Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A person observes the angle of elevation of the peak of a hill from a station to be α. He walks c metres along a slope inclined at an angle β and finds the angle of elevation of the peak of the hill to be ϒ. Show that the height of the peak above the ground is \[\frac{c \sin \alpha \sin \left( \gamma - \beta \right)}{\left( \sin \gamma - \alpha \right)}\]
उत्तर
Suppose, AB is a peak whose height above the ground is t+x.
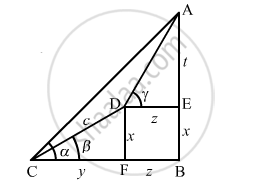
\[In \bigtriangleup DFC, \]
\[\sin\beta = \frac{x}{c} \]
\[ \Rightarrow x = c\sin\beta\]
\[and \]
\[\tan\beta = \frac{x}{y}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \frac{x}{\tan\beta} = \frac{c\sin\beta}{\sin\beta} \times \cos\beta = c\cos\beta . . . \left( 1 \right)\]
\[In ∆ ADE, \]
\[\tan\gamma = \frac{t}{z}\]
\[ \Rightarrow z = t \cot\gamma . . . \left( 2 \right)\]
\[\]
\[In ∆ ABC, \]
\[\tan\alpha = \frac{t + x}{y + z}\]
\[\]
\[ \Rightarrow t + x = \left( c\cos\beta\tan\alpha + tcot\gamma \right)\tan\alpha \left( from \left( 1 \right) and \left( 2 \right) \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow t - tcot\gamma\tan\alpha = c\cos\beta\tan\alpha - c\sin\beta \left( \because x = c\sin\beta \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow t\left( 1 - \frac{\sin\alpha\cos\gamma}{\cos\alpha\sin\gamma} \right) = c\left( \frac{\cos\beta\sin\alpha - \cos\alpha\sin\beta}{\cos\alpha} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow t\left( \frac{\sin\gamma\cos\alpha - \sin\alpha\cos\gamma}{\cos\alpha\sin\gamma} \right) = c\frac{\sin\left( \alpha - \beta \right)}{\cos\alpha}\]
\[ \Rightarrow t\frac{\sin\left( \gamma - \beta \right)}{\cos\alpha\sin\gamma} = c\frac{\sin\left( \alpha - \beta \right)}{\cos\alpha}\]
\[ \Rightarrow t = c\frac{\sin\gamma\sin\left( \alpha - \beta \right)}{\sin\left( \gamma - \beta \right)} . . . \left( 3 \right)\]
\[\text{ Now }, \]
\[AB = t + x = c\frac{\sin\gamma\sin\left( \alpha - \beta \right)}{\sin\left( \gamma - \beta \right)} + c\sin\beta \left( \text{ using }\left( 3 \right) \right)\]
\[ = c\left( \frac{\sin\gamma\sin\left( \alpha - \beta \right)}{\sin\left( \gamma - \beta \right)} + \sin\beta \right)\]
\[ = c\left[ \frac{\sin\gamma\sin\left( \alpha - \beta \right) + \sin\beta\sin\left( \gamma - \beta \right)}{\sin\left( \gamma - \beta \right)} \right]\]
\[ = c\left[ \frac{\sin\gamma\sin\alpha\cos\beta - \sin\beta\sin\gamma\cos\alpha + \sin\beta\sin\gamma\cos\alpha - \sin\beta\cos\gamma\sin\alpha}{\sin\left( \gamma - \beta \right)} \right]\]
\[ = c\left[ \frac{\sin\gamma\sin\alpha\cos\beta - \sin\beta\cos\gamma\sin\alpha}{\sin\left( \gamma - \beta \right)} \right]\]
\[ = c\left[ \frac{\sin\alpha\sin\left( \gamma - \beta \right)}{\sin\left( \gamma - \beta \right)} \right]\]
\[ = \frac{c\sin\alpha\sin\left( \gamma - \beta \right)}{\sin\left( \gamma - \beta \right)}\]
\[\text{ Hence proved } . \]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In ∆ABC, if a = 18, b = 24 and c = 30 and ∠c = 90°, find sin A, sin B and sin C.
