Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How many moles of acetic anhydride will be required to form glucose pentaacetate from 2M of glucose?
(a) 2
(b) 5
(c) 10
(d) 2.5
उत्तर
(c) 10
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw the simple Fisher projection formulae of D - (+) - glucose and D - (-) - fructose
Enumerate the reactions of D-glucose which cannot be explained by its open chain structure.
Enlist the properties of glucose that can not be explained on the basis of open chain structure of it
Write the product when D-glucose reacts with conc. HNO3.
Answer the following question.
What is the basic structural difference between glucose and fructose?
Write the reactions involved when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent:
H2N-OH
The following compound can be called as:
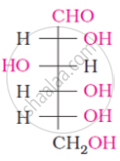
Oxime is formed by treating glucose with ____________.
Which one of the following compounds is different from the rest?
When glucose reacts with bromine water, the main product is ____________.
Glucose is found to exist in two different α and β crystalline forms. These forms can be obtained by:
(i) The α form of glucose is obtained by crystallisation from a concentrated solution of glucose at 303 K.
(ii) The β form of glucose is obtained by crystallisation from a concentrated solution of glucose at 303 K.
(iii) The β form is obtained by crystallisation from hot and saturated aqueous solution at 371 K.
(iv) The α form is obtained by crystallisation from hot and saturated aqueous solution at 371 K.
Reduction of glucose by HI suggest that ____________.
Which of the following reactions of glucose can be explained only by its cyclic structure?
Which is the least stable form of glucose?
The α-D glucose and β-D glucose differ from each other due to difference in carbon atom with respect to its ____________.
Choose the correct relationship for glucose and fructose:
The number of chiral carbons in ß-D(+) glucose is ____________.
Assertion: D (+) – Glucose is dextrorotatory in nature.
Reason: ‘D’ represents its dextrorotatory nature.
Write the reactions of D-glucose which can’t be explained by its open-chain structure. How can cyclic structure of glucose explain these reactions?
What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent?
HI
Account for the following:
What happens when D – glucose is treated with the following reagents
Bromine water
Account for the following:
What happens when D – glucose is treated with the following reagents
HNO3
The number of asymmetric carbon atoms in the glucose molecule in open and cyclic form is ______.
When D-glucose reacts with HI, it forms ______.
