Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
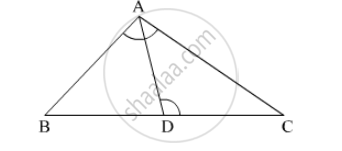
In the given figure, in ∆ABC, point D on side BC is such that, ∠BAC = ∠ADC. Prove that, CA2 = CB × CD
उत्तर
Given: ∠BAC = ∠ADC
To prove: CA2 = CB × CD
Proof: In ∆ABC and ∆DAC
∠BAC = ∠ADC (Given)
∠C = ∠C (Common)
By AA test of similarity
∆ABC ∼ ∆DAC
\[\therefore \frac{BC}{AC} = \frac{AC}{DC} \left( \text{ Corresponding sides are proportional } \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {AC}^2 = BC \times DC\]
Hence proved.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC
If `"AD"/"DB"=3/4` and AC = 15 cm, find AE
In ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC
If AD = 4x − 3, AE = 8x – 7, BD = 3x – 1 and CE = 5x − 3, find the volume of x.
In ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC
If AD = 2.5 cm, BD = 3.0 cm and AE = 3.75 cm, find the length of AC.
In a ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively. For the following case show that DE || BC
AB = 2cm, AD = 8cm, AE = 12 cm and AC = l8cm.
In a ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively. For the following case show that DE || BC
AB = 5.6cm, AD = 1.4cm, AC= 7.2 cm and AE = 1.8 cm.
In a ΔABC, P and Q are points on sides AB and AC respectively, such that PQ || BC. If AP = 2.4 cm, AQ = 2 cm, QC = 3 cm and BC = 6 cm, find AB and PQ.
M and N are points on the sides PQ and PR respectively of a ΔPQR. For the following case, state whether MN || QR
PM = 4cm, QM = 4.5 cm, PN = 4 cm and NR = 4.5 cm
D and E are the points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a ΔABC such that: AD = 8 cm, DB = 12 cm, AE = 6 cm and CE = 9 cm. Prove that BC = 5/2 DE.
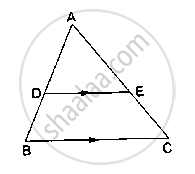
D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a ΔABC such that DE║BC.
If AB = 13.3cm, AC = 11.9cm and EC = 5.1cm, find AD.
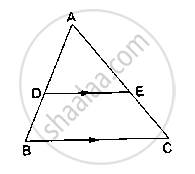
D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a ΔABC such that DE║BC.
If` (AD)/(AB) = 8/15 and EC = 3.5cm`, find AE.
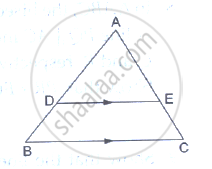
D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a ΔABC such that DE║BC. Find the value of x, when
AD = 4cm, DB = (x – 4) cm, AE = 8cm and EC = (3x – 19) cm.
Show that the line segment which joins the midpoints of the oblique sides of a trapezium is parallel sides
State and converse of Thale’s theorem.
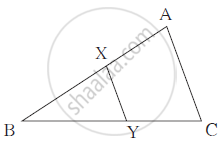
In the adjoining figure,
seg XY || seg AC, If 3AX = 2BX
and XY = 9 then find the length of AC.
Prove that, if a line parallel to a side of a triangle intersects the other sides in two district points, then the line divides those sides in proportion.
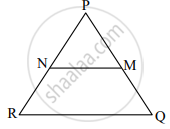
In ΔPQR, NM || RQ. If PM = 15, MQ = 10, NR = 8, then find PN.
In ΔABC, AB = 6 cm and DE || BC such that AE = `1/4` AC then the length of AD is ______.
In the given figure ΔABC ~ ΔPQR, PM is median of ΔPQR. If ar ΔABC = 289 cm², BC = 17 cm, MR = 6.5 cm then the area of ΔPQM is ______.
 |
 |
Prove that If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio. In the figure, find EC if `(AD)/(DB) = (AE)/(EC)` using the above theorem.

