Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a ∆ABC, AD is the bisector of ∠BAC. If AB = 6 cm, AC = 5 cm and BD = 3 cm, then DC =
विकल्प
11.3 cm
2.5 cm
3 : 5 cm
None of these
उत्तर
Given: In a ΔABC, AD is the bisector of `∠BAC`. AB = 6cm and AC = 5cm and BD = 3cm.
To find: DC
We know that the internal bisector of angle of a triangle divides the opposite side internally in the ratio of the sides containing the angle.
Hence,
`(AB)/(AC)=(BD)/(DC)`
`6/9=3/(DC)`
`DCxx(5xx3)/6`
`DC= 2.5cm`
Hence we got the result `b`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A 13m long ladder reaches a window of a building 12m above the ground. Determine the distance of the foot of the ladder from the building.
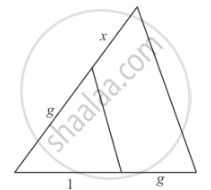
In each of the figures [(i)-(iv)] given below, a line segment is drawn parallel to one side of the triangle and the lengths of certain line-segment are marked. Find the value of x in each of the following :
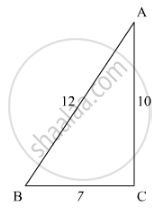
In the given figure, given that ∆ABC ∼ ∆PQR and quad ABCD ∼ quad PQRS. Determine the value of x, y, z in each case.
In each of the following figures, you find who triangles. Indicate whether the triangles are similar. Give reasons in support of your answer.
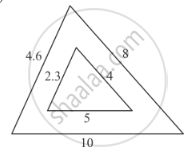
In each of the following figures, you find who triangles. Indicate whether the triangles are similar. Give reasons in support of your answer.

In ∆PQR, M and N are points on sides PQ and PR respectively such that PM = 15 cm and NR = 8 cm. If PQ = 25 cm and PR = 20 cm state whether MN || QR.
In ∆ABC, ∠A = 60°. Prove that BC2 = AB2 + AC2 − AB . AC.
In ∆ABC, ∠ABC = 135°. Prove that AC2 = AB2 + BC2 + 4 ar (∆ABC)
State SAS similarity criterion.
∆ABC ∼ ∆PQR such that ar(∆ABC) = 4 ar(∆PQR). If BC = 12 cm, then QR =
