Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A rectangular field is 80m long and 50m wide. A 4m wide runs through the centre of the field parallel to the length and breadth of the field. Find the total area of the roads.
उत्तर
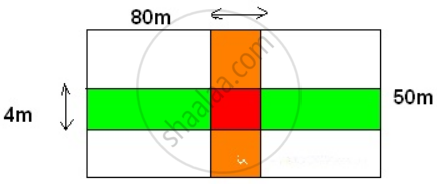
The road that run parallel to the length of the rectangular field (Shown in Green and Red) is a rectangle with length 80m and breadth 4m
Area
= 80 x 4
= 320m2
The road that run parallel to the breadth of the rectangular field (Shown in Orange and Red) is a rectangle with length 80m and breadth 4m
Area
= 50 x 4
= 200m2
The area in Red is include in both the rectangular roads is included in both the roads
⇒ Required area
= 320 + 200 - 4 x 4
= 320 + 200 - 16
= 504m2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
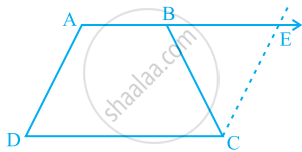
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || CD and AD = BC (see the given figure). Show that
- ∠A = ∠B
- ∠C = ∠D
- ΔABC ≅ ΔBAD
- diagonal AC = diagonal BD
[Hint: Extend AB and draw a line through C parallel to DA intersecting AB produced at E.]
In the following figures, ABCD is a parallelogram.

Find the values of x and y.
In the figure, given below, AM bisects angle A and DM bisects angle D of parallelogram ABCD. Prove that: ∠AMD = 90°.

In the given figure ABCD is a rhombus with angle A = 67°

If DEC is an equilateral triangle, calculate:
- ∠CBE
- ∠DBE
In a square ABCD, diagonals meet at O. P is a point on BC such that OB = BP.
Show that:
- ∠POC = `[ 22 ( 1°)/( 2 ) ]`
- ∠BDC = 2 ∠POC
- ∠BOP = 3 ∠CPO
In the figure, PT is parallel to SR. QTSR is a parallelogram and PQSR is a rectangle. If the area of ΔQTS is 60cm2, find:
(i) the area o || gm QTSR
(ii) the area of the rectangle PQRS
(iii) the area of the triangle PQS.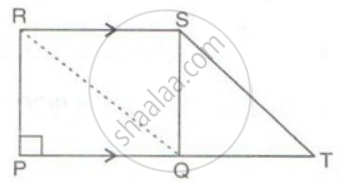
In the given figure area of ∥ gm PQRS is 30 cm2. Find the height of ∥ gm PQFE if PQ = 6 cm.
In the figure, if the area of ||gm PQRS is 84cm2; find the area of
(i) || gm PQMN
(ii) ΔPQS
(iii) ΔPQN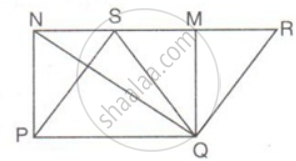
The area of a floor of a rectangular room is 360m2. If its length is 24cm, find its perimeter.
A rectangular hall of 40m by 24m is covered with carpets of size 6m x 4m. Find the number of carpets required to cover the hall.
Find the perimeter of a rhombus whose diagonals are 24cm and 10cm.
Find the area of a rhombus whose perimeter is 260cm and the length of one of its diagonal is 66cm.
A footpath of uniform width runs all around the inside of a rectangular garden of 40 m x 30 m. If the path occupies 136 m2, find the width of the path.
The opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length.
All the sides of a parallelogram are of equal length.
The opposite sides of a trapezium are parallel.
Give reasons for the following :
A rectangle can be thought of as a special parallelogram.
Examine whether the following is a polygon. If it is not, say why?
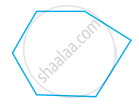
Examine whether the following is a polygon. If it is not, say why?

Name polygon.
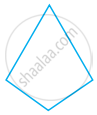
Make two more examples of this.
