Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
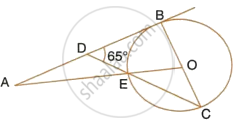
In the adjoining figure, O is the centre of the circle and AB is a tangent to it at point B. ∠BDC = 65°. Find ∠BAO.
उत्तर १
AB is a straight line.
∴ ∠ADE + ∠BDE = 180°
`=>` ∠ADE + 65° = 180°
`=>` ∠ADE = 115° ...(i)
AB i.e. DB is tangent to the circle at point B and BC is the diameter.
∴ ∠DB = 90°
In ΔBDC,
∠DBC + ∠BDC + ∠DCB = 180°
`=>` 90° + 65° + ∠DCB = 180°
`=>` ∠DCB = 25°
Now, OE = OC ...(Radii of the same circle)
∴ ∠DCB or ∠OCE = ∠OEC = 25°
Also,
∠OEC = ∠DEC = 25° ...(Vertically opposite angles)
In ΔADE,
∠ADE + ∠DEA + ∠DAE = 180°
From (i) and (ii)
115° + 25° + ∠DAE = 180°
`=>` ∠DAE or ∠BAO = 180° – 140° = 40°
∴ ∠BAO = 40°
उत्तर २
As AB is a tangent to the circle at B and OB is radius, OB + AB `=>` ∠CBD = 90°.
In ΔBCD,
∠BCD + ∠CBD + ∠BDC = 180°
∠BCD + 90° + 65° = 180°
∠BCD + 155° = 180°
∠BCD = 180° – 155°
∠BCD = 25°
∠BOE = 2∠BCE ...(Angle at centre = double the angle at the remaining part of circle)
∠BOE = 2 × 25°
∠BOE = 50°
∠BOA = 50°
In ΔBOA,
∠BAO + ∠ABO + ∠BOA = 180°
∠BAO + 90° + 50° = 180°
∠BAO + 140° = 180°
∠BAO = 180° – 140°
∠BAO = 40°
संबंधित प्रश्न
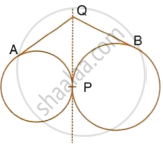
Two circle touch each other externally at point P. Q is a point on the common tangent through P. Prove that the tangents QA and QB are equal.
From the given figure, prove that : AP + BQ + CR = BP + CQ + AR.
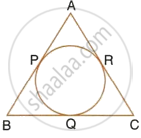
Also show that : AP + BQ + CR = `1/2` × Perimeter of ΔABC.
From a point P outside a circle, with centre O, tangents PA and PB are drawn. Prove that:
∠AOP = ∠BOP
Tangents AP and AQ are drawn to a circle, with centre O, from an exterior point A. Prove that : ∠PAQ = 2∠OPQ
In quadrilateral ABCD; angles D = 90°, BC = 38 cm and DC = 25 cm. A circle is inscribed in this quadrilateral which touches AB at point Q such that QB = 27 cm, Find the radius of the circle.
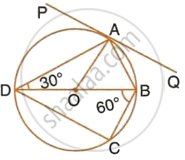
In the following figure, PQ is the tangent to the circle at A, DB is the diameter and O is the centre of the circle. If ∠ADB = 30° and ∠CBD = 60°, calculate:
- ∠QAB,
- ∠PAD,
- ∠CDB.
If PQ is a tangent to the circle at R; calculate:
- ∠PRS,
- ∠ROT.
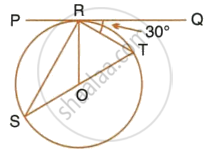
Given O is the centre of the circle and angle TRQ = 30°.
PT is a tangent to the circle at T. If ∠ ABC = 70° and ∠ ACB = 50° ; calculate : ∠ APT
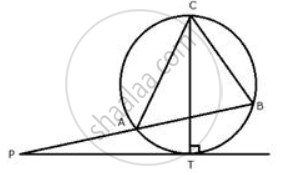
PT is a tangent to the circle at T. If ∠ ABC = 70° and ∠ ACB = 50° ; calculate : ∠ APT
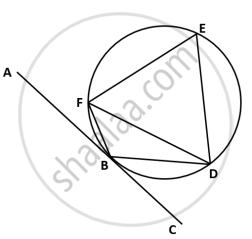
In the given figure, AC is a tangent to circle at point B. ∆EFD is an equilateral triangle and ∠CBD = 40°. Find:
- ∠BFD
- ∠FBD
- ∠ABF
