Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the figure, ∠BCD = ∠ADC and ∠ACB =∠BDA. Prove that AD = BC and ∠A = ∠B.
उत्तर
∠BCD = ∠ADC
∠ACB = ∠BDA
∠BCD + ∠ACB = ∠ADC + ∠BDA
⇒ ∠ACD = ∠BDCACD = BDC
In ΔACD and ΔBCD
∠ACD =∠BDCACD = BDC
∠ADC = ∠BCD
ADC = BCD
CD = CD
Therefore, ΔACD ≅ ΔBCD ...(ASA criteria)
Hence, AD = BC and ∠A = ∠B.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
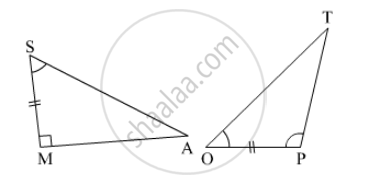
In the pair of triangles in the following figure, parts bearing identical marks are congruent. State the test and the correspondence of vertices by the triangle in pairs is congruent.
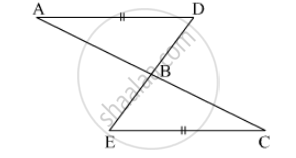
In the adjacent figure, seg AD ≌ seg EC Which additional information is needed to show that ∆ ABD and ∆ EBC will be congruent by A-A-S test?
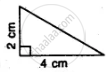
If the following pair of the triangle is congruent? state the condition of congruency :
In ΔABC and ΔDEF, ∠B = ∠E = 90o; AC = DF and BC = EF.
State, whether the pairs of triangles given in the following figures are congruent or not:

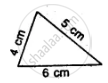
State, whether the pairs of triangles given in the following figures are congruent or not:

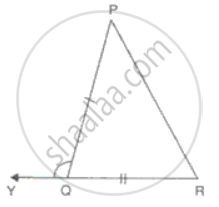
In ΔABC and ΔPQR and, AB = PQ, BC = QR and CB and RQ are extended to X and Y respectively and ∠ABX = ∠PQY. = Prove that ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR.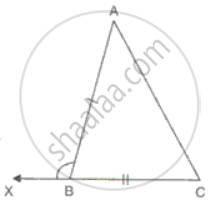
AD and BE are altitudes of an isosceles triangle ABC with AC = BC. Prove that AE = BD.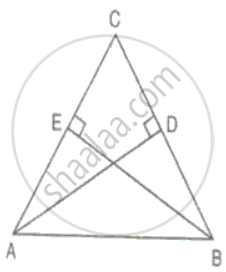
PQRS is a quadrilateral and T and U are points on PS and RS respectively such that PQ = RQ, ∠PQT = ∠RQU and ∠TQS = ∠UQS. Prove that QT = QU.
In triangles ABC and DEF, AB = FD and ∠A = ∠D. The two triangles will be congruent by SAS axiom if ______.
In triangles ABC and PQR, ∠A = ∠Q and ∠B = ∠R. Which side of ∆PQR should be equal to side AB of ∆ABC so that the two triangles are congruent? Give reason for your answer.
