Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
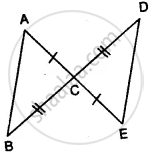
In the given figure, prove that:
(i) ∆ ACB ≅ ∆ ECD
(ii) AB = ED
उत्तर
(i) In Δ ACB and Δ ECD,
AC = CE ................(given)
∠ACB = ∠DCE ............(vertically opposite angles)
BC = CD .............(given)
∴ Δ ACB ≅ Δ ECD ..............(S.A.S. Axiom)
(ii) Hence AB = ED ................(c.p.c.t.)
Hence proved.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a ΔABC, if AB = AC and ∠B = 70°, find ∠A.
In two right triangles one side an acute angle of one are equal to the corresponding side and angle of the othe Prove that the triangles are congruent.
In the following example, a pair of triangles is shown. Equal parts of triangles in each pair are marked with the same sign. Observe the figure and state the test by which the triangle in each pair are congruent.
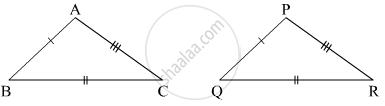
By ______ test
Δ ABC ≅ ΔPQR
In the pair of triangles in the following figure, parts bearing identical marks are congruent. State the test and the correspondence of vertices by the triangle in pairs is congruent.

In the pair of triangles given below, the parts shown by identical marks are congruent. State the test and the one-to-one correspondence of vertices by which the triangles in the pair are congruent, the remaining congruent parts.

Which of the following pairs of triangles are congruent? Give reasons
ΔABC;(∠B = 70°,BC = 6cm,∠C = 50°);
ΔXYZ;(∠Z = 60°,XY = 6cm,∠X = 70°).
Two right-angled triangles ABC and ADC have the same base AC. If BC = DC, prove that AC bisects ∠BCD.
If AB = QR, BC = PR and CA = PQ, then ______.
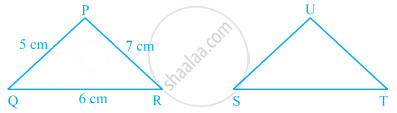
If ∆PQR is congruent to ∆STU (see figure), then what is the length of TU?
Two figures are congruent, if they have the same shape.
