Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
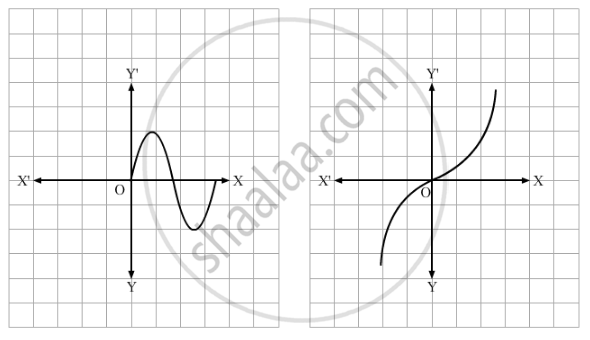
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = x3 − x
उत्तर
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = x3 − x
Injection test :
Let x and y be any two elements in the domain (R), such that f(x) = f(y).
f(x) = f(y)
x3−x=y3−y
Here, we cannot say x=y.
For example, x=1 and y=-1
x3−x =1−1= 0
y3−y=(−1)3−(−1)−1+1=0
So, 1 and -1 have the same image 0 .
So, f is not an injection.
Surjection test :
Let y be any element in the co-domain (R), such that f(x) = y for some element x in R (domain).
f(x) = y
x3 − x = y
By observation we can say that there exist some x in R, such that x3 - x = y.
So, f is a surjection and f is not a bijection.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: Z → Z given by f(x) = x2
Let f: N → N be defined by f(n) = `{((n+1)/2, ",if n is odd"),(n/2,",n is even"):}` for all n ∈ N.
State whether the function f is bijective. Justify your answer.
Let A = R − {3} and B = R − {1}. Consider the function f: A → B defined by `f(x) = ((x- 2)/(x -3))`. Is f one-one and onto? Justify your answer.
Give examples of two functions f: N → Z and g: Z → Z such that g o f is injective but gis not injective.
(Hint: Consider f(x) = x and g(x) =|x|)
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Z → Z, defined by f(x) = x2 + x
If A = {1, 2, 3}, show that a one-one function f : A → A must be onto.
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = x and g(x) = |x| .
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = ex g(x) = loge x .
Find fog and gof if : f(x) = c, c ∈ R, g(x) = sin `x^2`
` if f : (-π/2 , π/2)` → R and g : [−1, 1]→ R be defined as f(x) = tan x and g(x) = `sqrt(1 - x^2)` respectively, describe fog and gof.
If f : R → R be defined by f(x) = x3 −3, then prove that f−1 exists and find a formula for f−1. Hence, find f−1(24) and f−1 (5).
If f : R → (−1, 1) defined by `f (x) = (10^x- 10^-x)/(10^x + 10 ^-x)` is invertible, find f−1.
Let f be a function from R to R, such that f(x) = cos (x + 2). Is f invertible? Justify your answer.
If A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and B = {a, b, c, d}, define any four bijections from A to B. Also give their inverse functions.
Which of the following graphs represents a one-one function?
Write the domain of the real function f defined by f(x) = `sqrt (25 -x^2)` [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
A function f from the set of natural numbers to integers defined by
`{([n-1]/2," when n is odd" is ),(-n/2,when n is even ) :}`
The function
\[f : R \to R\] defined by\[f\left( x \right) = \left( x - 1 \right) \left( x - 2 \right) \left( x - 3 \right)\]
(a) one-one but not onto
(b) onto but not one-one
(c) both one and onto
(d) neither one-one nor onto
Let
\[A = \left\{ x \in R : x \leq 1 \right\} and f : A \to A\] be defined as
\[f\left( x \right) = x \left( 2 - x \right)\] Then,
\[f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\] is
If \[f\left( x \right) = \sin^2 x\] and the composite function \[g\left( f\left( x \right) \right) = \left| \sin x \right|\] then g(x) is equal to
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
If the set A contains 7 elements and the set B contains 10 elements, then the number one-one functions from A to B is
Write about strlen() function.
If A = {a, b, c, d} and f = {a, b), (b, d), (c, a), (d, c)}, show that f is one-one from A onto A. Find f–1
Let A be a finite set. Then, each injective function from A into itself is not surjective.
If the set A contains 5 elements and the set B contains 6 elements, then the number of one-one and onto mappings from A to B is ______.
Which of the following functions from Z into Z are bijections?
If f(x) = (4 – (x – 7)3}, then f–1(x) = ______.
The function f : R → R defined by f(x) = 3 – 4x is ____________.
Which of the following functions from Z into Z is bijective?
Let f : R `->` R be a function defined by f(x) = x3 + 4, then f is ______.
Let f : R → R, g : R → R be two functions such that f(x) = 2x – 3, g(x) = x3 + 5. The function (fog)-1 (x) is equal to ____________.
A general election of Lok Sabha is a gigantic exercise. About 911 million people were eligible to vote and voter turnout was about 67%, the highest ever

Let I be the set of all citizens of India who were eligible to exercise their voting right in the general election held in 2019. A relation ‘R’ is defined on I as follows:
R = {(V1, V2) ∶ V1, V2 ∈ I and both use their voting right in the general election - 2019}
- Three friends F1, F2, and F3 exercised their voting right in general election-2019, then which of the following is true?
An organization conducted a bike race under 2 different categories-boys and girls. Totally there were 250 participants. Among all of them finally, three from Category 1 and two from Category 2 were selected for the final race. Ravi forms two sets B and G with these participants for his college project. Let B = {b1,b2,b3} G={g1,g2} where B represents the set of boys selected and G the set of girls who were selected for the final race.
Ravi decides to explore these sets for various types of relations and functions.
- Let R: B → G be defined by R = { (b1,g1), (b2,g2),(b3,g1)}, then R is ____________.
Raji visited the Exhibition along with her family. The Exhibition had a huge swing, which attracted many children. Raji found that the swing traced the path of a Parabola as given by y = x2.
Answer the following questions using the above information.
- Let f: R → R be defined by f(x) = x2 is:
Let [x] denote the greatest integer ≤ x, where x ∈ R. If the domain of the real valued function f(x) = `sqrt((|[x]| - 2)/(|[x]| - 3)` is (–∞, a) ∪ [b, c) ∪ [4, ∞), a < b < c, then the value of a + b + c is ______.
Let f(n) = `[1/3 + (3n)/100]n`, where [n] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to n. Then `sum_(n = 1)^56f(n)` is equal to ______.
Let A = R – {2} and B = R – {1}. If f: A `→` B is a function defined by f(x) = `(x - 1)/(x - 2)` then show that f is a one-one and an onto function.
