Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A triode value operates at Vp = 225 V and Vg = −0.5 V.
The plate current remains unchanged if the plate voltage is increased to 250 V and the grid voltage is decreased to −2.5 V. Calculate the amplification factor.
उत्तर
Amplification factor for a triode valve,
\[\mu = \frac{\text{Change in Plate Voltage}}{\text{Change in Grid Voltage}}\]
At constant plate current,
\[\mu = \left(\frac{\delta V_P}{\delta V_G}\right)_{i_P = constant} \]
\[\mu = \frac{250 - 225}{2 . 5 - 0 . 5}\]
\[\mu = \frac{25}{2} = 12 . 5\]
This implies that the amplification factor of the triode is 12.5
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
With the help of neat labelled circuit diagram explain the working of half wave rectifier using semiconductor diode. Draw the input and output waveforms.
Explain the working of P-N junction diode in forward and reverse biased mode.
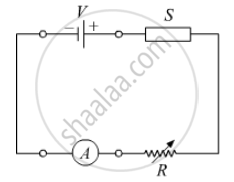
In the following diagram 'S' is a semiconductor. Would you increase or decrease the value of R to keep the reading of the ammeter A constant when S is heated? Give reason for your answer.
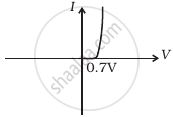
Draw its I – V characteristics of photodiode
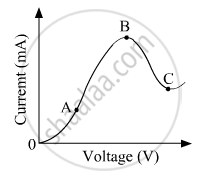
The graph shown in the figure represents a plot of current versus voltage for a given semiconductor. Identify the region, if any, over which the semiconductor has a negative resistance.
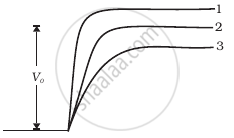
With reference to semi-conductors answer the following :
(i) What is the change in the resistance of the semi-conductor with increase in temperature ?
(ii) Name the majority charge carriers in n-type semi-conductor.
(iii) What is meant by doping ?
Of the diodes shown in the following diagrams, which one is reverse biased?
A – pn junction has a depletion layer of thickness .of the order of
The expected energy of the electron at absolute zero is called:-
In Figure, Vo is the potential barrier across a p-n junction, when no battery is connected across the junction ______.
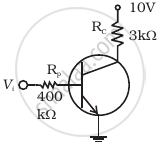
In the circuit shown in figure, when the input voltage of the base resistance is 10 V, Vbe is zero and Vce is also zero. Find the values of Ib, Ic and β.
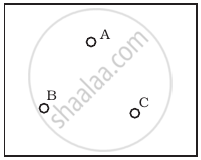
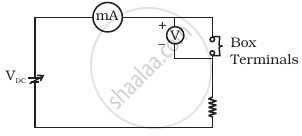
Consider a box with three terminals on top of it as shown in figure (a):
 (a) |
Three components namely, two germanium diodes and one resistor are connected across these three terminals in some arrangement. A student performs an experiment in which any two of these three terminals are connected in the circuit shown in figure (b).
 (b) |
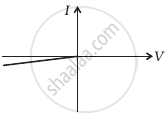
The student obtains graphs of current-voltage characteristics for unknown combination of components between the two terminals connected in the circuit. The graphs are
(i) when A is positive and B is negative
 (c) |
(ii) when A is negative and B is positive
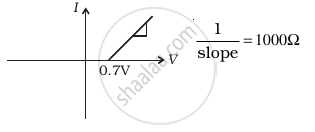 (d) |
(iii) When B is negative and C is positive
|
(e) |
(iv) When B is positive and C is negative
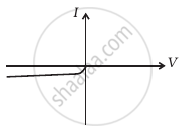 (f) |
(v) When A is positive and C is negative
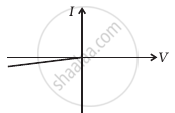 (g) |
(vi) When A is negative and C is positive
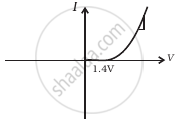 (h) |
From these graphs of current-voltage characteristics shown in figure (c) to (h), determine the arrangement of components between A, B and C.
Differentiate between the threshold voltage and the breakdown voltage for a diode.
Write the property of a junction diode which makes it suitable for rectification of ac voltages.
Explain the formation of the barrier potential in a p-n junction.
Answer the following giving reasons:
A p-n junction diode is damaged by a strong current.
Describe briefly the following term:
breakdown voltage in reverse biasing
With reference to a semiconductor diode, define the depletion region.
What is meant by forward biasing of a semiconductor diode?