Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction, it ______.
विकल्प
raises the potential barrier.
reduces the majority carrier current to zero.
lowers the potential barrier.
None of the above.
उत्तर
When a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction, it lowers the potential barrier.
Explanation:
When a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction, it lowers the value of potential barrier. In the case of a forward bias, the potential barrier opposes the applied voltage. Hence, the potential barrier across the junction gets reduced.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(i) Explain with the help of a diagram the formation of depletion region and barrier potential in a pn junction.
What happens when a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction?
In the following diagram, is the junction diode forward biased or reverse biased ?
With reference to semiconductor devices, define a p-type semiconductor and a Zener diode.
Draw a labelled diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show how output voltage varies with time if the input voltage is a sinusoidal voltage.
Show on a graph, the variation of resistivity with temperature for a typical semiconductor.
The power delivered in the plate circular of a diode is 1.0 W when the plate voltage is 36 V. Find the power delivered if the plate voltage is increased to 49 V. Assume Langmuir-Child equation to hold.
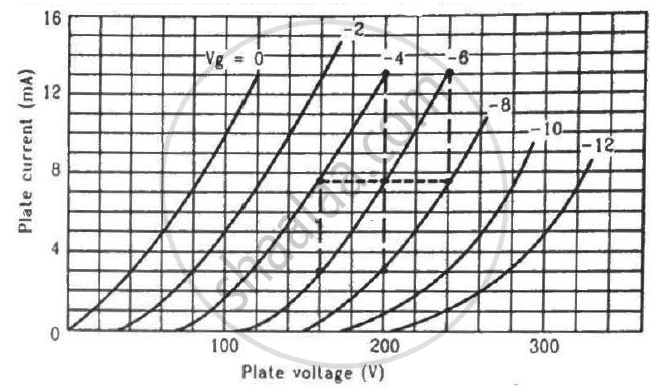
Find the values of rp, µ and gm of a triode operating at plate voltage 200 V and grid voltage −6. The plate characteristics are shown in the figure.
Answer the following question.
Why photodiodes are required to operate in reverse bias? Explain.
A – pn junction has a depletion layer of thickness .of the order of
In the circuit shown in figure, if the diode forward voltage drop is 0.3 V, the voltage difference between A and B is ______.

When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor ______.
- electrons move from lower energy level to higher energy level in the conduction band.
- electrons move from higher energy level to lower energy level in the conduction band.
- holes in the valence band move from higher energy level to lower energy level.
- holes in the valence band move from lower energy level to higher energy level.
In the depletion region of a diode ______.
- there are no mobile charges.
- equal number of holes and electrons exist, making the region neutral.
- recombination of holes and electrons has taken place.
- immobile charged ions exist.
The breakdown in a reverse biased p–n junction diode is more likely to occur due to ______.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is small.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is large.
- strong electric field in a depletion region if the doping concentration is small.
- strong electric field in the depletion region if the doping concentration is large.
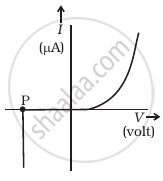 (a) |
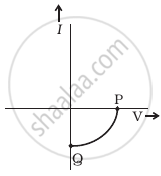 (b) |
- Name the type of a diode whose characteristics are shown in figure (A) and figure (B).
- What does the point P in figure (A) represent?
- What does the points P and Q in figure (B) represent?
A semiconductor device is connected in series with a battery, an ammeter and a resistor. A current flows in the circuit. If. the polarity of the battery is reversed, the current in the circuit almost becomes zero. The device is a/an ______.
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying V-I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in (i) forward biasing and (ii) reverse biasing. Draw the typical V-I characteristics of a silicon diode.
With reference to a semiconductor diode, define the depletion region.
An ideal PN junction diode offers ______.
