Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If f : R → R is defined by f(x) = 10 x − 7, then write f−1 (x).
उत्तर
\[Let f^{- 1} \left( x \right) = y . . . \left( 1 \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow f\left( y \right) = x\]
\[ \Rightarrow 10y - 7 = x\]
\[ \Rightarrow 10y = x + 7\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \frac{x + 7}{10}\]
\[ \Rightarrow f^{- 1} \left( x \right) = \frac{x + 7}{10} \left( \text{ From}\left( 1 \right) \right)\]
\[\]
\[\]
\[\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: Z → Z given by f(x) = x3
Show that the modulus function f: R → R given by f(x) = |x| is neither one-one nor onto, where |x| is x, if x is positive or 0 and |x| is − x if x is negative.
Find the number of all onto functions from the set {1, 2, 3, …, n} to itself.
Let S = {a, b, c} and T = {1, 2, 3}. Find F−1 of the following functions F from S to T, if it exists.
F = {(a, 2), (b, 1), (c, 1)}
Let f: R → R be the Signum Function defined as
f(x) = `{(1,x>0), (0, x =0),(-1, x< 0):}`
and g: R → R be the Greatest Integer Function given by g(x) = [x], where [x] is greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then does fog and gof coincide in (0, 1]?
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection : f : N → N given by f(x) = x2
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = sinx
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Q − {3} → Q, defined by `f (x) = (2x +3)/(x-3)`
Set of ordered pair of a function ? If so, examine whether the mapping is injective or surjective :{(a, b) : a is a person, b is an ancestor of a}
Let f : R → R and g : R → R be defined by f(x) = x2 and g(x) = x + 1. Show that fog ≠ gof.
Find fog and gof if : f(x) = c, c ∈ R, g(x) = sin `x^2`
Let f be any real function and let g be a function given by g(x) = 2x. Prove that gof = f + f.
` if f : (-π/2 , π/2)` → R and g : [−1, 1]→ R be defined as f(x) = tan x and g(x) = `sqrt(1 - x^2)` respectively, describe fog and gof.
Let
f (x) =`{ (1 + x, 0≤ x ≤ 2) , (3 -x , 2 < x ≤ 3):}`
Find fof.
Consider f : R → R given by f(x) = 4x + 3. Show that f is invertible. Find the inverse of f.
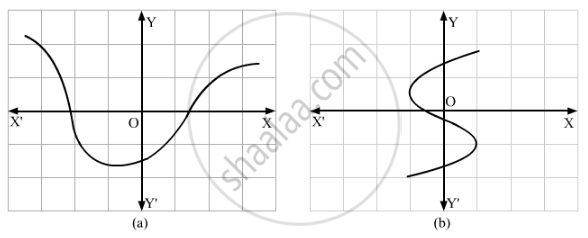
Which one of the following graphs represents a function?
Let A = {x ∈ R : −4 ≤ x ≤ 4 and x ≠ 0} and f : A → R be defined by \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{\left| x \right|}{x}\]Write the range of f.
Let `f : R - {- 3/5}` → R be a function defined as `f (x) = (2x)/(5x +3).`
f-1 : Range of f → `R -{-3/5}`.
Write the domain of the real function f defined by f(x) = `sqrt (25 -x^2)` [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
If a function g = {(1, 1), (2, 3), (3, 5), (4, 7)} is described by g(x) = \[\alpha x + \beta\] then find the values of \[\alpha\] and \[ \beta\] . [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let
f : R → R be given by
\[f\left( x \right) = \left[ x^2 \right] + \left[ x + 1 \right] - 3\]
where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then, f(x) is
(d) one-one and onto
The function \[f : [0, \infty ) \to \text {R given by } f\left( x \right) = \frac{x}{x + 1} is\]
Which of the following functions form Z to itself are bijections?
A function f from the set of natural numbers to the set of integers defined by
\[f\left( n \right)\begin{cases}\frac{n - 1}{2}, & \text{when n is odd} \\ - \frac{n}{2}, & \text{when n is even}\end{cases}\]
Let \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{\alpha x}{x + 1}, x \neq - 1\] Then, for what value of α is \[f \left( f\left( x \right) \right) = x?\]
Let \[f\left(x\right) = x^3\] be a function with domain {0, 1, 2, 3}. Then domain of \[f^{-1}\] is ______.
Let A be a finite set. Then, each injective function from A into itself is not surjective.
Let f: `[2, oo)` → R be the function defined by f(x) = x2 – 4x + 5, then the range of f is ______.
The smallest integer function f(x) = [x] is ____________.
Given a function If as f(x) = 5x + 4, x ∈ R. If g : R → R is inverse of function ‘f then
The domain of the function `cos^-1((2sin^-1(1/(4x^2-1)))/π)` is ______.
Let f: R→R be a continuous function such that f(x) + f(x + 1) = 2, for all x ∈ R. If I1 = `int_0^8f(x)dx` and I2 = `int_(-1)^3f(x)dx`, then the value of I1 + 2I2 is equal to ______.
If log102 = 0.3010.log103 = 0.4771 then the number of ciphers after decimal before a significant figure comes in `(5/3)^-100` is ______.
The solution set of the inequation log1/3(x2 + x + 1) + 1 > 0 is ______.
Number of integral values of x satisfying the inequality `(3/4)^(6x + 10 - x^2) < 27/64` is ______.
Let f(n) = `[1/3 + (3n)/100]n`, where [n] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to n. Then `sum_(n = 1)^56f(n)` is equal to ______.
Let A = {1, 2, 3, ..., 10} and f : A `rightarrow` A be defined as
f(k) = `{{:(k + 1, if k "is odd"),( k, if k "is even"):}`.
Then the number of possible functions g : A `rightarrow` A such that gof = f is ______.
