Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Let \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{1 - x} . \text{Then}, \left\{ f o \left( fof \right) \right\} \left( x \right)\]
विकल्प
\[\text{x for all x} \in R\]
\[\text{x for all x} \in R - \left\{ 1 \right\}\]
\[\text{x for all x} \in R - \left\{ 0, 1 \right\}\]
none of these
उत्तर
\[\text{Domain of f}:\]
\[1 - x \neq 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow x \neq 1\]
\[\text{Domain of f} = R - \left\{ 1 \right\}\]
\[\text{Range of f}: \]
\[y = \frac{1}{1 - x}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 1 - x = \frac{1}{y}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 1 - \frac{1}{y}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \frac{y - 1}{y}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y \neq 0\]
\[\text{Range of f} = R - \left\{ 0 \right\}\]
\[So,f: R - \left\{ 1 \right\} \to R - \left\{ 0 \right\} andf: R - \left\{ 1 \right\} \to R - \left\{ 0 \right\} \]
\[\text{Range of f is not a subset of the domain of f}.\] \[\text{Domain}\left( fof \right)=\left\{ x: x\text{in domain of f and f}\left( x \right) \ \text{in domain of f} \right\}\]
\[\text{Domain}\left( fof \right)=\left\{ x: x \ in R - \left\{ 1 \right\}\text{and}\frac{1}{1 - x} \in R - \left\{ 1 \right\} \right\}\]
\[ \text{Domain}\left( fof \right)=\left\{ x: x \neq 1 \text{and}\frac{1}{1 - x} \neq 1 \right\}\]
\[\text{Domain}\left( fof \right)=\left\{ x: x \neq 1 \text{and}1 - x \neq 1 \right\}\]
\[\text{Domain}\left( fof \right)=\left\{ x: x \neq 1 \text{and}x \neq 0 \right\}\]
\[\text{Domain}\left( fof \right)=R - \left\{ 0, 1 \right\}\]
\[\left( \text{f of} \right)\left( x \right) = f\left( f\left( x \right) \right) = f\left( \frac{1}{1 - x} \right) = \frac{1}{1 - \frac{1}{1 - x}} = \frac{1 - x}{1 - x - 1} = \frac{1 - x}{- x} = \frac{x - 1}{x}\]
\[\text{For range of f of}, x \neq 0\]
\[\text{Now,f of} : R - \left\{ 0, 1 \right\} \to R - \left\{ 0 \right\} \text{and}f: R - \left\{ 1 \right\} \to R - \left\{ 0 \right\}\]
\[\text{Range of f of is not a subset of domain of f}.\]
\[\text{Domain}\left( f o\left( fof \right) \right)=\left\{ x: x \text{in domain of f of and}\left( fof \right)\left( x \right) \text{in domain of f} \right\}\]
\[\text{Domain}\left( f o\left( \text{f of} \right) \right)=\left\{ x: x \in R - \left\{ 0, 1 \right\}\text{and}\frac{x - 1}{x} \in R - \left\{ 1 \right\} \right\}\]
\[ \text{Domain}\left( f o\left( fof \right) \right)=\left\{ x: x \neq 0, 1 \text{ and }\frac{x - 1}{x} \neq 1 \right\}\]
\[\text{Domain}\left( f o\left( fof \right) \right)=\left\{ x: x \neq 0, 1 \text{ and }x-1 \neq x \right\}\]
\[\text{Domain}\left( f o\left( fof \right) \right)=\left\{ x: x \neq 0, 1 \text{ and }x \in R \right\}\]
\[\text{Domain}\left( f o\left( f of \right) \right)=R - \left\{ 0, 1 \right\}\]
\[\left( fo\left( fof \right) \right)\left( x \right) = f\left( \left( fof \right)\left( x \right) \right)\]
\[ = f\left( \frac{x - 1}{x} \right)\]
\[ = \frac{1}{1 - \frac{x - 1}{x}}\]
\[ = \frac{x}{x - x + 1}\]
\[ = x\]
\[\text{So},\left( fo\left( fof \right) \right)\left( x \right) = x, \text{where}x \neq 0, 1\]
So, the answer is (c).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the modulus function f: R → R given by f(x) = |x| is neither one-one nor onto, where |x| is x, if x is positive or 0 and |x| is − x if x is negative.
Give an example of a function which is not one-one but onto ?
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Q → Q, defined by f(x) = x3 + 1
Let A = {1, 2, 3}. Write all one-one from A to itself.
