Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the given figure, D is a point on side BC of ΔABC such that ∠ADC=∠BAC . Prove that AD is the bisector of ∠BAC.
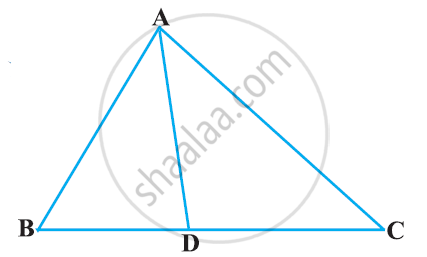
उत्तर
Let us extend BA to P such that AP = AC. Join PC.
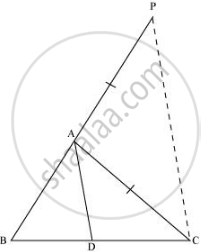
It is given that,
(BD)/(CD) = (AB)/(AC)
=> "BD"/"CD" = "AP"/"AC"
By using the converse of basic proportionality theorem, we obtain
AD || PC
⇒ ∠BAD = ∠APC (Corresponding angles) … (1)
And, ∠DAC = ∠ACP (Alternate interior angles) … (2)
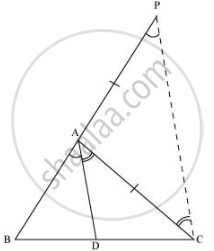
By construction, we have
AP = AC
⇒ ∠APC = ∠ACP … (3)
On comparing equations (1), (2), and (3), we obtain
∠BAD = ∠APC
⇒ AD is the bisector of the angle BAC.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the following figure, DE || AC and DF || AE. Prove that `("BF")/("FE") = ("BE")/("EC")`

In ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC
If AD = 8cm, AB = 12 cm and AE = 12 cm, find CE.
In a ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively. For the following case show that DE || BC
AD = 5.7 cm, BD = 9.5 cm, AE = 3.3 cm and EC = 5.5 cm.
In ΔABC, D is the midpoint of BC and AE⊥BC. If AC>AB, show that `AB^2= AD^2+1/4 BC^2 −BC.DE `
State the basic proportionality theorem.
In the given figure, in ∆ABC, point D on side BC is such that, ∠BAC = ∠ADC. Prove that, CA2 = CB × CD
In fig., line BC || line DE, AB = 2, BD = 3, AC = 4 and CE = x, then find the value of x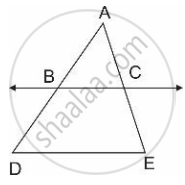
A and B are respectively the points on the sides PQ and PR of a triangle PQR such that PQ = 12.5 cm, PA = 5 cm, BR = 6 cm and PB = 4 cm. Is AB || QR? Give reasons for your answer.
In figure, PA, QB, RC and SD are all perpendiculars to a line l, AB = 6 cm, BC = 9 cm, CD = 12 cm and SP = 36 cm. Find PQ, QR and RS.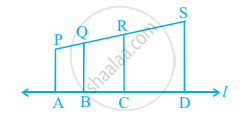
Prove that If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio. In the figure, find EC if `(AD)/(DB) = (AE)/(EC)` using the above theorem.

