Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the given figure, prove that:
(i) ∆ ACB ≅ ∆ ECD
(ii) AB = ED
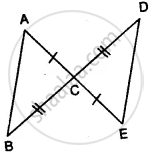
Solution
(i) In Δ ACB and Δ ECD,
AC = CE ................(given)
∠ACB = ∠DCE ............(vertically opposite angles)
BC = CD .............(given)
∴ Δ ACB ≅ Δ ECD ..............(S.A.S. Axiom)
(ii) Hence AB = ED ................(c.p.c.t.)
Hence proved.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If ΔDEF ≅ ΔBCA, write the part(s) of ΔBCA that correspond to `bar(EF)`
In an isosceles triangle, if the vertex angle is twice the sum of the base angles, then the measure of vertex angle of the triangle is
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle in which ∠B = 2∠C. D is a point on side BC such that ADbisects ∠BAC and AB = CD. BE is the bisector of ∠B. The measure of ∠BAC is
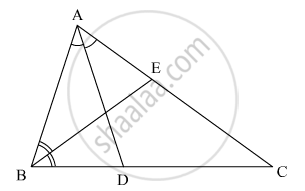
In the given figure, ∠P ≅ ∠R seg, PQ ≅ seg RQ. Prove that, ΔPQT ≅ ΔRQS.

In the pair of triangles in the following figure, parts bearing identical marks are congruent. State the test and the correspondence of vertices by the triangle in pairs is congruent.
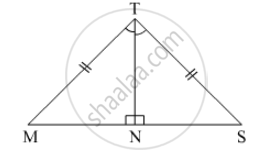
Prove that:
- ∆ ABD ≅ ∆ ACD
- ∠B = ∠C
- ∠ADB = ∠ADC
- ∠ADB = 90°
Which of the following pairs of triangles are congruent? Give reasons
ΔABC;(∠B = 90°,BC = 6cm,AB = 8cm);
ΔPQR;(∠Q = 90°,PQ = 6cm,PR = 10cm).
A is any point in the angle PQR such that the perpendiculars drawn from A on PQ and QR are equal. Prove that ∠AQP = ∠AQR.
In triangles ABC and PQR, ∠A = ∠Q and ∠B = ∠R. Which side of ∆PQR should be equal to side BC of ∆ABC so that the two triangles are congruent? Give reason for your answer.
“If two sides and an angle of one triangle are equal to two sides and an angle of another triangle, then the two triangles must be congruent.” Is the statement true? Why?
