Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In ΔABC, D is the midpoint of BC and AE⊥BC. If AC>AB, show that `AB^2= AD^2+1/4 BC^2 −BC.DE `
उत्तर
In right-angled triangle AED, applying Pythagoras theorem, we have:
`AB^2=AE^2+ED^2` ...........(1)
In right-angled triangle AED, applying Pythagoras theorem, we have:
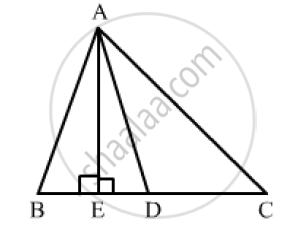
`AD^2=AE^2+ED^2`
`⇒ AE^2=AD^2-ED^2` ...............(2)
Therefore,
`AB^2=AD^2-ED^2+EB^2` (from(1) and (2))
`AB^2=AD^2-ED^2+(BD-DE)^2`
`=AD^2-ED^2+(1/2BC-DE)^2`
`=AD^2-DE^2+1/4BC^2+DE^2-BC.DE`
`=AD^2+1/4BC^2-BC.DE`
This completes the proof.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the given figure, PS is the bisector of ∠QPR of ΔPQR. Prove that `(QS)/(SR) = (PQ)/(PR)`

In ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC
If AD = 6 cm, DB = 9 cm and AE = 8 cm, find AC.
In ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC
If AD = 2.5 cm, BD = 3.0 cm and AE = 3.75 cm, find the length of AC.
D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a ΔABC such that DE║BC.
If `(AD)/(DB) = 4/7` and AC = 6.6cm, find AE.
Draw an isosceles triangle with base 5 cm and height 4 cm. Draw a triangle similar to the triangle drawn whose sides are `2/3` times the sides of the triangle.
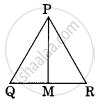
In the given figure ΔABC ~ ΔPQR, PM is median of ΔPQR. If ar ΔABC = 289 cm², BC = 17 cm, MR = 6.5 cm then the area of ΔPQM is ______.
 |
 |
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC and P and Q are points on AD and BC, respectively such that PQ || DC. If PD = 18 cm, BQ = 35 cm and QC = 15 cm, find AD.
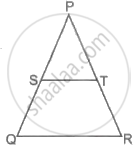
In the given figure, Sand Tare points on sides PQ and PR, respectively of ΔPQR such that ST is parallel to QR and SQ = TR. Prove that ΔPQR is an isosceles triangles.
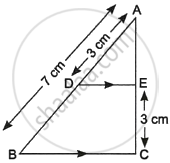
In the given figure, DE || BC. If AD = 3 cm, AB = 7 cm and EC = 3 cm, then the length of AE is ______.
State and prove Basic Proportionality theorem.
