In what ratio, the line joining (–1, 1) and (5, 7) is divided by the line x + y = 4?
Find the equation of a line making an angle of 150° with the x-axis and cutting off an intercept 2 from y-axis.
Find the lines through the point (0, 2) making angles \[\frac{\pi}{3} \text { and } \frac{2\pi}{3}\] with the x-axis. Also, find the lines parallel to them cutting the y-axis at a distance of 2 units below the origin.
Find the equation of a line for p = 4, α = 150°.
Find the equation of a line for p = 8, α = 300°.
Find the equation of the line on which the length of the perpendicular segment from the origin to the line is 4 and the inclination of the perpendicular segment with the positive direction of x-axis is 30°.
Find the equation of the straight line upon which the length of the perpendicular from the origin is 2 and the slope of this perpendicular is \[\frac{5}{12}\].
The length of the perpendicular from the origin to a line is 7 and the line makes an angle of 150° with the positive direction of Y-axis. Find the equation of the line.
Find the value of θ and p, if the equation x cos θ + y sin θ = p is the normal form of the line \[\sqrt{3}x + y + 2 = 0\].
Find the equation of the straight line which makes a triangle of area \[96\sqrt{3}\] with the axes and perpendicular from the origin to it makes an angle of 30° with Y-axis.
Find the equation of a straight line on which the perpendicular from the origin makes an angle of 30° with x-axis and which forms a triangle of area \[50/\sqrt{3}\] with the axes.
Reduce the equation \[\sqrt{3}\] x + y + 2 = 0 to slope-intercept form and find slope and y-intercept;
Reduce the following equation to the normal form and find p and α in y − 2 = 0.
Find the values of θ and p, if the equation x cos θ + y sin θ = p is the normal form of the line \[\sqrt{3}x + y + 2 = 0\].
Reduce the equation 3x − 2y + 6 = 0 to the intercept form and find the x and y intercepts.
Find the point of intersection of the following pairs of lines:
2x − y + 3 = 0 and x + y − 5 = 0
Find the point of intersection of the following pairs of lines:
bx + ay = ab and ax + by = ab.
Find the coordinates of the vertices of a triangle, the equations of whose sides are x + y − 4 = 0, 2x − y + 3 = 0 and x − 3y + 2 = 0.
Find the coordinates of the vertices of a triangle, the equations of whose sides are
y (t1 + t2) = 2x + 2a t1t2, y (t2 + t3) = 2x + 2a t2t3 and, y (t3 + t1) = 2x + 2a t1t3.
Find the area of the triangle formed by the line x + y − 6 = 0, x − 3y − 2 = 0 and 5x − 3y + 2 = 0.
Find the equations of the medians of a triangle, the equations of whose sides are:
3x + 2y + 6 = 0, 2x − 5y + 4 = 0 and x − 3y − 6 = 0
Prove that the lines \[y = \sqrt{3}x + 1, y = 4 \text { and } y = - \sqrt{3}x + 2\] form an equilateral triangle.
Prove that the following sets of three lines are concurrent:
\[\frac{x}{a} + \frac{y}{b} = 1, \frac{x}{b} + \frac{y}{a} = 1\text { and } y = x .\]
If a, b, c are in A.P., prove that the straight lines ax + 2y + 1 = 0, bx + 3y + 1 = 0 and cx + 4y + 1 = 0 are concurrent.
Find the equation of the straight line which has y-intercept equal to \[\frac{4}{3}\] and is perpendicular to 3x − 4y + 11 = 0.
Find the coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular from the point (−1, 3) to the line 3x − 4y − 16 = 0.
Determine whether the point (−3, 2) lies inside or outside the triangle whose sides are given by the equations x + y − 4 = 0, 3x − 7y + 8 = 0, 4x − y − 31 = 0 .
Write the area of the figure formed by the lines a |x| + b |y| + c = 0.
A point equidistant from the line 4x + 3y + 10 = 0, 5x − 12y + 26 = 0 and 7x+ 24y − 50 = 0 is
Find the equation of the straight line which passes through the point (1, – 2) and cuts off equal intercepts from axes.
The line which cuts off equal intercept from the axes and pass through the point (1, –2) is ______.
Reduce the following equation into slope-intercept form and find their slopes and the y-intercepts.
x + 7y = 0
Reduce the following equation into normal form. Find their perpendicular distances from the origin and angle between perpendicular and the positive x-axis.
y − 2 = 0
