Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
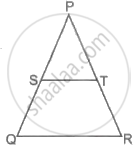
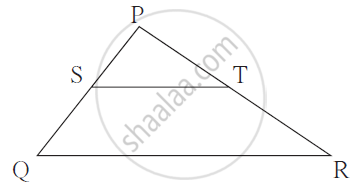
In the given figure, Sand Tare points on sides PQ and PR, respectively of ΔPQR such that ST is parallel to QR and SQ = TR. Prove that ΔPQR is an isosceles triangles.
उत्तर
Given: In ΔPQR, ST || QR and SQ = TR.
To prove: ΔPQR is an isosceles triangle.
Proof: ST || QR.
As a result of the basic proportionality theorem,
`(PS)/(SQ) = (PT)/(TR)` ......(i)
Now, SQ = TR ......(ii)
∴ `(PS)/(TR) = (PT)/(TR)`
⇒ PS = PT ......(iii)
Adding equations (ii) and (iii),
PS + SQ = PT + TR
⇒ PQ = PR
Since, PQ = PR
Thus, ΔPQR is an isosceles triangle.
Hence proved.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the given figure, PS is the bisector of ∠QPR of ΔPQR. Prove that `(QS)/(SR) = (PQ)/(PR)`

In ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC
If `"AD"/"DB"=3/4` and AC = 15 cm, find AE
In ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC
If AD = 8cm, AB = 12 cm and AE = 12 cm, find CE.
In a ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively. For the following case show that DE || BC
AD = 5.7 cm, BD = 9.5 cm, AE = 3.3 cm and EC = 5.5 cm.
In three line segments OA, OB, and OC, points L, M, N respectively are so chosen that LM || AB and MN || BC but neither of L, M, N nor of A, B, C are collinear. Show that LN ||AC.
D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a ΔABC such that DE║BC.
If AD = 3.6cm, AB = 10cm and AE = 4.5cm, find EC and AC.
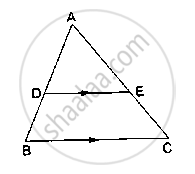
D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a ΔABC such that DE║BC. Find the value of x, when
AD = (7x – 4) cm, AE = (5x – 2) cm, DB = (3x + 4) cm and EC = 3x cm.
A guy wire attached to a vertical pole of height 18 m is 24m long and has a stake attached to the other end. How far from the base of the pole should the stake be driven so that the wire will be taut?
Find the length of a diagonal of a rectangle whose adjacent sides are 30cm and 16cm.
In ΔABC, D is the midpoint of BC and AE⊥BC. If AC>AB, show that `AB^2= AD^2+1/4 BC^2 −BC.DE `
Find the length of each side of a rhombus whose diagonals are 24cm and 10cm long.
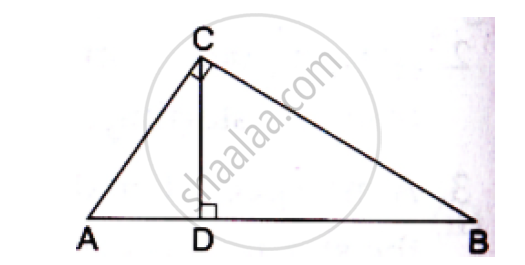
In the given figure, ∠ACB 90° CD ⊥ AB Prove that `(BC^2)/(AC^2)=(BD)/(AD)`
In the given figure, D is the midpoint of side BC and AE⊥BC. If BC = a, AC = b, AB = c, AD = p and AE = h, prove that
(i)`B^2=p^2+ax+a^2/x`
(ii)` c^2=p^2-ax+a^2/x`
(iii) `b^2+c^2=2p^2+a^2/2`
(iv)`b^2-c^2=2ax`

Each of the equal sides of an isosceles triangle is 25 cm. Find the length of its altitude if the base is 14 cm.
In Δ PQR, points S and T
are the midpoints of sides PQ
and PR respectively.
If ST = 6.2 then find the length of QR.
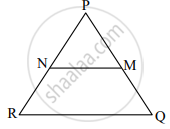
In ΔPQR, NM || RQ. If PM = 15, MQ = 10, NR = 8, then find PN.
A line is parallel to one side of triangle which intersects remaining two sides in two distinct points then that line divides sides in same proportion.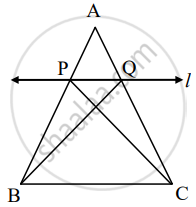
Given: In ΔABC line l || side BC and line l intersect side AB in P and side AC in Q.
To prove: `"AP"/"PB" = "AQ"/"QC"`
Construction: Draw CP and BQ
Proof: ΔAPQ and ΔPQB have equal height.
`("A"(Δ"APQ"))/("A"(Δ"PQB")) = (["______"])/"PB"` .....(i)[areas in proportion of base]
`("A"(Δ"APQ"))/("A"(Δ"PQC")) = (["______"])/"QC"` .......(ii)[areas in proportion of base]
ΔPQC and ΔPQB have [______] is common base.
Seg PQ || Seg BC, hence height of ΔAPQ and ΔPQB.
A(ΔPQC) = A(Δ______) ......(iii)
`("A"(Δ"APQ"))/("A"(Δ"PQB")) = ("A"(Δ "______"))/("A"(Δ "______"))` ......[(i), (ii), and (iii)]
`"AP"/"PB" = "AQ"/"QC"` .......[(i) and (ii)]
In fig., PS = 2, SQ = 6, QR = 5, PT = x and TR = y. Then find the pair of value of x and y such that ST || side QR.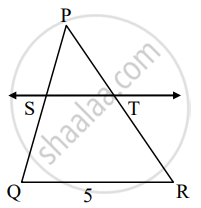
Prove that If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio. In the figure, find EC if `(AD)/(DB) = (AE)/(EC)` using the above theorem.

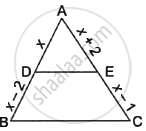
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle in which DE||BC. If AD = x, DB = x – 2, AE = x + 2 and EC = x – 1, then find the value of x.