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = 2x + 3 and g(x) = x2 + 5 .
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = x and g(x) = |x| .
Let R+ be the set of all non-negative real numbers. If f : R+ → R+ and g : R+ → R+ are defined as `f(x)=x^2` and `g(x)=+sqrtx` , find fog and gof. Are they equal functions ?
Find fog and gof if : f(x)= x + 1, g (x) = 2x + 3 .
If f(x) = 2x + 5 and g(x) = x2 + 1 be two real functions, then describe each of the following functions:
(1) fog
(2) gof
(3) fof
(4) f2
Also, show that fof ≠ f2
Let f, g, h be real functions given by f(x) = sin x, g (x) = 2x and h (x) = cos x. Prove that fog = go (fh).
State with reason whether the following functions have inverse :
f : {1, 2, 3, 4} → {10} with f = {(1, 10), (2, 10), (3, 10), (4, 10)}
Let f : R `{- 4/3} `- 43 →">→ R be a function defined as f(x) = `(4x)/(3x +4)` . Show that f : R - `{-4/3}`→ Rang (f) is one-one and onto. Hence, find f -1.
Let f : [−1, ∞) → [−1, ∞) be given by f(x) = (x + 1)2 − 1, x ≥ −1. Show that f is invertible. Also, find the set S = {x : f(x) = f−1 (x)}.
Which one of the following graphs represents a function?
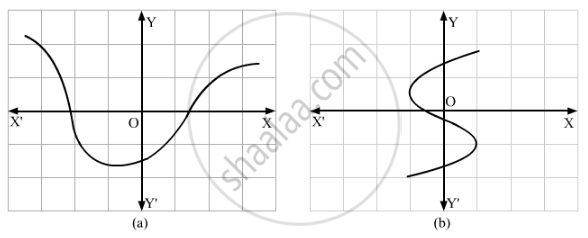
If f : C → C is defined by f(x) = (x − 2)3, write f−1 (−1).
Let \[f : \left( - \frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2} \right) \to R\] be a function defined by f(x) = cos [x]. Write range (f).
Let \[f : \left[ - \frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2} \right] \to\] A be defined by f(x) = sin x. If f is a bijection, write set A.
Write the domain of the real function
`f (x) = sqrt([x] - x) .`
The range of the function
\[f\left( x \right) =^{7 - x} P_{x - 3}\]
If the function\[f : R \to \text{A given by} f\left( x \right) = \frac{x^2}{x^2 + 1}\] is a surjection, then A =
The function
The function \[f : R \to R\] defined by
\[f\left( x \right) = 6^x + 6^{|x|}\] is
If \[f\left( x \right) = \sin^2 x\] and the composite function \[g\left( f\left( x \right) \right) = \left| \sin x \right|\] then g(x) is equal to
Which function is used to check whether a character is alphanumeric or not?
Write about strlen() function.
Let the function f: R → R be defined by f(x) = 4x – 1, ∀ x ∈ R. Then, show that f is one-one.
If A = {a, b, c, d} and f = {a, b), (b, d), (c, a), (d, c)}, show that f is one-one from A onto A. Find f–1
Are the following set of ordered pairs functions? If so, examine whether the mapping is injective or surjective.
{(a, b): a is a person, b is an ancestor of a}
Which of the following functions from Z into Z are bijections?
The number of bijective functions from set A to itself when A contains 106 elements is ____________.
Let X = {-1, 0, 1}, Y = {0, 2} and a function f : X → Y defiend by y = 2x4, is ____________.
Let f : [0, ∞) → [0, 2] be defined by `"f" ("x") = (2"x")/(1 + "x"),` then f is ____________.
The function f: R → R defined as f(x) = x3 is:
If f: R→R is a function defined by f(x) = `[x - 1]cos((2x - 1)/2)π`, where [ ] denotes the greatest integer function, then f is ______.
The solution set of the inequation log1/3(x2 + x + 1) + 1 > 0 is ______.
Let a and b are two positive integers such that b ≠ 1. Let g(a, b) = Number of lattice points inside the quadrilateral formed by lines x = 0, y = 0, x = b and y = a. f(a, b) = `[a/b] + [(2a)/b] + ... + [((b - 1)a)/b]`, then the value of `[(g(101, 37))/(f(101, 37))]` is ______.
(Note P(x, y) is lattice point if x, y ∈ I)
(where [.] denotes greatest integer function)