In triangle ABC, prove the following:
In triangle ABC, prove the following:
\[\frac{a^2 - c^2}{b^2} = \frac{\sin \left( A - C \right)}{\sin \left( A + C \right)}\]
In triangle ABC, prove the following:
In triangle ABC, prove the following:
In triangle ABC, prove the following:
In triangle ABC, prove the following:
In ∆ABC, prove that: \[a \sin\frac{A}{2} \sin \left( \frac{B - C}{2} \right) + b \sin \frac{B}{2} \sin \left( \frac{C - A}{2} \right) + c \sin \frac{C}{2} \sin \left( \frac{A - B}{2} \right) = 0\]
In ∆ABC, prove that: \[\frac{b \sec B + c \sec C}{\tan B + \tan C} = \frac{c \sec C + a \sec A}{\tan C + \tan A} = \frac{a \sec A + b \sec B}{\tan A + \tan B}\]
In triangle ABC, prove the following:
In ∆ABC, prove that \[a \left( \cos C - \cos B \right) = 2 \left( b - c \right) \cos^2 \frac{A}{2} .\]
In ∆ABC, prove that if θ be any angle, then b cosθ = c cos (A − θ) + a cos (C + θ).
In ∆ABC, if a2, b2 and c2 are in A.P., prove that cot A, cot B and cot C are also in A.P.
At the foot of a mountain, the elevation of it summit is 45°; after ascending 1000 m towards the mountain up a slope of 30° inclination, the elevation is found to be 60°. Find the height of the mountain.
If the sides a, b and c of ∆ABC are in H.P., prove that \[\sin^2 \frac{A}{2}, \sin^2 \frac{B}{2} \text{ and } \sin^2 \frac{C}{2}\]
In ∆ ABC, if a = 18, b = 24 and c = 30, find cos A, cos B and cos C.
In ∆ABC, prove the following:
\[2 \left( bc \cos A + ca \cos B + ab \cos C \right) = a^2 + b^2 + c^2\]
In ∆ABC, prove the following:
\[\frac{c - b \cos A}{b - c \cos A} = \frac{\cos B}{\cos C}\]
In ∆ABC, prove the following:
\[\sin^3 A \cos \left( B - C \right) + \sin^3 B \cos \left( C - A \right) + \sin^3 C \cos \left( A - B \right) = 3 \sin A \sin B \sin C\]
In \[∆ ABC, \frac{b + c}{12} = \frac{c + a}{13} = \frac{a + b}{15}\] Prove that \[\frac{\cos A}{2} = \frac{\cos B}{7} = \frac{\cos C}{11}\]
In \[∆ ABC, if \angle B = 60°,\] prove that \[\left( a + b + c \right) \left( a - b + c \right) = 3ca\]
Answer the following questions in one word or one sentence or as per exact requirement of the question.
Find the area of the triangle ∆ABC in which a = 1, b = 2 and \[\angle C = 60º\]
Answer the following questions in one word or one sentence or as per exact requirement of the question.In a ∆ABC, if b =\[\sqrt{3}\] and \[\angle A = 30°\] find a.
Answer the following questions in one word or one sentence or as per exact requirement of the question.
In a ∆ABC, if \[\cos A = \frac{\sin B}{2\sin C}\] then show that c = a.
Answer the following questions in one word or one sentence or as per exact requirement of the question.
In a ∆ABC, if sinA and sinB are the roots of the equation \[c^2 x^2 - c\left( a + b \right)x + ab = 0\] then find \[\angle C\]
Answer the following questions in one word or one sentence or as per exact requirement of the question.
In ∆ABC, if a = 8, b = 10, c = 12 and C = λA, find the value of λ.
Answer the following questions in one word or one sentence or as per exact requirement of the question.
If in a ∆ABC, \[\frac{\cos A}{a} = \frac{\cos B}{b} = \frac{\cos C}{c}\] then find the measures of angles A, B, C.
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
In a ∆ABC, if a = 2, \[\angle B = 60°\] and\[\angle C = 75°\]
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
In any ∆ABC, 2(bc cosA + ca cosB + ab cosC) =
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
In a triangle ABC, a = 4, b = 3, \[\angle A = 60°\] then c is a root of the equation
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
In any ∆ABC, \[a\left( b\cos C - c\cos B \right) =\]
Find the value of `(1 + cos pi/8)(1 + cos (3pi)/8)(1 + cos (5pi)/8)(1 + cos (7pi)/8)`
