Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
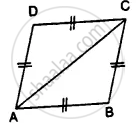
Prove that:
(i) ∆ ABC ≅ ∆ ADC
(ii) ∠B = ∠D
Solution
Proof:
(i) In ∆ ABC and ∆ ADC
AC = AC ...........(common)
AB = DC ............(given)
BC = AD ...........(given)
∴ ∆ ABC ≅ ∆ ADC ................(S.S.S. Axiom)
(ii) Hence ∠B = ∠D ...........(c.p.c.t.)
Hence proved.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
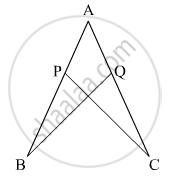
In the given figure, if AB = AC and ∠B = ∠C. Prove that BQ = CP.
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
If ABC ≅ ΔLKM, then side of ΔLKM equal to side AC of ΔABC is
In the following example, a pair of triangles is shown. Equal parts of triangles in each pair are marked with the same sign. Observe the figure and state the test by which the triangle in each pair are congruent.
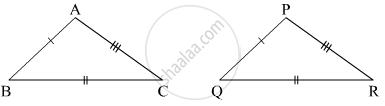
By ______ test
Δ ABC ≅ ΔPQR
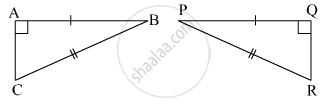
From the information shown in the figure, state the test assuring the congruence of ΔABC and ΔPQR. Write the remaining congruent parts of the triangles.
In the given figure, ∠P ≅ ∠R seg, PQ ≅ seg RQ. Prove that, ΔPQT ≅ ΔRQS.

In the pair of triangles given below, the parts shown by identical marks are congruent. State the test and the one-to-one correspondence of vertices by which the triangles in the pair are congruent, the remaining congruent parts.
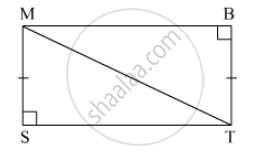
State, whether the pairs of triangles given in the following figures are congruent or not:
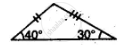
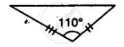
State, whether the pairs of triangles given in the following figures are congruent or not:

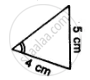
ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AB = BC and AD = CD. Show that BD bisects both the angles ABC and ADC.
Without drawing the triangles write all six pairs of equal measures in the following pairs of congruent triangles.
∆ABC ≅ ∆LMN
