Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A p-n photodiode is fabricated from a semiconductor with band gap of 2.8 eV. Can it detect a wavelength of 6000 nm?
उत्तर
Energy band gap of the given photodiode, Eg = 2.8 eV
Wavelength, λ = 6000 nm = 6000 × 10−9 m
The energy of a signal is given by the relation:
`"E" = ("hc")/lambda`
Where
h = Planck’s constant
= 6.626 × 10−34 Js
c = Speed of light
= 3 × 108 m/s
`"E" = (6.626 xx 10^(-34) xx 3 xx 10^8)/(6000 xx 10^(-9))`
= 3.313 × 10−20 J
But 1.6 × 10−19 J = 1 eV
∴ E = 3.313 × 10−20 J
`= (3.313 xx 10^(-20))/(1.6 xx 10^(-19)) = 0.207 " eV"`
The energy of a signal of wavelength 6000 nm is 0.207 eV, which is less than 2.8 eV − the energy band gap of a photodiode. Hence, the photodiode cannot detect the signal.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Meeta's father was driving her to school. At the traffic signal, she noticed that each traffic light was made of many tiny lights instead of a single bulb. When Meeta asked this question to her father, he explained the reason for this.
Answer the following questions based on above information:
(i) What were the values displayed by Meeta and her father?
(ii) What answer did Meeta's father give?
(iii) What are the tiny lights in traffic signals called and how do these operate?
If a small voltage is applied to a p-n junction diode, how will the barrier potential be affected when it is (i) forward biased
If a small voltage is applied to a p-n junction diode, how will the barrier potential be affected when it is(ii) reveres biased?
With what considerations in view, a photodiode is fabricated? State its working with the help of a suitable diagram.
Even though the current in the forward bias is known to be more than in the reverse bias, yet the photodiode works in reverse bias. What is the reason?
Carbon, silicon and germanium have four valence electrons each. These are characterised by valence and conduction bands separated by energy band gap respectively equal to (Eg)C, (Eg)Si and (Eg)Ge. Which of the following statements is true?
State its any ‘two’ uses of photodiode.
Briefly explain its working. Draw its V - I characteristics for two different intensities of illumination ?
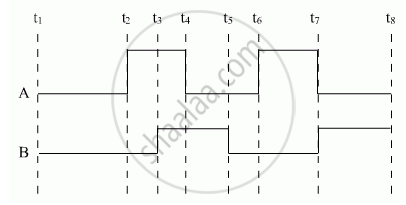
Show the output waveforms (Y) for the following inputs A and B of (i) OR gate (ii) NAND gate ?
How does a light emitting diode (LED) work? Give two advantages of LED’s over the conventional incandescent lamps.
What happens to the width of depletion player of a p-n junction when it is (i) forward biased, (ii) reverse biased?
Draw the circuit diagram of an illuminated photodiode in reverse bias. How is photodiode used to measure light intensity?
An ideal diode should pass a current freely in one direction and should stop it completely in the opposite direction. Which is closer to ideal-vacuum diode or a p-njunction diode?
Write the important considerations which are to be taken into account while fabricating a p-n junction diode to be used as a Light Emitting Diode (LED). What should be the order of band gap of an LED, if it is required to emit light in the visible range? Draw a circuit diagram and explain its action.
Write the important considerations which are to be taken into account while fabricating a p-n junction diode to be used as a Light Emitting Diode (LED). What should be the order of the band gap of an LED, if it is required to emit light in the visible range? Draw a circuit diagram and explain its action.
What is a solar cell?
The amplifiers X, Y and Z are connected in series. If the voltage gains of X, Y and Z are 10, 20 and 30, respectively and the input signal is 1 mV peak value, then what is the output signal voltage (peak value)
- if dc supply voltage is 10V?
- if dc supply voltage is 5V?
How can a photodiode be used to measure light intensity?
What energy conversion takes place in a solar cell?
