Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In triangles ABC and PQR, ∠A = ∠Q and ∠B = ∠R. Which side of ∆PQR should be equal to side BC of ∆ABC so that the two triangles are congruent? Give reason for your answer.
Solution
Given: In triangle ABC and PQR,
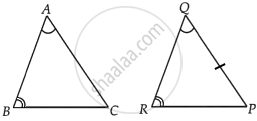
∠A = ∠Q and ∠B = ∠R ...[Given]
BC = RP ...[For the triangle to be congruent]
Hence, it will be congruent by AAS congruent rule.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the measure of each angle of an equilateral triangle.
Prove that the sum of three altitudes of a triangle is less than the sum of its sides.
In the following example, a pair of triangles is shown. Equal parts of triangle in each pair are marked with the same sign. Observe the figure and state the test by which the triangle in each pair are congruent.
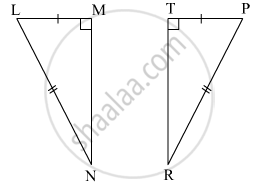
By ______ test
ΔLMN ≅ ΔPTR
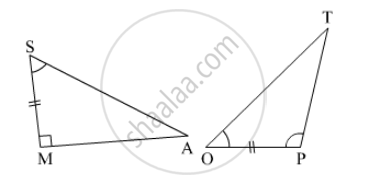
In the pair of triangles in the following figure, parts bearing identical marks are congruent. State the test and the correspondence of vertices by the triangle in pairs is congruent.

In the pair of triangles in the following figure, parts bearing identical marks are congruent. State the test and the correspondence of vertices by the triangle in pairs is congruent.
The following figure shown a triangle ABC in which AB = AC. M is a point on AB and N is a point on AC such that BM = CN.
Prove that:
State, whether the pairs of triangles given in the following figures are congruent or not:
Δ ABC in which AB = 2 cm, BC = 3.5 cm and ∠C = 80° and Δ DEF in which DE = 2 cm, DF = 3.5 cm and ∠D = 80°.
In a circle with center O. If OM is perpendicular to PQ, prove that PM = QM.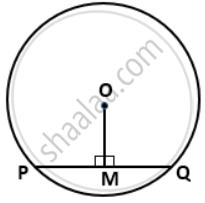
In ΔABC, X and Y are two points on AB and AC such that AX = AY. If AB = AC, prove that CX = BY.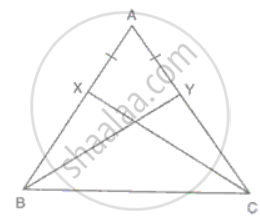
Without drawing the triangles write all six pairs of equal measures in the following pairs of congruent triangles.
∆STU ≅ ∆DEF
