Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A first-order reaction is 50% completed in 40 minutes at 300 K and in 20 minutes at 320 K. Calculate the activation energy of the reaction. (Given : log 2 = 0·3010, log 4 = 0·6021, R = 8·314 JK–1 mol–1)
उत्तर
Given
t1/2 = 40 min at temperature (T1) = 300 K
t1/2 = 20 min at temperature (T2) = 320 K
t1/2 = 40 min, t1/2 = 20 min
`k_1 = 0.693/40`
`k_2 = 0.693/20`
According to Arrhenius equation
`log (k_2/k_1) = "E"_"a"/(2.303 " R") [1/"T"_1 - 1/"T"_2]`
`= "E"_"a"/(2.303 " R") [("T"_2 - "T"_1)/("T"_1"T"_2)]`
`log ((0.0693/20)/(0.0693/40)) = "E"_"a"/(2.303 xx 8.314) [(320 - 300)/(300 xx 320)]`
`therefore 0.3010 = "E"_"a"/19.147 [0.0002083]`
Ea = 27664 J/mol
Ea = 27.7 kJ/mol
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(b) Rate constant ‘k’ of a reaction varies with temperature ‘T’ according to the equation:
`logk=logA-E_a/2.303R(1/T)`
Where Ea is the activation energy. When a graph is plotted for `logk Vs. 1/T` a straight line with a slope of −4250 K is obtained. Calculate ‘Ea’ for the reaction.(R = 8.314 JK−1 mol−1)
What will be the effect of temperature on rate constant?
The activation energy for the reaction \[\ce{2 HI_{(g)} -> H2_{(g)} + I2_{(g)}}\] is 209.5 kJ mol−1 at 581K. Calculate the fraction of molecules of reactants having energy equal to or greater than activation energy?
The rate constant for the decomposition of N2O5 at various temperatures is given below:
| T/°C | 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 |
| 105 × k/s−1 | 0.0787 | 1.70 | 25.7 | 178 | 2140 |
Draw a graph between ln k and `1/"T"` and calculate the values of A and Ea. Predict the rate constant at 30º and 50ºC.
In the Arrhenius equation for a first order reaction, the values of ‘A’ of ‘Ea’ are 4 x 1013 sec-1 and 98.6 kJ mol-1 respectively. At what temperature will its half life period be 10 minutes?
[R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1]
Define activation energy.
Write a condition under which a bimolecular reaction is kinetically first order. Give an example of such a reaction. (Given : log2 = 0.3010,log 3 = 0.4771, log5 = 0.6990).
Predict the main product of the following reactions: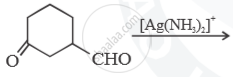
The rate of chemical reaction becomes double for every 10° rise in temperature because of ____________.
Why does the rate of a reaction increase with rise in temperature?
Oxygen is available in plenty in air yet fuels do not burn by themselves at room temperature. Explain.
What happens to most probable kinetic energy and the energy of activation with increase in temperature?
The rate constant for a reaction is 1.5 × 10–7 sec–1 at 50°C. What is the value of activation energy?
The activation energy in a chemical reaction is defined as ______.
Explain how and why will the rate of reaction for a given reaction be affected when the temperature at which the reaction was taking place is decreased.
The activation energy of one of the reactions in a biochemical process is 532611 J mol–1. When the temperature falls from 310 K to 300 K, the change in rate constant observed is k300 = x × 10–3 k310. The value of x is ______.
[Given: ln 10 = 2.3, R = 8.3 J K–1 mol–1]
A first-order reaction is 50% complete in 30 minutes at 300 K and in 10 minutes at 320 K. Calculate activation energy (Ea) for the reaction. [R = 8.314 J K−1 mol−1]
[Given: log 2 = 0.3010, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021]
It is generally observed that the rate of a chemical reaction becomes double with every 10oC rise in temperature. If the generalisation holds true for a reaction in the temperature range of 298K to 308K, what would be the value of activation energy (Ea) for the reaction?
