Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the following diagram, lines l, m and n are parallel to each other. Two transversals p and q intersect the parallel lines at points A, B, C and P, Q, R as shown.
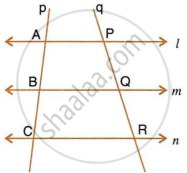
Prove that : `(AB)/(BC) = (PQ)/(QR)`
Solution
Join AR.

In ΔACR, BX || CR.
By Basic Proportionality theorem,
`(AB)/(BC) = (AX)/(XR)` ...(1)
In ∆APR, XQ || AP.
By Basic Proportionality theorem,
`(PQ)/(QR) = (AX)/(XR)` ...(2)
From (1) and (2), we get,
`(AB)/(BC) = (PQ)/(QR)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
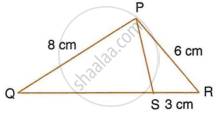
PQR is a triangle. S is a point on the side QR of ΔPQR such that ∠PSR = ∠QPR. Given QP = 8 cm, PR = 6 cm and SR = 3 cm.
- Prove ΔPQR ∼ ΔSPR.
- Find the length of QR and PS.
- `"area of ΔPQR"/"area of ΔSPR"`
In ∆ABC, right – angled at C, CD ⊥ AB.
Prove:
`"CD"^2 = "AD"xx "DB"`
In ∆ABC, ∠B = 90° and BD ⊥ AC.
- If CD = 10 cm and BD = 8 cm; find AD.
- If AC = 18 cm and AD = 6 cm; find BD.
- If AC = 9 cm and AB = 7 cm; find AD.
Triangle ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC = 13 cm and BC = 10 cm. AD is
perpendicular to BC. If CE = 8 cm and EF ⊥ AB, find:
i)`"area of ADC"/"area of FEB"` ii)`"area of ΔAFEB"/"area of ΔABC"`

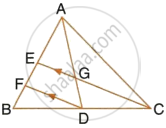
In the following figure, AD and CE are medians of ΔABC. DF is drawn parallel to CE. Prove that :
- EF = FB,
- AG : GD = 2 : 1
The ratio between the areas of two similar triangles is 16 : 25. State the ratio between their :
- perimeters.
- corresponding altitudes.
- corresponding medians.
On a map, drawn to a scale of 1 : 20000, a rectangular plot of land ABCD has AB = 24 cm and BC = 32 cm. Calculate :
- the diagonal distance of the plot in kilometer.
- the area of the plot in sq. km.
In triangle ABC, AP : PB = 2 : 3. PO is parallel to BC and is extended to Q so that CQ is parallel to BA.
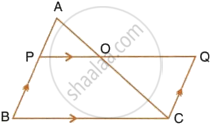
Find:
- area ΔAPO : area ΔABC.
- area ΔAPO : area ΔCQO.
In the give figure, ABC is a triangle with ∠EDB = ∠ACB. Prove that ΔABC ∼ ΔEBD. If BE = 6 cm, EC = 4 cm, BD = 5 cm and area of ΔBED = 9 cm2. Calculate the:
- length of AB
- area of ΔABC

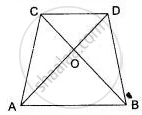
In fig. ABCD is a trapezium in which AB | | DC and AB = 2DC. Determine the ratio between the areas of ΔAOB and ΔCOD.