Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
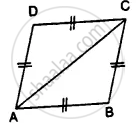
Prove that:
(i) ∆ ABC ≅ ∆ ADC
(ii) ∠B = ∠D
उत्तर
Proof:
(i) In ∆ ABC and ∆ ADC
AC = AC ...........(common)
AB = DC ............(given)
BC = AD ...........(given)
∴ ∆ ABC ≅ ∆ ADC ................(S.S.S. Axiom)
(ii) Hence ∠B = ∠D ...........(c.p.c.t.)
Hence proved.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If ΔDEF ≅ ΔBCA, write the part(s) of ΔBCA that correspond to `bar(EF)`
If ΔDEF ≅ ΔBCA, write the part(s) of ΔBCA that correspond to `bar(DF)`
Prove that the sum of three altitudes of a triangle is less than the sum of its sides.
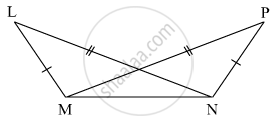
As shown in the following figure, in ΔLMN and ΔPNM, LM = PN, LN = PM. Write the test which assures the congruence of the two triangles. Write their remaining congruent parts.
In ΔTPQ, ∠T = 65°, ∠P = 95° which of the following is a true statement?
A is any point in the angle PQR such that the perpendiculars drawn from A on PQ and QR are equal. Prove that ∠AQP = ∠AQR.
In ΔPQR, LM = MN, QM = MR and ML and MN are perpendiculars on PQ and PR respectively. Prove that PQ = PR.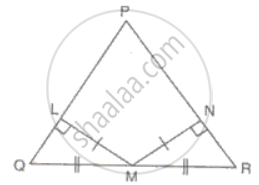
Two right-angled triangles ABC and ADC have the same base AC. If BC = DC, prove that AC bisects ∠BCD.
In triangles ABC and DEF, AB = FD and ∠A = ∠D. The two triangles will be congruent by SAS axiom if ______.
The congruent figures super impose each other completely.
