Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the following diagram, lines l, m and n are parallel to each other. Two transversals p and q intersect the parallel lines at points A, B, C and P, Q, R as shown.
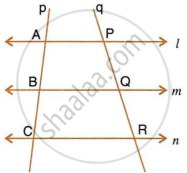
Prove that : `(AB)/(BC) = (PQ)/(QR)`
उत्तर
Join AR.

In ΔACR, BX || CR.
By Basic Proportionality theorem,
`(AB)/(BC) = (AX)/(XR)` ...(1)
In ∆APR, XQ || AP.
By Basic Proportionality theorem,
`(PQ)/(QR) = (AX)/(XR)` ...(2)
From (1) and (2), we get,
`(AB)/(BC) = (PQ)/(QR)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In ∆ ABC, ∠B = 2 ∠C and the bisector of angle B meets CA at point D. Prove that:
(i) ∆ ABC and ∆ ABD are similar,
(ii) DC: AD = BC: AB
In ∆ABC, right – angled at C, CD ⊥ AB.
Prove:
`"CD"^2 = "AD"xx "DB"`
In ∆ABC, ∠B = 90° and BD ⊥ AC.
- If CD = 10 cm and BD = 8 cm; find AD.
- If AC = 18 cm and AD = 6 cm; find BD.
- If AC = 9 cm and AB = 7 cm; find AD.
In the given figure, P is a point on AB such that AP : PB = 4 : 3. PQ is parallel to AC.
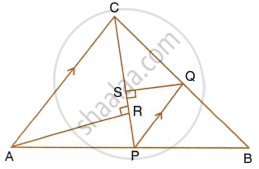
- Calculate the ratio PQ : AC, giving reason for your answer.
- In triangle ARC, ∠ARC = 90° and in triangle PQS, ∠PSQ = 90°. Given QS = 6 cm, calculate the length of AR.
In the given figure, AX : XB = 3 : 5
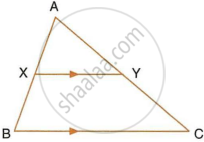
Find:
- the length of BC, if the length of XY is 18 cm.
- the ratio between the areas of trapezium XBCY and triangle ABC.
In the figure, given below, ABCD is a parallelogram. P is a point on BC such that BP : PC = 1 : 2. DP produced meets AB produces at Q. Given the area of triangle CPQ = 20 cm2.

Calculate:
- area of triangle CDP,
- area of parallelogram ABCD.
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle. DE is parallel to BC and `(AD)/(DB)=3/2`
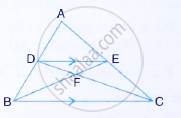
(1) Determine the ratios `(AD)/(AB) and (DE)/(BC)`
(2 ) Prove that ∆DEF is similar to ∆CBF Hence, find `(EF)/(FB)`.
(3) What is the ratio of the areas of ∆DEF and ∆BFC.
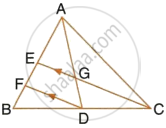
In the following figure, AD and CE are medians of ΔABC. DF is drawn parallel to CE. Prove that :
- EF = FB,
- AG : GD = 2 : 1
A triangle ABC with AB = 3 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 4 cm is enlarged to ΔDEF such that the longest side of ΔDEF = 9 cm. Find the scale factor and hence, the lengths of the other sides of ΔDEF.
In fig. ABCD is a trapezium in which AB | | DC and AB = 2DC. Determine the ratio between the areas of ΔAOB and ΔCOD.