Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
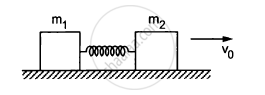
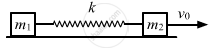
Two blocks of masses m1 and m2 are connected by a spring of spring constant k (See figure). The block of mass m2 is given a sharp impulse so that it acquires a velocity v0 towards right. Find (a) the velocity of the centre of mass, (b) the maximum elongation that the spring will suffer.
उत्तर
Given,
Velocity of mass, m2 = v0
Velocity of mass, m1 = 0
(a) Velocity of centre of mass is given by,
\[v_{cm} = \frac{m_1 v_1 + m_2 v_2}{m_1 + m_2}\]
\[\Rightarrow v_{cm} = \frac{m_1 \times 0 + m_2 \times v_0}{m_1 + m_2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow v_{cm} = \frac{m_2 v_0}{m_1 + m_2}\]
(b) Let the maximum elongation in spring be x.
The spring attains maximum elongation when velocities of both the blocks become equal to the velocity of centre of mass.
i.e. v1 = v2 = vcm
On applying the law of conservation of energy, we can write:
Change in kinetic energy = Potential energy stored in spring
\[\Rightarrow \frac{1}{2} m_2 v_0^2 - \frac{1}{2}( m_1 + m_2 ) \left( \frac{m_2 v_0}{m_1 + m_2} \right)^2 = \frac{1}{2}k x^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow m_2 v_0^2 \left( 1 - \frac{m_2}{m_1 + m_2} \right) = k x^2\]
`Rightarrow = V_o[(m_1m_2)/((m_1+m_2)K)]^(1/2)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the linear momentum of a particle is known, can you find its kinetic energy? If the kinetic energy of a particle is know can you find its linear momentum?
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Take "the table plus the ball" as the system. friction between the table and the ball is then an internal force. As the ball slows down, the momentum of the system decreases. Which external force is responsible for this change in the momentum?
When a nucleus at rest emits a beta particle, it is found that the velocities of the recoiling nucleus and the beta particle are not along the same straight line. How can this be possible in view of the principle of conservation of momentum?
In one-dimensional elastic collision of equal masses, the velocities are interchanged. Can velocities in a one-dimensional collision be interchanged if the masses are not equal?
Consider the following two statements:
(A) The linear momentum of a particle is independent of the frame of reference.
(B) The kinetic energy of a particle is independent of the frame of reference.
The quantities remaining constant in a collisions are
A block moving in air breaks in two parts and the parts separate
(a) the total momentum must be conserved
(b) the total kinetic energy must be conserved
(c) the total momentum must change
(d) the total kinetic energy must change
A uranium-238 nucleus, initially at rest, emits an alpha particle with a speed of 1.4 × 107m/s. Calculate the recoil speed of the residual nucleus thorium-234. Assume that the mass of a nucleus is proportional to the mass number.
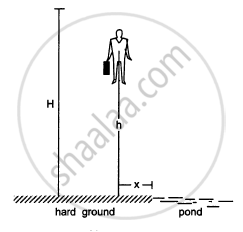
A man of mass M having a bag of mass m slips from the roof of a tall building of height H and starts falling vertically in the following figure. When at a height h from the ground, the notices that the ground below him is pretty hard, but there is a pond at a horizontal distance x from the line of fall. In order to save himself he throws the bag horizontally (with respect to himself) in the direction opposite to the pond. Calculate the minimum horizontal velocity imparted to the bag so that the man lands in the water. If the man just succeeds to avoid the hard ground, where will the bag land?
A ball of mass 50 g moving at a speed of 2.0 m/s strikes a plane surface at an angle of incidence 45°. The ball is reflected by the plane at equal angle of reflection with the same speed. Calculate (a) the magnitude of the change in momentum of the ball (b) the change in the magnitude of the momentum of the ball.
A gun is mounted on a railroad car. The mass of the car, the gun, the shells and the operator is 50 m where m is the mass of one shell. If the velocity of the shell with respect to the gun (in its state before firing) is 200 m/s, what is the recoil speed of the car after the second shot? Neglect friction.
Consider a head-on collision between two particles of masses m1 and m2. The initial speeds of the particles are u1 and u2 in the same direction. the collision starts at t = 0 and the particles interact for a time interval ∆t. During the collision, the speed of the first particle varies as \[v(t) = u_1 + \frac{t}{∆ t}( v_1 - u_1 )\]
Find the speed of the second particle as a function of time during the collision.
A ball of mass m moving at a speed v makes a head-on collision with an identical ball at rest. The kinetic energy of the balls after the collision is three fourths of the original. Find the coefficient of restitution.
A bullet of mass 25 g is fired horizontally into a ballistic pendulum of mass 5.0 kg and gets embedded in it. If the centre of the pendulum rises by a distance of 10 cm, find the speed of the bullet.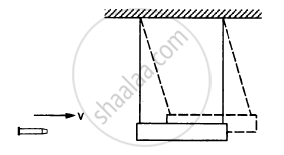
A small block of superdense material has a mass of 3 × 1024kg. It is situated at a height h (much smaller than the earth's radius) from where it falls on the earth's surface. Find its speed when its height from the earth's surface has reduce to to h/2. The mass of the earth is 6 × 1024kg.
The following figure shows a rough track, a portion of which is in the form of a cylinder of radius R. With what minimum linear speed should a sphere of radius r be set rolling on the horizontal part so that it completely goes round the circle on the cylindrical part.

The following figure shows a small spherical ball of mass m rolling down the loop track. The ball is released on the linear portion at a vertical height H from the lowest point. The circular part shown has a radius R.
(a) Find the kinetic energy of the ball when it is at a point A where the radius makes an angle θ with the horizontal.
(b) Find the radial and the tangential accelerations of the centre when the ball is at A.
(c) Find the normal force and the frictional force acting on the if ball if H = 60 cm, R = 10 cm, θ = 0 and m = 70 g.

The track shown is figure is frictionless. The block B of mass 2m is lying at rest and the block A or mass m is pushed along the track with some speed. The collision between Aand B is perfectly elastic. With what velocity should the block A be started to get the sleeping man awakened?

